There are several classifications of singing voices in accordance with various characteristics: voice strength, mobility, clarity, etc. The most common classification is based on the artist’s gender and his musical range. Thus, female voices include soprano, mezzo-soprano and contralto, and male voices include countertenor, tenor, baritone and bass. Moreover, some of them are divided into narrower subspecies. AiF.ru tells how different types of singing voices differ.
Click to enlarge
Voice timbre, types
The most pleasant timbre is considered to be a voice that has the correct modulation, both in high and low tones. In fact, any voice can be cast with the right approach. This means giving it a professional sound. To do this, you need to learn to control the frequency of your voice, as well as the emotional coloring. This is easy to do with the help of a vocal specialist. To determine your own timbre, you need to know what voice timbres there are in general. There are several main types:
1. Men's. There are three types of timbre of a man's voice:
- tenor. This is the highest male voice. It can be lyrical or dramatic.
- baritone;
- bass. The lowest voice timbre in comparison with the above. It can be central or melodious.
2. Women's. The timbres of the female voice also have 3 types:
- soprano. This is a very high pitched voice. There are lyric soprano, dramatic and coloratura.
- mezzo-soprano;
- contralto. It's a low voice.
The timbres of singing voices are divided in the same way.
Male performance
Experts divide the vocals of the strong half of humanity into tenor, baritone and bass groups. This corresponds to high, middle and low registers. Each group has a more detailed gradation, which takes into account timbre, sound, lightness, and features when playing the upper and lower notes of the range.
In the world of music, not long ago there was a real discovery that cannot be imitated - this is the Kazakh performer Dimash Kudaibergenov, who works in 6 octaves.
Tenor group
This is a popular and beautiful male voice, capable of taking “royal C” in the upper octave. The range is very wide and covers octaves from minor to second. A distinctive feature of tenor soloists is a strong upper register. There are several high-pitched voices in this group:
- Tenor altino has the highest notes to F of the second octave. Rare voice. The timbre is light, light, with silvery top notes. Part of the Astrologer in the opera The Golden Cockerel.
- Lyrical. Performers work in the range up to the first octave - B of the third octave. The voice is mobile, with graceful light coloraturas, the sound is melodious, carefree, warm. Typically, musicians with such abilities perform arias of hero-lovers (Lensky in Onegin, Count Almaviva in The Barber of Seville).
- Characteristic. Has a sound effect, such as a slight ringing of bells or a silvery tone. Indispensable for creating a bright, memorable image.
- Dramatic (sometimes distinguished as lyrical-dramatic). More dense and dynamic in the lower register, and sounding strong and powerful in the upper register. Such metallic-tinged vocals perfectly convey the drama of events. May not take the upper C. The composers created the roles of Herman (The Queen of Spades), Calaf (Turandot), Othello (Othello), and Manrico (Il Trovatore).
- Countertenor. Sounds like a mezzo-soprano. The ability to sing in a developed falsetto technique is valued in the music of the Baroque period.
- Baritone tenor. It is located on the border between tenor and baritone, but the upper range part is less developed. Mime part (The Ring of the Nibelung).
Many wonderful classical opera roles have been written for tenors by Russian and foreign composers: Gounod (Faust), Jose (Carmen), Prince (The Love for Three Oranges). Famous tenors - P. Domingo, M. Lanza, E. Caruso, S. Lemeshev, I. Kozlovsky, E. Pavarotti, L. Sobinov.
Baritone Characteristics
The average male voice captivates with its velvety sound and ability to demonstrate dramatic emotional intensity. The range of baritone singing voices covers from A of the major octave to the next A of the first octave. The baritone is conventionally divided into the following types:
- Lyrical. It is close in timbre to the tenor, but has a peculiar dense tone and high tessitura.
- Lyrical-dramatic. The brightness of the sound, rich timbre and strength allow performers to take on a variety of roles.
- Dramatic. Sounds powerful in the upper range and central register. The sound is dense and dark. It differs in that it has a low tessitura, but at the climax it easily hits the extreme notes. Opera characters performed by a dramatic baritone are always strong personalities, positive or negative.
- Bass-baritone. Some experts distinguish it as intermediate between bass and baritone due to the intense sound in the central register of lower notes that are more massive than those of a regular baritone.
The baritone roles do not leave anyone indifferent - these are Eugene Onegin in the opera of the same name, Prince Igor (“Prince Igor”), Andrei Bolkonsky (“War and Peace”), Aleko and Iago (“Othello”), Demon (“The Demon”). Famous baritones - G. Pray, D. Hvorostovsky, T. Hampson, V. Skorobogatov, V. Petrov.
Types of Bass
The bass voice has the greatest amplitude of sound vibration, so it can more dynamically indicate contrasts when singing. A low voice in men is very rare, so such vocals are indispensable in church choral singing. It is distinguished by rare beauty, depth, and richness of sound.
Bass is submissive to notes in the range from F of the major octave to F of the first. There are 4 types of bass voices:
- High (cantata). Reaches F of the first octave. Reminiscent of a baritone bass, it sounds bright and strong, but is soft and compact in the upper and midrange.
- Central. Performs high tessitura notes, as well as low notes up to F of the large octave. The voice sounds full and spacious, the timbre is beautifully filled.
- Low (profundo). It is distinguished by a velvety timbre and rich color; low notes sound unusually strong right up to the D of the first octave. They are not characterized by grace and passages.
- Octavists. Such performers use the lower register up to the counter-octave note. The voices are inactive, dense, heavy. This type of singing is practically not used in modern opera.
Some experts believe it is appropriate to distinguish bass voices by timbre and distinguish baritone, characteristic, deep, comic.
Composers create musical parts specifically taking into account the sound characteristics of bass voices, because some hum like bells, others are heard harshly, and others give a long peal. For this reason, the characters performed by the singers are also different - these are majestic heroes, respected fathers of families, and funny grotesque images.
Famous roles include Susanin (“Ivan Susanin”), Melnik (“Rusalka”), Moroz (“Snow Maiden”), Sea Tsar and Varangian Guest (“Sadko”). The owners of such voices are I. Petrov, Yu. Statnik, F. Chaliapin, B. Shtokolov, Jose van Dam.
How to change your voice tone
Many people would like their voice to sound different. This is especially true for singers, actors, TV presenters and all those who have to communicate for a long time.
The timbre of the voice largely depends on the characteristics of the human body. The volume, shape of the trachea and oral resonator, as well as the tightness of the closure of the vocal cords are of great importance. Therefore, it is not possible to radically change the sound of the voice.
However, you can give the timbre the necessary coloring by adding low or high overtones and achieving their ideal balance. There are various exercises for this, for example, pronouncing the soft fricative “r”.
The shape of the lips and the position of the tongue have a great influence on the timbre. You can experiment, for example, changing the position of the jaw and talking with a fixed lower lip.
At the age of three, a person’s voice pattern changes and he becomes more constrained. We diligently control volume and intonation, strain our ligaments and, as a result, use only a small part of our capabilities. How to restore your natural voice, how to expand your vocal range? Exercises and techniques will also help you with this. You can find out more detailed information about them by watching the video:
Exclusive on stage
Sometimes singers are so professional that they are able to perform parts with different characters. Such votes are usually called “absolute”.
For example, the famous singer Maria Callas was able to master all soprano roles - from dramatic to coloratura. Her appearance on stage in exquisite outfits and furs caused a sensation. But such opportunities open up only to unique voices with careful development of sound techniques.
It is almost impossible to determine the type of voice of a beginning singer, since the degree of range and timbre change during training.
What affects voice timbre
- First of all, smoking should be noted. The longer the experience of this addiction, the lower the timbre of the voice.
- Poor nutrition, chronic lack of sleep. You need to understand that any mood, be it good or bad, affects the timbre of your voice.
- Hypothermia, cold. Everything is obvious here. You need to protect yourself from the cold, try not to drink ice-cold drinks and give up ice cream.
- The period of growing up. During adolescence, the timbre of the voice becomes rougher. Of course, it is impossible to change this process.
Vocal abilities in children
Children's voices sound higher than adults'. This is explained by the fact that the vocal muscle in a child under 11-13 years of age is not fully formed. Children's vocals are classified according to their range, regardless of the gender of the child:
- alto - low notes;
- soprano - high notes.
A boy's thin child's voice is called a treble and is divided into low, medium, and high. During the process of mutation of the vocal apparatus, the vocal abilities in children change and may completely disappear.
Take a hearing test online
What does a hearing test tell you?
An online hearing test allows you to quickly and easily determine your hearing status. In just 3 minutes you can determine its spiciness. The result of the hearing test is called an “audiogram” and is an indication for doctor’s prescriptions.
We suggest the following hearing tests: signs of hearing loss; online frequency hearing test; hearing test in noise; speech recognition; modeling signs of hearing loss.
Take a hearing test
Voiced and unvoiced sounds
Above the vocal cords is the supraglottic tube (above the larynx). The extension tube consists of the pharyngeal cavity and the cavities of the mouth and nose. If you do not take into account the nasal cavity, the extension tube will look like a tube open on one side.
In this extension tube, the sound coloring of vowel sounds is formed from the hoarse, resonant noise that passes through the glottis. Actively changing the position of the tongue and lips changes the shape of the resonant cavity, as well as the length of the extension pipe. Thus, during speaking, the typical resonant frequencies of the tract, or formants, appear. The frequencies and amplitudes of these formants are the determining indicators when pronouncing vowel sounds. Ever watch carefully the movements of a news anchor's lips. You will learn based on the position of the mouth how lip reading works. When pronouncing [a], the mouth is slightly open, [o] and [y] are pronounced with elongated lips. Consonants are formed due to a certain position of the lips. In phonetics, a distinction is made between voiced and unvoiced sounds. (Figure 2)
Figure 2: An initial signal is generated in the vocal folds, which is transformed by resonances in the extension tube, so that it eventually becomes a language signal.
Dull sounds occur when the glottis is wide open, so that air can easily penetrate to the end of the vocal tract.
The difference between voiced and unvoiced sounds can be clearly seen by conducting two experiments: hold your hand while speaking on the larynx. If you feel vibration, the sound is ringing; if there is no vibration, then the sound is considered dull. The second experiment is to close your ears and press on the tragus on both sides and at the same time slowly say: “One, two, three, four, five...”. During acoustic isolation with a closed ear canal, you will notice the difference between dull and voiced sounds: soft noises and rattling vibrations.
Voiceless sounds - hissing (whistling) or fricative consonants and stops. During whispering, the vocal cords are used only indirectly. The air flow released during whispering is weak, and it creates small vibrations in the slightly open, calm glottis. These vibrations are acoustically perceived as quiet noise, completely devoid of sound design. In this case, there is no power and sound resonance enhancement of the vocal cords. In the extension pipe, in the same way as during sound voice production, the same resonances are formed, only they are much quieter.
Spectrogram
A spectrogram (sonogram) or visualized speech is a three-dimensional, visual representation of sounds in two-dimensional graphics. The sequence of signals is represented by a time index (abscissa and ordinate axis) and frequency (abscissa axis or longitudinal axis). Sound intensity is represented as relative darkening or color intensity scaling (third dimension) of the time and frequency images.
Reading and interpreting a spectrogram needs to be learned, since under certain circumstances an overabundance of information appears. In this way, it is possible to recognize the processes of establishment and attenuation of oscillations, interference, and even more so pathological changes in the functioning of the speech apparatus (Figure 3). The sonogram gives an idea of the sound study; the field of study is marked by the abscissa and ordinate axes. Sound reflection levels are measured using an acoustic probe, associated with a specific location in the field of study, and these areas are colored black depending on the intensity.
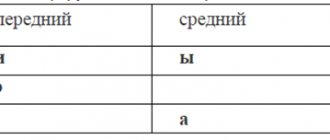
Figure 3: Spectrogram (sonogram) with the position of the formants of vowels i, u, a.
Talking Parrot
After this scientific excursion into the sound system of language and its analysis, I would like to tell you one more story. A good friend of mine was very proud to be a parrot owner. The African gray parrot (Grey parrot) was named Walter and was over 30 years old. Walter was a smart guy. He could repeat not only his own name and the name of my friend, but also quite quickly reproduced people’s addresses in full. In addition, he could say small sentences, such as: “I like you” or “You are a coward.” Tilting his head to the side, looking up and down with his captivating gaze, he presented his repertoire to selected visitors.
With his very loud and clear voice, he could whistle, so that his ears began to hurt. It played all sorts of sounds, such as a vacuum cleaner or a razor. Man and animal are capable of becoming close friends, and, of course, Walter managed to do this. He was very affectionate and snuggled against my friend’s cheek as they “chatted.” But at the same time he was timid and made a hell of a noise when he was excited. Walter lived in a very beautiful large enclosure with all kinds of toy rubbish, sometimes he flew out of there and swung on the chandelier.
One day on a bad spring day, Walter was sitting on a chandelier, and suddenly a strong gust of wind blew open the loosely closed terrace door. Walter, of course, panicked: he screamed and wheezed, and then flew out through the open terrace door. My friend, of course, heard the noise, but, unfortunately, came into the room too late. Walter is already gone...
Parrots can imitate speech sounds. In the wild, birds recognize each other by the characteristic sounds of their species. Many birds can not only whistle and sing beautifully, but also amazingly reliably imitate all kinds of noises.
How is this possible?
And birds have a larynx, but without vocal cords and an epiglottis. Birds produce sounds from the so-called lower larynx (syrinx), located deep in the chest, near the place where the windpipe divides before entering the lungs. Here there are oscillatory membranes, which, just like the vocal cords, can change their tension thanks to the muscles. Since the vocal organs of birds are located in two branches of the windpipe, some songbirds can sing with two voices. Listen to the nightingale singing one quiet summer evening - you will receive great acoustic pleasure! (Figures 4 and 5).
Figure 4: The avian larynx (syrinx) contains two glottis. Therefore, some songbirds can sing with two voices.
Figure 5: Walter the gray parrot could perfectly “pronounce” not only his name.
Parrots, for example, have a thick beak and a thick tongue, thanks to this (by changing the position of the tongue), they can, like humans, articulate a large number of sounds. This feature helped Walter. A very nice man found him and brought him to the police station. Walter reported there the name of his owner and his address. Walter expressed his joy at meeting his owner very loudly, imitating the sounds of a siren.
Summarizing
- Humans and many animals can form speech sounds.
- The development of sound speech is possible only in humans thanks to their mental abilities.
- The human speech apparatus consists of the larynx, tongue, lips, and also includes the oral cavity, nose and pharynx.
- Voiced sounds (vowels, umlauts, nasals, smooth consonants, fricative sonorants and obstruent consonants) initially arise from vibrations of the vocal cords, and then sound is formed in the supernatant (sound formants).
- Voiceless sounds (consonants, hissing and fricative consonants, as well as stops) arise without the participation of the vocal cords.
- A spectrogram (sonogram, visualized speech) is a graphical representation of signals that depend on the frequency of vibrations, the course of the process over time and intensity.
Ulla Vogdt Material taken from Hörakustik magazine, No. 1 2021
Take a hearing test online
What does a hearing test tell you?
An online hearing test allows you to quickly and easily determine your hearing status. In just 3 minutes you can determine its spiciness. The result of the hearing test is called an “audiogram” and is an indication for doctor’s prescriptions.
We suggest the following hearing tests: signs of hearing loss; online frequency hearing test; hearing test in noise; speech recognition; modeling signs of hearing loss.
Take a hearing test
Read more on the topic “Useful information about hearing”
Why you don't need a hearing aid
The Academy of Hearing has been working with people suffering from hearing loss for over ten years. During this time, we have collected a whole collection of rumors, myths and misconceptions that surround this disease and the means of its correction - a hearing aid. We collected the most popular ones and asked our experts to comment on them in an easy, understandable and ironic way of “bad advice.”
Tinnitus: causes, treatment methods, consequences
Tinnitus is a widespread phenomenon and one of the most common diagnoses in the practice of treating ENT diseases. In 1999, in Germany, on behalf of the German League of Physicians, a large study was conducted in the field of auditory acoustics, during which it was found that tinnitus entails psychosomatic disorders such as sleep disturbances, depression and increased audiological stress.
How often should you change your hearing aids?
Do you remember what feelings and emotions you experienced when you first put on your hearing aid? How much brighter and more fulfilling has your life become, filled with clear sounds and voices? If several years have passed since then, are you sure that your hearing is still as good? Often, people who use hearing aids begin to notice over time that they begin to hear “somehow differently.”
Hearing aid or hearing amplifier: making the right choice!
Typically, a person loses their hearing gradually. First, the quietest, most inexpressive sounds and subtlest nuances “disappear.” Because of this, it is difficult for a person to ascertain a change in his ability to hear. Quite often, people try to ignore minor hearing loss until the truly important sounds for everyday life, such as the cry of a child or the sound of a car approaching, begin to disappear from the range of audible sounds.
Determining your voice type
Often people who start singing are perplexed about why they need to know their voice type.
A professional can give a simple answer: so as not to spoil your voice and give your talents the opportunity to fully express themselves. Thus, those with low voices are not recommended to take high notes. And vice versa. And it’s easier to select the compositions for performance if you know the features of your type. So how do you determine your singing voice type? Let's say right away: it is very difficult to do this at home. In vocal studios, professionals listen to voices from outside, and they draw conclusions. But, as a rule, this is almost impossible to do during one meeting. There is an opinion that there are voices that are not at all suitable for vocals. But that's not true. A really good teacher will definitely identify the characteristics of your voice, even if it takes a lot of time. By what parameters does the teacher determine the type:
- Timbre . This is actually the "color" of the voice. Some have a soft voice, some have a harsh voice, some have a chesty sound, some prefer to sing quietly, some try to put as much force into the sound as possible... Timbre is the unique properties of the voice given to man by nature and his character.
- Range . This is the power of voice. The wider the range, the more likely a person is to become a singer. It is determined when the vocalist sings or performs a composition in his own key.
- Tonality . Individual feature of the voice. Each type has its own tonality that is convenient for it. But vocalists who have a wide range of voices play with tonality easily. This “play” can be clearly heard in the French version of the composition “Belle”, which is performed by vocalists with different types of voices.
- Tessitura . The part of the range that is most convenient for the performer. Knowing your tessitura, the easiest way is to decide which compositions will be most convenient for you to perform. And, having decided, you can order your own unique compositions. We will help you create your song.
And, of course, practice will help you determine your type. Sing yourselves. Start simple, move on to complex ones, and don’t be afraid to try and make mistakes. Sing not only with a teacher, but also at home and in the studio. Recording your own voice will allow you to hear yourself from the outside, determine your weaknesses and strengths, your capabilities, and therefore find out your voice type.
What is it that you cannot do without in the profession of a vocalist, or simply in singing? Without love. To vocals, to yourself, to your own voice, to those who support you, to the world around you, to whom you are going to give songs... The ability to sing is a wonderful gift from the world to you. So give him your heart in return.