Aphasia after stroke and more
Aphasia is most common in older people who have had a stroke
. However, speech destruction occurs in young people and even in children who have suffered infectious diseases, traumatic brain injuries, or brain tumors. The form of aphasia depends on which part of the brain is affected. And the direction in which speech restoration specialists will work depends on the form.
Diagnosis of aphasia
Experts from different fields are involved in uncovering the mechanisms of this complex disease: neurophysiologists, neurologists, speech therapists, psychologists, etc. The diagnosis is made after the localization of the lesion in the brain has been determined. The complexity of the disorder depends on the size of the lesion, the nature of the circulatory disorder and the characteristics of the intact components of speech activity.
It is known that the highest mental functions of a person are carried out as a result of the work of the cortex of the two hemispheres of the brain and its subcortical structures. Aphasia is caused by damage to the dominant hemisphere, the right in left-handed people and the left in right-handed people.
This is how the frontal lobes of the cortex carry out programming, regulation of mental activity and correction of its results. The right frontal lobe carries out non-speech actions, the left is responsible for the movement of the tongue and the entire body, plans speech and mental activity, and predicts its impact on the situation. The temporal lobes of the cortex are responsible for listening and understanding speech. The right temporal lobe captures and differentiates non-speech sounds, the left is responsible for the perception of both individual sounds of language and their synthesis into groups of words. The occipital lobes of the cortex perform the functions of collecting and processing information through vision, the parietal lobes - through the tactile-kinesthetic sense.
Diagnosis of the activity of cerebral cortex functions in aphasia is carried out in the following areas:
|
Up
Main forms of aphasia
There are several classifications of aphasia; in our country, the classification of A.R. is widespread. Luria, abroad – Lichtheim-Wernicke classification. There is also a simplified classification: posterior form of aphasia - damage to the superior temporal and inferior parietal areas of the brain, and anterior form - damage to the posterior frontal regions. Classic descriptions examine not only lesions of the speech areas of the brain, but also adjacent non-speech areas of the cortex.
Features of the development of aphasia are different. In cases of circulatory disorders and brain injuries, speech disorder occurs sharply and immediately. With sluggish circulatory disorders and gradual growth of a brain tumor, the symptoms of aphasia appear slowly, as the brain zones are covered.
Treatment approaches
Effective therapy is based on eliminating the immediate cause of the development of speech disorder. If a tumor lesion or intracranial hematoma is detected, treatment is carried out with neurosurgery, radiation or chemotherapy. Neuroinfections are eliminated using antifungal, antibacterial or antiviral drugs. Strokes are subject to thrombolytic or hemostatic treatment.
Correction of speech disorders is based on:
- Regular speech therapy sessions
They are carried out to increase the volume of auditory-verbal memory. They must be started immediately after the onset of the disease, without delaying a visit to a speech therapist for the rehabilitation period. Initially, exercises with visual perception of an object are used, which makes them easier to remember. Next, the specialist complicates the lessons - the patient writes simple dictations by ear, learns fragments of sentences, word chains, songs and poems. To improve expressive speech, active work is being carried out to clarify the meaning of words and systematize them into separate groups.
In parallel with the treatment of the main pathology, rehabilitation measures begin with the patient. An important part of therapy is communication with medical staff, speech therapist and loved ones. As a result of constant verbal contact and speech therapy exercises, auditory-verbal memory is restored. In addition, patients are advised to exercise therapy, massage and visit a psychotherapist.
Symptoms of aphasia
Signs and symptoms of aphasia may be invisible to others, as compensatory processes are activated that conceal speech defects. In the early stages of the disease, symptoms may appear or disappear completely, so it is difficult to draw a clear line between impaired and normal speech. Aphasia is a systemic disorder in which not only the pronunciation side suffers, but also the understanding of speech, lexical and grammatical structure, reading and writing. Symptoms of aphasia also manifest themselves in neurological and mental abnormalities. Motor functions suffer, patients experience paralysis of the limbs and articulatory muscles. Voluntary movements acquired throughout life experience are impaired. So the patient seems to forget how to use cutlery and household items. Memory and attention are severely impaired, and thought processes are inhibited.
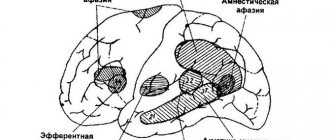
A.R. Luria identifies six main forms of aphasia: acoustic-gnostic (sensory), acoustic-mnestic, afferent motor, efferent motor, semantic and dynamic.
Up
Let's understand the reasons
The diagnosis is made by a neurologist, but a mandatory component of the diagnosis is a consultation with a speech therapist. He must establish to what extent various functions are preserved or, conversely, lost: understanding speech, diction, writing, counting. The doctor pays attention to the patient’s general condition and reflexes.
A consultation with a child psychiatrist may also be required. This specialist will determine whether the patient’s condition is associated with mental disorders and whether his nervous system requires medication support to achieve the best results.
A consultation with a psychologist completes the diagnosis. His task is to understand whether help is needed in adapting to his condition and whether the child needs support to actively participate in rehabilitation activities.
Sensory aphasia
Acoustic-gnostic (sensory) aphasia
occurs when the superior temporal gyrus is damaged.
A distinctive symptom of sensory aphasia is a lack of listening comprehension of the speech
of others.
Not only phonemic hearing is lost, but also the ability to distinguish voice timbre, intonation, and differentiate non-speech sounds: the sound of water, the creaking of a door, etc. Writing is grossly impaired, acalculation is observed - inability to count.
In patients with sensory aphasia, as a rule, motor function is not impaired, and the lack of self-control of speech leads to the fact that they do not immediately realize their illness, so they become mobile and talkative.
The understanding of the meaning of words also changes; names with different meanings are perceived equally (cane-guest-nail). When asked to show a barrel in the picture, they point to a kidney. , literal paraphasia
occurs - inappropriate use of sounds in a word or their replacement. Reading remains the most preserved function, since the optical and kinesthetic analyzers are involved.
Instrumental diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, instrumental diagnostics is necessary. The patient is prescribed electroencephalography. This is a technique for studying the electrical activity of the brain by placing electrodes in specific areas on the surface of the head.
To clearly see the structure of the brain, to identify traces of hemorrhages, inflammation, and malignant neoplasms, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is prescribed. If it is necessary to clarify the integrity of blood vessels, identify aneurysms and other vascular disorders, then angiography may be required. Carrying out a comprehensive diagnosis makes it possible to differentiate aphasia from alalia, hearing loss and other pathologies.
Treatment of the disease directly depends on the form. It takes a long time to restore speech. It depends on a number of conditions: the cause of its appearance, the exact location of the damage, the degree of speech disorder, and the age of the patient.
An individual treatment plan is developed for the patient, which pays attention to drug therapy, physiotherapy, art therapy and classes with a speech pathologist. Drug therapy includes the prescription of antibacterial drugs, nootropics and other drugs (depending on the clinical picture). For example, in case of massive pathological changes that cause vasogenic edema, the doctor prescribes corticosteroids. To prevent epilepsy attacks, it is necessary to take anticonvulsants.
Exercises for correction
For some, it is easier to start pronouncing sounds and then move on to more complex words, while for others, on the contrary, it is much easier to say words and then isolate sounds. There are many exercises that significantly contribute to the correction of the disease. If you have problems understanding speech, it is recommended to first take three steps:
- Show in the picture where a specific detail of the image is located.
- Answer simple questions. For example: “Are you sitting on a chair now?”, “Are you walking in the fresh air now?”
- Take simple steps. For example, open a notebook and clench your fist.
This is an approximate plan; a speech pathologist-speech pathologist may give other tasks. In this case, the main thing is that the person learns to understand what is required of him. Articular gymnastics are often performed. A speech therapist teaches a person the correct pronunciation of sounds and composing phrases using special exercises. The doctor carries out work aimed at remembering the names of various objects and their purposes.
Acoustic-mnestic aphasia
Cause
acoustic-mnestic aphasia - damage to the middle and posterior parts of the temporal region.
It is characterized by symptoms such as a decrease in auditory-verbal memory
due to inhibition of auditory control. When listening to each new word, the patient loses understanding of the previous one, hence the repeated repetition of the same syllable or word. An aphasic who suffers from the acoustic-mnestic form cannot repeat 3-4 words in a row with different meanings. For example, sky, hand, grass, spoon, repeats either the first or the last word. Phonemic hearing and correct articulation are preserved, which results in verbosity that compensates for communication difficulties. The nominative function of speech, retelling based on plot pictures, suffers. Misunderstanding of the meaning of words leads to verbal paraphasia - substitution of words in a sentence, merging one word into one in writing. Along with writing, counting and reading are impaired.
Up
Semantic aphasia
Semantic aphasia occurs when the parieto-occipital region of the dominant hemisphere is damaged. The patient has difficulty finding the right word when naming objects; instead of a noun, they may say a verb or an adjective that describes the properties or functions of this object. Replace a word with a whole phrase (verbal paraphasia). For example, instead of the word chair they say white sit. They lose their understanding of proverbs, metaphors, and catchphrases, and form lexical and grammatical structures incorrectly. With limited vocabulary, articulation is preserved. Written speech is characterized by agrammatism, stereotypical phrases, the absence of complex sentences and a reduced number of adjectives.
Afferent motor aphasia
This form of the disease - afferent motor aphasia - is a consequence of damage to the postcentral and inferior parietal parts of the cerebral cortex. One of the variants of afferent motor aphasia is a violation of spatial praxis of various organs of articulation, the inability to pronounce words in spontaneous speech. Chaotic movements of the tongue and lips lead to mixing or substitution of sounds
in a word.
This is explained by the lack of kinesthetic assessment of the level of occlusion of the organs of articulation during speech production. Patients suffering from afferent motor aphasia split a closed syllable into two open ones and miss consonant sounds (tap-ki - ta-ki). Speech understanding
also , since they do not recognize words with similar sounds in place and method of articulation. They do not realize the difference between verbs denoting spatial relationships (run, run around), and have difficulty understanding the indirect cases of personal pronouns.
The second option (“conductive aphasia”) is characterized by relatively intact situational speech, but the statements are cliché-like. Repetition and naming of words are impaired
and objects.
Hence, rearrangements of syllables (no-ga - ga-no) and omissions of vowels arise, but the visual idea of the presence of a sound in a word is preserved, for example, when the letter “e” is omitted, the patient puts dots over the adjacent letter. Usually, with afferent motor aphasia, reading and writing are severely impaired
, this depends on the severity of oral apraxia. In writing, as in spoken speech, there is confusion and omission of sounds. In some cases, writing is intact, which is explained by apraxia of the pharynx and larynx, which serve only as a preset for all articulatory movements.
Up
Possible complications
Acoustic-mnestic aphasia leads to impairment of auditory-verbal memory. A speech defect is accompanied by a deterioration in a person’s socialization - he has difficulty communicating with people around him, and cannot read, write or count. This gradually reduces the level of quality of life, leading to the formation of persistent depression.
The pathology is often accompanied by a neurological deficit, which intensifies the patient’s own feelings of inferiority. Many patients are diagnosed with disability. It is important to note that acoustic-mnestic aphasia is not a cognitive disorder. Thinking and other brain functions are completely preserved. In the absence of treatment, speech dysfunction becomes persistent and difficult to correct in the future.
Efferent motor aphasia
Efferent motor aphasia occurs when the premotor parts of the frontal lobes of the brain (Broca's area) are damaged and is accompanied by symptoms such as movement disorders
and difficulties in mastering the motor program.
In severe cases, when there is poor circulation after a stroke, speech may be completely absent. The motor function of the articulatory apparatus suffers, since the signal about the beginning and termination of a speech act is delayed, which causes inertia, stereotypical speech, and perseveration
- repetitions of the same syllable or word. The patient cannot switch from one articulatory posture to another in a timely manner, which is why expressive speech suffers. Difficulties arise in repeating a series of sounds or syllables, in naming objects. In conversation, patients miss verbs, prepositions, and swallow endings. Speech is ungrammatical, reminiscent of telegraphic style. In written speech, they confuse the order of letters in a word and find it difficult to choose the correct letter. In severe cases, reading and writing are completely impossible. In mild cases, the patient can write down the word by ear, omitting sounds at the junction of consonants or rearranging them. Understanding of speech is also impaired, especially the figurative meaning of expressions and polysemantic words.
Our specialists
Tarasova Svetlana Vitalievna
Expert No. 1 in the treatment of headaches and migraines. Head of the Center for the Treatment of Pain and Multiple Sclerosis.
Somnologist.
Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Doctor of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 23 years.Derevianko Leonid Sergeevich
Head of the Center for Diagnostics and Treatment of Sleep Disorders.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Vertebrologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 23 years.
Bezgina Elena Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 24 years.
Dyachenko Ksenia Vasilievna
Head of the center for the treatment of dizziness and balance disorders.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category.
Angioneurologist. Neurorehabilitation specialist. Physiotherapist. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 19 years.Drozdova Lyubov Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist. Vertebroneurologist. Ozone therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 17 years.
Zhuravleva Nadezhda Vladimirovna
Head of the center for diagnosis and treatment of myasthenia gravis.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Experience: 16 years.
Palagin Maxim Anatolievich
The doctor is a neurologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 6 years.
Dynamic aphasia
Dynamic aphasia
is marked by damage to the posterior frontal parts of the dominant hemisphere, which are responsible for planning and regulating speech activity.
Consequently, difficulty arises when constructing a detailed statement, and in severe cases, its complete impossibility. At the same time, the patient correctly pronounces individual sounds, words and short sentences, since there are no articulation difficulties. But in situational speech, general aspontaneity
,
echolalia and echopraxia
, when an aphasic person repeats after a person not only words, but also lip movements. Violation of internal speech planning leads to primitiveness of syntactic structures, the presence of agrammatisms and speech patterns, and difficulties in retelling. Reading and writing functions are intact.
Prevention of violations
Preventive measures are aimed at the primary prevention of diseases that can lead to speech disorders. Neurologists make a number of general recommendations:
- use protective helmets during professional activities and some sports;
- if you have diseases of the internal organs, for example, diabetes mellitus or atherosclerosis, promptly seek medical help and follow the instructions of your doctor;
- follow the principles of a healthy diet: give up fast food, fried or smoked foods, add fruits, vegetables, lean meat and other healthy foods to your diet;
- regularly engage in sports - cardio training and exercises in the gym;
- Avoid drinking alcohol and smoking.
If you experience difficulty finding words or other symptoms, you should immediately seek medical help.