With normal speech development, children aged 4.5-5 years can by ear determine the presence or absence of a specific sound in a word. Naturally, if their parents or teachers worked with them. Phonemic hearing (not to be confused with physiological hearing) is responsible for this skill. It helps the child recognize and distinguish sounds, understand their sequence and location. Thanks to phonemic hearing, children distinguish similar words and understand their meaning. This is an important part of speech development.
If a child confuses sounds or hears them in a word at 5 years old, this may indicate a phonemic hearing disorder. This is a special case of GSD (general speech underdevelopment). Subsequently, this can lead to difficulties in teaching the child to write and read.
How does phonemic hearing develop?
Phonemic hearing is formed during the child’s communication with family and surrounding people. Therefore, experts advise talking to the baby, reading books and poems to him from the moment he is born. The most significant progress in the development of phonemic hearing is observed between the ages of six months and two years. However, the parts of the cerebral cortex responsible for its functioning are finally formed by the age of 5-7 years.
- From birth to 1 year. The child begins to respond to loud sounds three weeks after birth, and to quiet sounds after 2 months. At 3 months, babies are good at identifying their sources, turning their gaze in their direction. At 4 months the child can imitate sounds, and at 5 months he understands his name. At one year of age, the baby is able to distinguish frequently used words.
- From 1 year to 2 years. At this age, there is an active development of phonemic hearing. The child manages to distinguish sounds in his native language. By the age of two, children can identify erroneous phonemes by ear. The child is able to tell which word was pronounced correctly.
- From 2 to 4 years. By the age of three, the baby stops confusing similar sounds. The correct syllabic structure of the word is also formed. Although there may be problems when pronouncing sounds, for example, children say “na-ni-na” together with “car”.
- From 4 to 6 years. At the age of five, the baby learns to determine the number and sequence of sounds in a word. This is an important stage on which the development of reading and writing skills depends. A six-year-old child can distinguish between the tempo and volume of speech.
Of course, every child has their own developmental standards. But strong deviations may indicate phonetic-phonemic underdevelopment.
Peculiarities of manifestation of delayed speech development in children 4 years old
Features of delayed speech development in children 4 years old are slow or fast speech, blurred sounds, omissions of letters or syllables. Some children do not pronounce words at all or abbreviate them, replacing words with syllables, gestures, and facial expressions.
Characteristic symptoms:
- difficulties in formulating the question and in answering the question addressed to him; the answers are usually monosyllabic (“yes”, “no”, “there”, “here”);
- poor vocabulary - usually uses only those words that are used in everyday life;
- incorrect pronunciation of complex words;
- skipping syllables and sounds;
- lack of skills in composing a simple story or sentence based on a picture;
- replacing words that sound similar;
- There are no hissing or whistling sounds in the articulation, or the patient pronounces them incorrectly;
- replacing sounds with easier ones to pronounce;
- lack of criticism of speech errors in oneself and other people.
Why does a child confuse sounds?
If a 5-year-old child confuses sounds, this indicates phonetic-phonemic underdevelopment. This speech disorder is associated with defects in pronunciation and speech perception. Most often, FFN is diagnosed at the age of 5-7 years.
Experts distinguish three degrees of phonetic-phonemic underdevelopment:
- light. It is difficult for a child to find differences between sounds that he cannot pronounce. At the same time, the ability for phonemic analysis is preserved;
- average The child has serious problems with phonemic analysis. He has difficulty distinguishing the large number of sounds present in his speech;
- heavy. The child is unable to identify sounds. He does not distinguish them, and also cannot determine their location in the word.
If a child confuses phonemes, then first of all it is necessary to contact a specialist and identify the cause of the FFN.
The role of parents in the treatment of mental retardation at 4 years of age
Eliminating speech development delays in 4-year-old children is a matter for specialists with the appropriate education and skills. But parents also play a big role. First of all, the situation in the family has an impact on the child’s condition, including the development of speech. Conflicts and quarrels, even if the baby is not involved in them, affect the child’s psyche. This is fraught with a slowdown in the pace of development.
In addition, in some families no one takes care of the children. They are left to their own devices. If there are prerequisites, for example, close relatives have a speech pathology, then we can talk about a hereditary factor. Such a child will have speech delays.
The next point is the presence of a person with incorrect speech in your environment. The baby will imitate him and speak incorrectly. Experts recommend protecting your child as much as possible from people with pathological speech. That is why parents should always speak correctly, pronouncing all sounds clearly and slowly. You cannot lisp the baby or distort words - this rule must be followed by all family members.
Overprotection also contributes to delayed speech development in children 4 years old. Don't demand anything supernatural from your child. Each person develops at his own pace. By overloading your son or daughter with activities, without leaving a minute of free time, you only make things worse: this is constant stress for children. This can cause other defects to appear: stuttering, enuresis, sleep disturbances.
Reasons for FFN
Phonetic-phonemic underdevelopment can be congenital or acquired. In the first case, the child may confuse sounds due to:
- abnormalities during fetal formation;
- infectious and endocrine diseases of the mother during pregnancy;
- severe toxicosis;
- Rh conflict between child and mother;
- birth injuries (asphyxia, entanglement, etc.).
Acquired FFN occurs due to:
- infectious diseases suffered in the first months of life;
- hereditary factor;
- traumatic brain injury;
- pedagogical neglect;
- emotional shock during the period of formation of speech skills;
- traumatic situation;
- negative environmental influences.
To find out why a child is lagging behind in speech development and confuses sounds, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a neurologist and speech therapist.
Treatment
A speech therapist at 3-5 years old can determine whether there are speech therapy problems that can cause dysgraphia. If necessary, he will recommend special classes.
Treatment of dysgraphia should be comprehensive, and the success of the intervention directly depends on how closely and productively patients and treating specialists interact with each other.
Speech therapists and psychologists treat various types of dysgraphia. Naturally, it is advisable to choose those who have been working with such patients for a long time. Along with writing correction, you will need to develop memory and improve concentration.
It should be remembered that dysgraphia is not a death sentence. The desire to get rid of it and perseverance help cure the pathology forever and without a trace.
Corrective work
Correcting phonetic-phonemic underdevelopment requires a lot of effort and time. In mandatory cases, the child is assigned group or individual lessons with a speech therapist. With FFN, it is necessary to correct sound pronunciation, develop phonetic skills and prepare for learning to read and write.
During speech therapy sessions with the child, the following is developed:
- correct pronunciation of sounds and articulation;
- phonemic analysis and speech synthesis;
- passive and active vocabulary;
- skills of coherent speech, composing phrases and sentences;
- competent writing and reading.
To help the baby stop getting confused by sounds, experts use logarithmics, educational games, visual materials, and so on. Classes with a teacher make the child more attentive, calm and teach him to concentrate on performing specific tasks. To improve the pronunciation of sounds, fine and gross motor skills are also developed. It is recommended to visit a child psychologist. This will help neutralize the effects of stress or emotional trauma that could lead to FFF.
Methods for diagnosing dysgraphia
If you yourself have noticed “funny” writing mistakes that your child makes when doing school assignments, or your class teacher has pointed them out to you, you should consult a speech therapist. The doctor's opinion will be most valuable and reliable if you bring several school notebooks to the appointment.
The need for an integrated approach
Each speech disorder consists of a complex of symptoms. Therefore, the examination of the child must be comprehensive. A neurologist examines for neurological diseases that may interfere with the correct formation of written speech (such as hyperactivity, ADHD, neurosis-like conditions, etc.). A child psychologist will help identify emotional aspects that prevent a child from fully mastering writing, problems with memory and attention. A child psychotherapist will confirm the absence of mental retardation, autism spectrum and mental illness. Additionally, the state of vision and hearing is examined. The speech therapist will establish the level of formation of the grammatical structure of speech, the development of motor functions, the state of phonemic analysis, the consistency of the vocabulary, and deviations in the formation of sound pronunciation.
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Forecast and preventive measures
If a child is confused about sounds, it is important to contact a speech therapist in a timely manner. With regular classes and the help of parents, speech underdevelopment can be eliminated within a year. Depending on the severity of FFN, the work takes from 1 to 12 months.
Parents have a strong influence on the development of oral language skills. Very often, problems with pronunciation of sounds arise due to pedagogical neglect. Therefore, it is recommended to work with the baby from the moment of his birth. Mothers who have experienced difficult childbirth and pregnancy should be especially careful. It is important to visit specialists in a timely manner and not let the situation take its course.
Methods of treating RDD at 4 years of age
Correction of delayed speech development in children 4 years old takes place with the participation of a speech therapist, neurologist, psychologist, and ENT doctor. First, a diagnosis is carried out, during which specialists identify the cause of the defect, find out the features of the course of the antenatal, intranatal (childbirth period) and postpartum period. They study the outpatient card, previous diseases, the nature of physical and neuropsychic development up to one year and at an older age.
This is followed by the stage of hardware examination methods to clarify the diagnosis and exclude organic pathology of the ear, brain, and articulation organs. Electroencephalography, X-ray, MRI or CT scan of the brain, and audiometry are performed. After an accurate diagnosis has been made, treatment for mental retardation begins at 4 years of age: it should be comprehensive, using various methods.
Held:
- Drug treatment - nootropics, sedatives, vitamins, as well as herbal medicines;
- Speech therapy correction - speech therapy massage of the tongue, lips, facial muscles, articulation gymnastics, breathing exercises;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures, including magnetic therapy, acupuncture;
- General massage;
- Physiotherapy.
All treatment procedures are prescribed by a specialist. He knows the characteristics of your child’s 4-year-old RRD, the cause, and based on this he selects an individual treatment regimen. It is unacceptable to independently prescribe a drug, even if it is herbal, to change the dose of a medicine prescribed by a doctor or to cancel it.
An important component of successful treatment is eliminating the cause of the defect. Conflicts, quarrels, mental and physical stress should be avoided.
With the timely start of the correctional program, the absence of severe neurological and mental pathology, and the active participation of the child and parents in the treatment process, the prognosis is favorable. Children's pathological pronunciation of sounds disappears, they begin to speak correctly, clearly and expressively. They ask and answer questions competently. The vocabulary is gradually expanding.
A 4-year-old child diagnosed with RRD is being registered at a dispensary. Specialists monitor him and monitor his further development of speech skills. This is necessary to prevent relapse of the disease. If this happens, it is important to start therapy on time.
Eliminating dysgraphia with exercises
Of course, a child suffering from dysgraphia must be shown to a specialist. We need a correct diagnosis of the disease, which will allow us to select the necessary exercises. Parents can also help their baby by providing additional activities. Here are some exercises for such activities:
- correct the text . We take the text and place extra letters in it. The child must find them and cross them out;
- insert the missing letter . Prepare a text with missing letters in words. At first it may be just a few words. Then the text can be enlarged when the child’s skill in finding missing letters is well developed. This game is an excellent prevention of dysgraphia;
- labyrinth _ The goal of this exercise is to learn to draw a line of sufficient length without lifting the pen from the paper. Great for training gross motor skills in children of all ages;
- Let's write a dictation . Start dictating a text consisting of the simplest words. Gradually make the task more difficult. It is important to work systematically and regularly. Then the child’s correct writing skills will constantly improve;
- Let's play letters . Preparing magnetic letters. We make up their words. Then you can write these words down in your notebook.
Dysgraphia and its types
Dysgraphia is a disorder in the writing process that manifests itself in regular errors of one type when writing.
With a normally formed intellect, most often these disorders go along with vocabulary disorders, when a person experiences difficulties in correctly pronouncing words - dyslexia. Separately, dysgraphia and dyslexia are quite rare.
There are several types of dysgraphia:
- Acoustic. With this type, the child pronounces all the letters, but when writing, he may experience difficulties with sounds that sound paired.
- Ungrammatical. This type of dysgraphia is usually detected only in the second or third grade of school, when the child has already learned the basic rules of grammar. The problem is the declension by gender and number. Incorrect agreement of the main parts of the sentence. Most often, this type of dysgraphia is present in children with underdeveloped speech.
- Optical. Children with this type of dysgraphia make mistakes when writing, adding extra details to letters or not finishing them completely.
- Mirror writing is also a type of optical dysgraphia. If a child loses a word when writing or writes it again, allows syllables in a word to be swapped, or misses spaces between words, we should talk about a violation of language analysis and synthesis.
- Articulatory-acoustic dysgraphia is present in children with speech defects who transfer incorrect pronunciation to writing.
A child may have one of the listed types of dysgraphia, or several.
Confirmation of the diagnosis and correction of dysgraphia is carried out with the help of a speech therapist and independent work to eliminate the causes. It is important to consult a specialist at the first suspicion of the presence of a particular deviation. Each type of dysgraphia requires its own approaches and its own program is selected for each child.
What are the criteria for determining dysgraphia?
There is no early diagnosis of the disease. Until you start teaching your child to write, you won’t be able to identify dysgraphia. Various tests and testing exercises in the early stages will not give much. The problem manifests itself most often in 1st-2nd grade. Here are the signs by which you can determine your susceptibility to the disease:
- The baby records his speech with constant phonetic mistakes. Instead of “b” he constantly writes “p”, and “d” always turns into “t”;
- syllables are formed incorrectly;
- There are always extra letters in words;
- necessary words are regularly missed;
- words are written together;
- the child's handwriting is uneven and illegible;
- the schoolboy tries, puffs, but still writes extremely slowly;
- the baby is silent, and if he speaks, then, fearing mistakes, he does it briefly and monosyllabically;
- “dysgraphic”, realizing that he is not like everyone else, tries to avoid communicating with children of his age.
Recommendations for parents
When teaching your child to read and write at home, try not to harm the learning process with your actions. Parents are quite capable of helping their child achieve literacy. It appears thanks to stable skills that have formed so firmly that they have become a habit.
What will benefit?
- Self-test . Teach your child to reflect first on oral and then on written speech. We wrote the word and thought about it. Is there a mistake here? Over time, thought patterns will form: the child will begin to analyze words before writing.
- Accurate copying helps . Tell the student to carefully copy the text from the book or textbook. Choose a large font to start with. This exercise trains mindfulness.
- Regularity is the best friend of a child who wants to become more literate. If your child is too lazy to sit down at the table and write, do not follow his lead, offering other activities in return. At least 20 minutes a day should be devoted to writing.
- Pay attention to children's handwriting . Graphic symbols and the accuracy of their depiction directly affect literacy: the endings of words are remembered, the difference between letters and the sounds that stand behind them is realized.
What can hinder progress?
Here are the most common mistakes that parents make and prevent children from mastering competent writing as quickly as possible.
- When studying, you can rarely overdo it with praise and positive grades. It often seems to adults that the child has moved forward, but the successes are too insignificant to praise for them. The approval of elders is the best support for a child. Encourage any success in the difficult task of achieving literacy.
- Don’t scold your child, reproaching him for bad reviews from teachers: “I’m ashamed to listen to what teachers say about you! You do the worst work in your class!” A feeling of guilt will be added to the listed problems, but the student will not become more successful from your criticism.
- Make it clear that you are always ready to help. You should not leave your child alone with problems that are beyond his capabilities. Keep your promise by asking every day how your child evaluates his own progress and offering to check his homework.
Basic principles of helping children with dysgraphia
- Don't insist that your child spends hours studying at the table. Do exercises for your back, fingers, and hands. Ventilate the room. Half an hour a day is the optimal duration of the lesson.
- Buy a spelling dictionary and gradually teach your child how to use it. Visual memory and analytical thinking will begin to work.
- Do not scold your child for mistakes - stress blocks rational thinking and the child may fall into a stupor. Show sympathy and support the baby: it’s not easy for him.
- If the situation worsens, contact a tutor who deals with such disorders.
What you can do on your own to correct dysgraphia
To correct missing letters, you need to work with your child on a special type of writing. When an adult reads a word to a child and then asks him to write as many lines as there are syllables in the word. After this, he reads the word again and offers to write how many letters are in the word by putting the corresponding number of dots.
If the child does not write the letter correctly in a stressed syllable or omits the endings, then invite him to play a game similar to cities. Depending on the word that is causing difficulty, ask him to name the word, for example, with the last letter in your word, or with the third letter from the end or the second in the word. To complicate the task, you can set a condition that the words must be on a specific topic.
A good training would be to ask your child to come up with a story using the words you have given, and then offer to write it on paper. After this, check the words with the child and, if there are mistakes, invite him to highlight difficult places in the word using his imagination.
To improve handwriting - cutting out, coloring by numbers, tracing by dots. It is necessary to provide the child with the opportunity to develop fine motor skills and, in some cases, look for additional incentives to increase interest in these activities.
Problems with pronunciation of sounds can be solved by practicing in front of a mirror. Copying words according to a model, when the child is given a word that he must pronounce letter by letter, then write down and compare with the model.
Development of attention. The child is presented with a certain text and asked to cross out from it all the given letters that appear. The choice of letter should be based on the one that causes the most difficulty.
A role-playing game in which you will portray a student and the child a teacher will accentuate and develop the child’s attention well. The point of this lesson is that the child must dictate and check the text you have written. When writing a text, you need to make the most ridiculous mistakes and let your child find and correct them on his own.
How to prevent dysgraphia in a preschooler?
- A preschooler should know and play various role-playing games and games with certain rules. This teaches him to regulate his behavior and actions. It is involuntary regulation that becomes the basis for competent writing.
- A child’s bright, rich speech in the preschool period allows him to master the rules and use them when writing much faster. The development of speech is directly related to the richness of speech addressed to the child. Talk to him often.
- The child should spend a lot of time outside so that the brain is saturated with oxygen.
- An excellent simulator for working to eliminate dysgraphia is visiting a sports section or dancing.
- Playing the piano has a positive effect on the development of motor skills and the development of competent writing.
- If, when teaching a child letters and words, he has a question about which letter should be written, then you should not tell the child two options. You must always answer clearly and clearly the correct option. It is unacceptable, for example, when asked what letter is written, to say “here it is written “A”, not “O”. Your answer must contain only the correct option.
- If a child writes with an error, then correct it imperceptibly, do not focus attention on his mistakes, but only record the correct spelling.
Reading fiction as a way to develop literacy
A very popular and effective method for preventing and correcting dysgraphia in children is based on reading literature.
It is important to note that the child must read exactly as the word is written.
You should not show distrust and think that the child will use words like this in oral speech; no, he perfectly understands how to speak, and reading with pronounced correctness will allow him to remember words on a subconscious level, developing literacy.
All children learn to read by syllables, but as they master reading technology, they gradually stop paying attention to syllables. To correct and prevent dysgraphia, it will be useful to draw the child’s attention to syllables. Let the child read the text for 5-10 minutes a day not as we speak, but as we write. It is important that at this time there are parents nearby who can correctly correct the child in a gentle manner and encourage him to lament correctly again. Using visual, auditory and motor memory, the child will subconsciously remember how to write words correctly.
You can conduct classes with words that cause difficulties for the child. A parent can prepare a short text from the words that the child writes with errors and invite him to read them correctly out loud several times.
Note! When checking your child’s work, you should not highlight errors in red, as this enhances the memorization of incorrect spelling. The best option for consolidation would be to write out and work through the necessary words by reading aloud.
Selecting books for classes is an important task. Scientists have noticed that reading classical works has the greatest effect on preventing and correcting dysgraphia. This is how they advise reading I. Bunin, L. Tolstoy, etc.
You should not conduct classes on eliminating dysgraphia and preventing it using the first text materials that come to hand. A child will not be interested in reading newspaper text or magazine articles intended for adults. There is a connection between remembering the correct spelling and interest in the text. Spend a little time choosing the right literature, and you will see the result not only in the correct spelling of words.
The use of classic texts of Russian literature saturates the child’s speech, allows him to enrich his knowledge and awakens a taste for reading. Instill in your children a love of books!
If you liked the article, please share a link to it
How to teach a child to write dictations correctly at school
In order for your child to get high marks for dictations at school, you need to follow several simple but important principles.
- Painstaking work on mistakes is required. Review each teacher's comment with your child. Try to understand what you missed during class that caused the error.
- Make cards for particularly difficult cases, and return to them from time to time. You need to review the material you have covered a couple of times a week.
- Conduct home dictations so that your child gets used to this test format. This will reduce tension during school tests.
- Do not forget about the development of oral speech, which greatly affects literacy. Read your favorite books together, write down unclear words in your personal dictionary. Ask your child to retell the stories they read often.
- Let the child play the role of teacher. The parent sits down at the table and writes a text from dictation, making several mistakes. The child checks the work of his father or mother, comments, gives recommendations, and explains the material independently. This exercise relieves stress and fear of dictations.
The ability to write correctly and competently develops up to the age of 10, so do not be upset if children have difficulty remembering the rules in elementary school. Any problems can be solved with the help of parents, psychologists, speech therapists and the efforts of the child himself.
Russian language for students in grades 1-4
We develop thinking skills, prepare for Olympiads and improve results in the Russian language in an interactive format
find out more
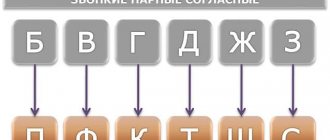
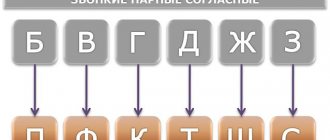
Let's sort out the pairs
To make it easier to remember paired and unpaired deaf and voiced sounds, we connect vision. Let's visualize pairs of consonants in table form.
For this purpose, you can compose a phonemic tale about how vowels and consonants lived in the Russian language, some consonants had siblings, while others did not. We draw two icons on the left side of the sheet that will indicate voicedness and deafness (for example, a bell and headphones). Opposite the bell we write the ringing ones, opposite the headphones – their deaf brothers. Count together how many pairs of brothers are there in our language? That's right, 6. Let the child visually see which letters are paired.
Sometimes brothers change places in words. For example, a paired voiced voice at the end of a word becomes voiceless (tooth, shore, train), and paired voiced voices before other voiced ones become voiced (backpack, request).
But there are consonants that do not have brothers. They do not turn into anyone and therefore are friends only with “their own”. Now in the table we add unpaired voiced ones above the voiced ones, and unpaired voiceless ones under the voiceless ones. With such visual perception, it will be easier for the child to remember the rule: M, L, N, R, Y - only voiced ones, X, C, Ch, Shch - only deaf ones.