Definition and characteristics
Speech styles are varieties of literary language, distinguished in accordance with the role (function) they perform in communication. They are used in various spheres of public life - everyday conversations, scientific works, fiction, journalistic addresses, and so on.
Each of the functional styles of the Russian language consists of both neutral and specific expressive means . Their features depend on the following factors:
- sphere of communication - everyday, political, professional, social and others;
- the goal is to briefly and succinctly convey information, awaken certain emotions, call to action and motivation, establish contact, and so on;
- method - contact, non-contact, mass, personal.
Differences in styles appear at all levels - from intonation and stress placement to the nature of grammatical and syntactic structures, spelling, and vocabulary. In practice, they often mix and interact, especially in oral communication. Incorrect use of stylistic features can create ambiguity or misinterpretation of speech, which is why it is important to avoid this. Substyles are also distinguished. They are used in specific areas of texts, mainly scientific ones.
Styles are used in different genres. They mean types of texts - from a fiction novel or poem to a scientific report, article, official order, interview. Each of them must meet certain requirements for the means of expression and the method of their organization.
What it is
In short, the characteristics of styles differ from each other in their terminology, method of presenting information, and acceptable words (verbal means of expression) for use for communication purposes.
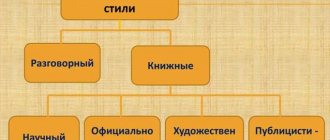
Speech styles are classified according to their purpose and place of use; they are also called “genres of language.” Functional speech styles are divided into 5 types according to the conditions and purposes of communication:
- journalistic;
- scientific;
- official business;
- art;
- colloquial.
To understand the topic, we need to take a closer look at speech styles.
Scientific style
The main task of the scientific style is to convey information to the listener or reader, to communicate systematized facts and practical information. It is divided into five substyles:
- academic - articles, reports, monographs, distinguished by consistency of presentation, accuracy of information, supporting facts with convincing arguments;
- informative - abstracts, annotations, summaries, descriptions with detailed scientific information about the subject;
- reference - catalogues, encyclopedias with a brief, succinct presentation of facts;
- educational - aimed at an unprepared audience, therefore it contains many illustrations, explanations, examples understandable to the common man (includes textbooks, teaching aids);
- popular science - designed to interest the reader, therefore it presents facts in an accessible, entertaining, interesting form (articles, essays, specialized literature).
All substyles are used in written speech and are equally widely used in the humanities, natural and exact sciences. Their common features and distinctive features:
- emphasized logic of presentation;
- unambiguous meaning of all sentences - the possibility of ambiguous interpretation is eliminated by explanations, clarifications and other means;
- information richness;
- lack of figurative expressions, poor set of expressive language means;
- analytical and argumentative, persuasive;
- neutrality of vocabulary, frequent use of special terms and professional vocabulary;
- extensive use of introductory and clarifying structures;
- the use of abstract concepts that cannot be represented in the real world (matter, energy, point, projection);
- the use of prefixes mini-, micro-, nano-, macro- and so on;
- complex sentences with explanatory conjunctions (because of this, as a consequence);
- homogeneous lexical composition, absence of colloquial words and expressions;
- narration from one person throughout the entire text;
- the predominance of impersonal sentences;
- interrogative constructions to attract the reader's attention.
It is easy to understand that the text belongs to the scientific style by the general “dryness” of the presentation, but the use of expressive artistic means is sometimes allowed to make the information more convincing.
Conversational or everyday
The most common style in modern society. It is used in household, informal-professional, household and other areas. Most often used orally. It develops very quickly and is filled with new speech features. Over time, the distinctive features of colloquial speech move into other styles, enriching them with new linguistic means: words, meanings, lexical constructions.
The main genres of everyday style: personal diary, informal note, personal letter, friendly dialogue or correspondence between two or more people. Its features:
- bright emotional coloring, expressiveness, a large number of interrogative and exclamatory sentences;
- frequent use of interjections, particles, conjunctions, introductory constructions and other words and phrases that do not carry actual meaning;
- permissibility of repetition of words and sounds;
- short, simple sentences;
- incomplete, unfinished phrases, the meaning of which can be understood from the context of the speech situation;
- ease, simplicity, familiarity of presentation;
- the use of abbreviated condensate words (oncoming lane - oncoming lane) and doublet words (city dweller meaning citizen, wolf instead of she-wolf);
- constant use of humor, irony, sarcasm, proverbs, sayings;
- imagery, inclusion of value judgments and personal opinions of the speaker;
- the predominance of verbs and pronouns in speech, the relatively rare use of nouns;
- lack of preparation, improvisation, lack of strict logic and presentation plan;
- free word order in sentences;
- use of diminutive suffixes.
One of the main features of conversational style is the importance of not only the content of the text, but also extra-speech factors such as intonation, facial expressions, gestures, and body language. Their correct understanding is necessary for the correct perception of information in everyday conversation. Knowledge of the speech etiquette of a particular area or community is also key in perceiving the message.
Official or business
The official style of speech is used in managerial, administrative, legal and diplomatic spheres of human activity. It is used in documents and contracts, legislative regulations, business and some specific genres of literature, such as autobiography. There are 5 main substyles:
- legislative;
- business correspondence;
- clerical;
- diplomatic.
The style differs from others in that its features and rules of application are enshrined in official manuals and GOSTs for the purpose of standardization and unification. Therefore, it develops slowly and is little subject to change, regardless of time, location, cultural and other characteristics of the population. Distinctive features of the style:
- standardization;
- language that leaves no room for ambiguity or misinterpretation;
- conciseness;
- a combination of neutral, bookish and special vocabulary, the use of professional terminology;
- use of official speech stamps;
- the presence of archaisms (outdated words), absence of slang and neologisms;
- unambiguity of information, confirmed by references to its sources (articles in codes, clauses of the contract, and so on);
- abundance of verbal nouns (application, confirmation) used to reduce volume;
- direct word order;
- sentences with complex grammatical construction, use of participial and participial phrases;
- a large number of enumerations, homogeneous members of the sentence;
- use of passive designs (accepts board instead of accepts board);
- speech without any expressiveness, emotional or figurative coloring;
- narrative nature of the presentation;
- abundance of details and clarifications.
In colloquial speech, business style is rarely used and under specific circumstances. It can be found in courts, at diplomatic negotiations, in communication between entrepreneurs and business partners. The rules of formal speech in oral communication are less strict than in written documents.
Artistic or literary
Artistic style is used in literature. Its task is not only to convey information, but also to create accurate visual and emotional images in the reader, to make him experience certain feelings. Divided into three substyles:
- poetic - poems, poems;
- prose - stories, novels, novellas, short stories, fables;
- dramatic - plays, dramas, comedies, tragedies, tragicomedies.
The artistic style is expressive. It is believed that it is in it that the beauty of language is most clearly revealed. Its main features:
- expressiveness;
- constant use of artistic techniques - metaphors, comparisons, allegories, epithets, contrasts;
- figurative phrases;
- aesthetic significance;
- use of the author’s individual style;
- playing with sentence length and pacing to create emotional effect;
- the use of syntax as a means of expression;
- deviations in sentence structure;
- the use of speech means from other styles to achieve an emotional impact on the reader;
- freedom, lack of strict text structure.
Artistic style can be used in descriptions, discussions and narratives. It is considered the freest, since it practically does not limit the writer. The quality of information delivery largely depends on his talent, experience, abilities and diligence.
Narration. Design features
Narration is a type of speech that can be used to talk about certain events. The story can come from any person: both from the first and from the third (maybe from the second, but usually this is done for the sake of a literary experiment).
The narrative should be conducted logically and consistently. Any story must have all three basic stages: beginning, climax and denouement. The reader must understand the essence of the story, what the author wanted to tell him.
The narrative usually contains a large number of verbs that contribute to the development of the action. In general, this type of speech is very dynamic, and this is its main difference from the other two.
The presented type of speech can be divided into two subtypes: visual narration, which is characterized by changing images, whose purpose is to “show” the event, and informative. In this case, the text not only talks about the event, but also explains it and includes interesting facts.
Examples of narrative text
Narrative texts are found everywhere. Most of any books consist of them. Here is one example of narrative text:
I began to stroke the cat and thought how good my life was! The house is warm, cozy, smells of baking, the cat is purring. I could sit like this forever!
Journalistic texts
The task of this functional style of literary language is not only to convey information to the reader or listener, but also to have a certain psychological impact on him and to arouse public interest . It is divided into five substyles:
- newspaper and journalistic - informational articles, notes and reports, interviews;
- propaganda - leaflets, posters, appeals;
- political-ideological - official substyle used in party resolutions;
- mass political - used at rallies, public speeches and other public events of a similar nature.
In the classification table, the journalistic style occupies an intermediate place between official and artistic everyday styles. From the former he adopted standardization and rigor, from the latter - expressiveness and emotionality. Other features of this style:
- information saturation;
- simplicity and accessibility of presentation, targeting the general public;
- elements of appeal, declarativeness;
- a combination of imagery and brevity in the expression of thoughts;
- constant use of emotional amplifiers;
- commitment to a certain position or idea, value judgments;
- motivational words and phrases;
- the presence of speech cliches characteristic of business and newspaper language;
- use of socio-political terminology, including labels (pseudo-democrats, fascists);
- first person presentation;
- addressing the reader directly;
- use of rhetorical questions and exclamatory sentences;
- reverse order of parts of speech in sentences;
- minimal use of negative words;
- an attempt to play on the reader’s feelings, an attempt to hurt his emotions.
Journalistic texts must interact with the reader and motivate him to action. Therefore, all information posted must be understandable and accessible to a wide audience.
Choosing the right speaking style is important to convey information completely and accurately to readers. The use of syntactic and morphological structures, intonation, speech stamps, artistic means and other language tools is necessary to fulfill the main task of the text.
Test. How do types of speech differ from each other?
- What part of speech is most often found in descriptions?
- a) adjective;
- b) adverbs;
- c) verbs.
- What are the characteristics of reasoning?
- a) dynamics and abundance of actions;
- b) the presence of numerous characteristics;
- c) statement of the thesis and its detailed analysis, expression of the author’s thoughts on a particular topic.
- What part of speech is most often found in narrative texts?
- a) noun;
- b) adjective;
- c) verbs.