How to check paired consonants in a word?
In such cases, we remember that in writing paired consonant letters one should not rely on the pronunciation of the word. In Russian, many words are written differently from how they are heard. In writing, devoicing and voicing of consonants are not indicated. The morpheme retains its single spelling regardless of its sound, except in cases of alternation. Let's turn to the rule for writing paired consonants.
Rule In a word, the letter that appears in the form of this word or in a related word is written if the consonant is followed by a vowel or “l”, “m”, “n”, “r”, “v”.
To establish the true nature of the root consonants and check paired consonants, we take the following steps:
1. put the word with a doubtful final consonant in the plural form:
- crab - crabs;
- cover - covers;
- boot - boots;
- city - cities;
- refusal - refusals;
- voice - voices;
- response - responses.
The word "youth" does not have a plural form. Then we resort to another method of verification.
2. We form the singular or plural form of the genitive case, in which the words “many” or “no” will help us:
- youth - a lot of youth;
- jumble - no jumble;
- box - many boxes;
- gingerbread - no gingerbread.
After the dubious consonant, a vowel sound appeared, which clarified its sound.
3. Let’s look for a related word in which after the paired consonant being checked there will be a vowel sound or sonorant “n”, “l”, “m”, “r”:
- beach - beach;
- fold - fold;
- error - mistake, erroneous;
- paw - paw, little paw;
- cart - to carry;
- shirt - shirt.
In many words of the Russian language, most often borrowed, it is impossible to check paired consonants using a “control word”. These are vocabulary words whose spelling we will remember:
- joke
- railway station
- boots
- zigzag
- astronaut
- coupling
- backpack
- football
etc.
Paired consonants at the end and middle of a word
If a voiced consonant ends up at the end or before a voiceless consonant in the middle of a word, then this position is weak for it. When pronouncing at the end of a word, a phonetic process of deafening a voiced consonant inevitably occurs. Let's listen to how the final consonants sound in words:
- crab [n]
- cover [f]
- boot [k]
- city [t]
- youth [w]
- failure [s].
Definition Stunning is the replacement of a voiced consonant at the end or in the middle of a word with a paired voiceless consonant.
In the middle of words, a voiceless consonant affects the previous voiced one and changes the quality of its sound. The voiced one becomes like it and when pronouncing the word becomes deaf. Let's make sure of this:
- box [n]
- witchcraft [f]
- gingerbread [w]
- guess [t].
Similarly, doubts may arise about the spelling of words with final voiceless consonants:
- response (“k” or “g”)
- eralash (“w” or “w”)
- voice (“s” or “z”).
Voiceless consonants, when placed in front of voiced ones, also change their sound. There is a phonetic process of voicing of voiceless consonants:
- request [z']
- beat off [d]
- unload [z].
Definition Voicing is the replacement of a voiced consonant with a paired unvoiced consonant at the end or in the middle of a word before the unvoiced one.
As you can see, the sound of paired consonants and the spelling of the corresponding letters in the word do not coincide.
Additional materialSee more examples with paired consonants.
What are paired consonants?
Consonant sounds consist of noise and voice or only noise. Depending on the ratio of voice and noise in the Russian language, they distinguish
- voiced consonants
- voiceless consonants
Voiced consonants consist of noise and voice. When pronouncing them, tense vocal cords vibrate under the pressure of exhaled air: [b], [c], [d], [d], [g], [h].
DefinitionVoiced consonants are noisy sounds in the formation of which noise and voice are involved.
On the contrary, in speech there are consonant sounds that are formed entirely from noise:
[k], [p], [s], [t], [f], [x], [ts], [h'], [w], [w'].
When exhaled air passes, the vocal cords do not vibrate. The voice is not involved at all in their birth. These consonants sound muffled.
Definition Voiceless consonants are noisy sounds in the formation of which there is no voice.
Many noisy consonants are similar in phonetic characteristics, except for the sign of voicelessness/voice. From this point of view, such voiced and voiceless consonants, similar in their method of formation, form pairs with each other.
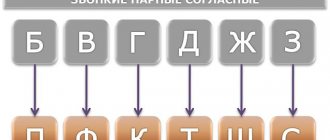
Let's write the voiced consonants vertically on the left in accordance with their places in the alphabet. This will make them easier to remember. And we present paired voiceless consonants on the right.
We will clearly demonstrate paired consonants in the following table.
And only sonorant consonants [th'], [l], [l '] [m], [m'][n], [n '][r], [r'] do not have a paired voiceless consonant, and voiceless consonants [x], [ch'], [ts], [sch'] - paired voiced consonant. These are unpaired voiced and voiceless consonants.
Paired voiced and voiceless consonants will help distinguish words:
- steam - bar;
- count - goal;
- melancholy - board;
- heat - ball.
Paired consonants also differ in softness/hardness.
Let's observe:
- raven [v] - rope [v']
- valley [d] - tree [d']
- hubbub [g] - coat of arms [g']
- juice [s] - village [s'].
Only the always hard paired consonants [zh] and [sh] do not have corresponding soft consonants:
- acorn [zh o l u t']
- gluttonous [p a g o r l' i v y ']
- rustle [shorah]
- silk [sho lk].
If paired consonants are in the middle or at the end, then they behave differently. Depending on which sound is nearby, the phonetic process of voicing or deafening occurs. Because of this, difficulties arise in writing words.
Let's see how paired consonant sounds change at the end and in the middle of words.
A system of work for differentiating paired voiced and voiceless consonants. - presentation
A system of work for differentiating paired voiced and voiceless consonants.
Objectives of the work: Overcoming deviations in the speech development of children (formation of linguistic means necessary for the implementation of full-fledged speech activity; Filling gaps in knowledge of program material in the Russian language, caused by a lag in the development of students' oral speech; Formation of speech functions and psychological prerequisites for mastering educational activities.
The first stage is the formation of phonemic analysis based on auxiliary means and external actions.
The second stage is the formation of the action of phonemic analysis in speech terms.
The third stage is the formation of the action of phonemic analysis in mental terms.
Choose words where the given sound was in first, second, third place. (for example, the sound “K” would be in 1st, 2nd, 3rd place: cat, window, current). Select words from a sentence with a certain number of sounds or write them down. Select subject pictures whose names have a certain number of sounds. Based on the plot picture, select words with a certain number of sounds. Find words for each sound that makes up the original word. The word is written on the board: K O SH K A Porridge windows fur coat goat stork Solve the rebus. From the names of the depicted objects, select the first sound. Name the resulting word. What sound is missing from the word: MOLE - CAT, LAMP - PAWS, etc.
1. Preliminary stage of work on each of the mixed sounds.
Clarification of sound articulation based on visual, auditory, tactile perception, kinesthetic sensations
Isolation of sound against the background of a syllable. To develop the ability to determine the presence of sound in a word. Determining the place of a sound in a word. Isolating a word with a given sound from a sentence.
2. The stage of auditory and pronunciation differentiation of mixed sounds.
Differentiation of isolated sounds. Select the initial sounds from words. Barrel - Kidney From this series of sounds, name those that are similar in articulation: b, a, p, t. Name the similarities and differences between these sounds.
Differentiation of sounds in syllables. Repeating syllables with sounds, first with the same vowel, then with different vowels. Come up with syllables with the given sounds. Transform the syllables by replacing the sound “Z” with the sound “S” and vice versa, for example, ZA – SA, ZO-.. Raise the corresponding letter After pronouncing the syllables. Dictation of syllables with sounds.
Differentiation of sounds in words. Determine what sound is in words. Guess the riddle, clarify what sound is in the word and determine its place. He looks like a shepherd. Every tooth is a sharp knife! He runs, baring his mouth, ready to attack the sheep. (WOLF). Choose words with sounds: at the beginning, in the middle, at the end of the word. Place pictures with sounds under the corresponding letters. Write the words in two columns. Determine the meaning of the words barrel, kidney. Compare the sounds of these words and find out what their difference is. Connect the word patterns and pictures.
Game “Who hid where?
Game “Two words make a third”
Differentiation of sounds in sentences. Based on the plot picture, come up with a sentence that contains words with sounds. Name the words, determine what sound it is and its place in the word. Repeat sentences with words that include sounds. Name words with the correct sounds. Complete the sentences, choosing the words that make sense. The store sells a beautiful ...... (owl, sofa) ..... - a night bird. Fill in the missing letters in the sentences. The sun is shining strongly. It's noisy. ut speeches. And. Make a sentence from the words. Write it down. Underline the letters. Katya, picked mushrooms, berries, etc. Selective dictation. Read the sentences. Are they compiled correctly? Fix them. Write it down correctly. The spider weaves a web. The boots put Petya under the table.
Differentiation of sounds in connected speech. Compose a story based on a series of plot pictures using words that include sounds. Insert missing letters into the text. Write down the story, replacing each picture with a word with the letter z or s. Dictation of texts with words including sounds. (visual, auditory, testing, creative)
Thus, written speech, unlike oral speech, is formed only in conditions of targeted learning, i.e. the mechanisms of written speech develop during the period of learning to read and write and are improved during further education. For mastering written speech, the degree of formation of phonetic-phonemic processes and the lexical-grammatical structure of speech is essential. Disadvantages of sound pronunciation, phonemic and lexico-grammatical development find more or less clear expression in writing in the form of confusion of letters, distortion of the syllabic structure of the word, errors in word formation, and poverty of syntactic structures in the written speech of schoolchildren. Specific errors, i.e. errors not related to the application of grammatical rules in the absence of speech therapy intervention remain in the writing of schoolchildren in subsequent years. This implies the importance of early detection and correction of dysgraphia.