Among the 42 phonemes of the Russian language, 36 are consonant sounds. These are sounds in the formation of which the elements of the oral cavity are largely involved: tongue, lips, teeth, palate. Unlike vowels, they are made of noise. Vowels come only from the voice, since the lungs and vocal cords are involved in their formation. But not all consonants are equally composed of noise. Among them there are those in which a significant part of the voice is present. They are called voiced consonants.
Classification of consonants
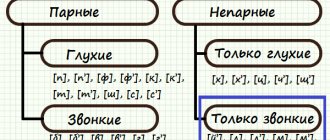
By noise level:
| By noise level | |
| Sonorous | — voice predominates, noise level is insignificant - [l], [m], [n], [r], [th]; |
| Noisy | - significant noise level. Noisy ones are divided into:
|
| By hardness | |
| Solid | [l], [d], [s], [g], [ts], [w], etc. |
| Soft | [l,], [d,], [s,], [w,], [h,], [th], etc. |
Among the voiced consonants, there are 9 sounds in which there is more voice than noise. These are sonorant sounds.
Articulation exercises
Clearly defined articulation is the key to beautiful and correct diction. Many children experience difficulty pronouncing certain sounds during the period of active development of their speech apparatus.
If a person has diction defects (burr, lisp, distorted pronunciation of individual sounds, etc.), it is necessary to correct such defects with the help of special exercises.
Speech gymnastics can be performed both in classes with a speech therapist and independently.
Let us note that pronouncing sonorant consonants causes the greatest difficulties for both children and adults. Such corrective exercises to develop the correct method of articulation can completely rid a person of speech defects.
All exercises must be performed in front of a mirror . The key to correct articulation is to perform movements only with the speech organs. Often, people with diction defects have the following feature: when articulating certain phonemes, movement is transferred to the limbs or parts of the body (for example, arms or legs).
Therefore, when performing corrective exercises, it is necessary to use a full-length mirror in order to identify excessive gestures in time.
Tongue twisters using words that contain specific hard-to-pronounce sounds can be a good way to develop pronunciation. After a persistent improvement in the articulation of the necessary sounds begins to appear, you can move on to pronouncing tongue twisters with an obstacle in the mouth. These could be small pebbles, nuts, candies or a wine cork.
Definition
Sonorant sounds are voiced consonant sounds in which the voice dominates the noise. The word “sonorous” comes from the Latin – “sonorous”, which translated into Russian means “sonorous”. The sonorant group includes eight paired softness-hardness ones and one soft unpaired one: [l] - [l'], [m] - [m'], [n] - [n'], [r] - [r '], [th].
Sonorous sounds, as a rule, are formed with the participation of the lungs, vocal cords, lips, tongue, and palate. Teeth are not involved in their formation. According to the place and method of formation, they are: labiolabial - [m], [m']; lingual-labial – [n], [n']; lingual-palatal – [l], [l'], [r], [r'], [th']. In terms of sound strength, they are all voiced.
Phonetic analysis and speech therapy
The name of sonorant sounds comes from the Latin word “sonorus”, which literally translates as “sonorous”. The choice of this name is explained by the fact that the voice participates in the formation of sound, despite the fact that the air flow that forms it in the oral cavity is able to find its own bypass paths, which is why it becomes not noisy at all.
In addition, at the end of a spoken word with such inclusions, deafening does not occur, as often happens in many other cases.
Sound characteristics
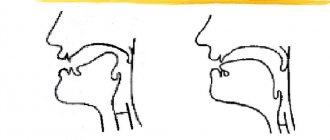
In order to understand what sonorant means in phonetic analysis, it is necessary first of all to understand the main characteristics of its sound pronunciation. Thus, experts distinguish at least two different groups, which directly depend on the position of the so-called velum palatine:
- Oral. This group of sonorous type sounds is characterized by the raising of the wall of the palate and its adjoining of the pharynx in the area of its posterior wall, as a result of which the passage into the nasal cavity for air flow is automatically blocked. As a result, the formation is oral or clean without the slightest hint of turbulence and other noise vibrations.
- Nasal or nasal. In this case, due to the fact that the velum goes down, the passage into the nasal cavity for a stream of air, on the contrary, opens, due to which it functions as a kind of auxiliary sound resonator during pronunciation.
Features of parsing
To consolidate the knowledge acquired in this area, it is recommended to resort to an exercise that has been popular since Soviet times, which involved parsing a word into individual phonemes. As for completing the task, most often it involves following the following algorithm of actions:
- At the first stage, the word is pronounced out loud (possibly several times for better perception of all its constituent elements).
- The second step involves writing this word in full accordance with the spelling rules.
- The transition to the next stage consists of breaking the word down into syllables with the obligatory designation of the only correct place of stress.
- Breaking down into individual syllables allows you to accurately indicate possible places where a word is transferred from one line to another, which is also an important exercise for phonetic analysis.
- Next, each letter is analyzed with a detailed description of all its sound characteristics (presence of a pair, hardness or softness, etc.). At the same stage, sonority should be identified, if it is present in the word being analyzed.
- After all the stages have been completed, all letters and sounds are counted, although these results often do not coincide, and this is the absolute norm.
Based on the results of the work performed, another analytical action is carried out aimed at determining the relationship between spelling and pronunciation. Simply put, the test taker is faced with the task of determining whether what was written corresponds to what was spoken.
Possible problems and their solutions
Recently, an increasing number of parents have had to visit speech pathologists due to poor pronunciation in their children. And most often, the reason for contacting is a child’s violation of the pronunciation of paired and unpaired consonants. This pathology tends to be called dyslalia, which is characterized by good hearing, but difficulty reproducing certain letters.
The placement of such letters can and should be done, the main thing is to give the speech therapist the opportunity to understand the root causes that provoked the current problem. Typically this list includes the following negative factors:
- Problems related to physiology. Sometimes impaired pronunciation is caused by anatomical features, which, in turn, can be primary (congenital) or secondary (acquired) in nature, often caused by the development of chronic ENT diseases.
- Neurology. Mental abnormalities can also cause delayed speech development or pathology.
- Educational deficiency. You should not think that speech abilities always develop automatically, because each child is individual, and what is easy for one is not given to another. That is why experts strongly recommend paying maximum attention to the development of children's speech in order to avoid the consolidation of any serious defects or errors in it.
- Bilingualism. Children raised by bilingual parents also often have serious pronunciation problems, especially if the adverbs used in the family are of incompatible phonetic structure.
- Environment. If in the child’s society there are other children or adults with problematic pronunciation, then there is a high probability that it was this factor that provoked the speech errors.
- Hearing impairment. An ideal ear for music is not a 100% guarantee of correct recognition of all phonemes in speech.
It is important to remember that the choice of correction and its success will directly depend on how correctly the specialist was able to establish the cause of the development of dyslalia. For example, if an anatomical pathology is detected, surgical intervention becomes indicated. If the reason for everything is the baby’s social circle, then it is advisable to change it. The speed of response is also of great importance, because the sooner treatment is started, the more lasting and sustainable results can be achieved in the future.
Complex therapy, which involves not only regular classes with a speech pathologist, but also constant home exercises with the child, has proven to be most effective.
Unpaired voiced sonorants
As noted above, all sonorants belong to voiced consonant sounds. Unlike most voiced consonants, sonorant sounds do not have voiceless pairs. If other consonants, such as [d], [d'], [b], [b'], [z], [z'] and others have paired voiceless [t], [t'], [p] , [p'], [s], [s'], then the sonorant sounds [l], [l'], [m], [m'], [n], [n'], [r], [ р'], [й'] do not have such a pair among voiceless consonants. All sonorant sounds according to this feature are unpaired. They are not deafened in any position: neither at the end of a word, nor before voiceless consonants. They are always pronounced loudly - with vocal force, and ordinary paired consonants at the end of a word and before voiceless consonants are pronounced dull.
This is easy to check by comparison:
"home": before
[m] – “frost”: moro [s]; “day”: de[n'] – “copper”: me[t']; “breakdown”: shelf[m]ka – boat: boat[t]ka; “slice”: do[l']ka – “radish”: re[t']ka.
- The consonants R, L, M, N, J are called sonorant.
- All only voiced, unpaired consonants help to remember the phrase:
LEMON IS PARADISE!
If you delete all the vowels in this sentence, then only voiced, unpaired consonant sounds will remain.
| Hard sonorous sounds | Sonorant sounds, with the exception of the sound [th'], have a pair of hardness: [l] - [l'], [m] - [m'], [n] - [n'], [r] - [r' ]. In certain positions they can be pronounced both softly and firmly: “elk”: [l]os – “salt”: so[l']; “mol”: [m]mol – “mel”: [m']mel; “bottom”: d[n]o – “day”: de[n’], “lynx”: [r]lyx – “door”: two[r’]. The sound [y'] is not pronounced firmly under any circumstances, and does not have a hardness pair: “egg” - [y'ay'tso]. It's just soft. In its sound, it is the closest of the sonorant sounds to vowel sounds, especially close to - [and]. Sometimes it is even called “and - short” |
| Voiced sonorant consonants | All sonorant sounds are only voiced sounds, there are no dull sounds among them!!! |
| Voiceless sonorous sounds | There are no dull sounds among sonorants!!! |
| Hissing sonorous sounds | There are no hissing sonorous sounds!!! |
Basic concepts of the question
The basic definition may lead to the idea that sonorant sounds in the Russian language are the easiest to pronounce, since it does not require much effort. In fact, everything is not as simple as it might seem at first glance, and in order to understand what the peculiarity of sonorant sounds is, it is necessary to delve deeper into this concept, studying its classification, role in phonetics and in language as a whole.
Classification of consonants
First of all, you need to learn to distinguish sonorant sounds from non-sonorant ones by carefully studying the general classification of consonants. It is no secret that they all differ from each other not only in typology, but also depending on the place of formation, which means the area responsible for the beginning of sound formation. According to the theory, all consonants are divided according to these characteristics into the following groups:
- Labial. Formation depends entirely on the position of the lips in relation to each other and other organs. Thus, the pronunciation of one sound may require only closing the lips, while another will be formed when the upper or lower teeth touch the inside of the lips.
- Coronal. The pronunciation of these sounds is ensured by touching the tip of the tongue to the inside of the upper or lower incisors, as well as the alveoli of varying intensity.
- Dorsal. These sounds are formed by the interaction of the tongue and the palate.
- Pharyngeal or throat. It is created without the participation of the tongue, palate, teeth and alveoli with the participation of the larynx alone.
- Glottal. It differs from the pharyngeal in that to pronounce consonants, the vocal cords are closed.
It is noteworthy that sonorant sounds can be included in any of these groups. At the same time, they form an individual group according to the degree of sonority. And in order to learn to distinguish such sounds from the sounds that are obtained when pronouncing other consonants, it is recommended that you familiarize yourself with the following table:
| Sound group name | General characteristics of pronunciation |
| Approximant | In fact, they do not belong to either vowels or consonants, occupying a middle position between them. An example is the English letter “W”. |
| Sonorous | Practically do not create noise during pronunciation or create it in a minimal amount |
| Fricatives | Sound production becomes possible only when the vocal tract is not completely closed. |
| Sounds produced by the slow release of air from the larynx | Pronunciation is corrected by slowing the release of air from the vocal tract |
It is worth noting that sonorant sounds include some approximant, characterized by a similar fricative formation, but without accompanying noise. In addition, this group often includes nasal consonants, formed by lowering the soft palate, due to which air passes through the openings of the nose, single-stroke consonants (flaps), produced only by the force of the organ of articulation, as well as trembling ones, creating vibration.
Meaning in Russian
All sonorant sounds above fricatives, having the property of forming the apex of a syllable in linguistic forms, are sensitive to their sonority. At the same time, sounds that are pronounced with special pressure, restrict the air flow, thereby provoking wave turbulence, or are whistling, are not considered sonorous. In Russian, the following sounds are considered sonorous:
- “R” - despite the fact that this sound is tremulous, it is formed as a result of the tongue touching the area of the alveoli (the basal area of the teeth), being above the fricatives, and therefore related to sonorants.
- “L” - the pronunciation of this sound involves passing an air flow through the tip of the tongue directly while touching the alveoli.
- “M” - this sonorous sound is a nasal sound, since when it is pronounced, air is passed through the nose while the upper and lower lips are closed in parallel and creates turbulence in the lungs.
- “N” - a sound is produced when the tip of the tongue touches the upper incisors.
- “Y” - pronunciation is ensured by the ascent and closure of the back of the tongue with the palate, without the formation of a turbulent flow.
It is noteworthy that all softened versions of these sounds will be considered sonorous. Contrasting (opposite) to these sounds will be those that invariably cause turbulence in the vocal tract during pronunciation. In addition, it is worth highlighting a certain blurriness between approximant and voiced fricative sounds formed in the region of the posterior laryngeal wall, because of which they are very easy to confuse with sonorants.
Sometimes pharyngeal type consonants act as semivowels that correspond to the sound “a”, or they completely change their tonality, eventually becoming hard, forming fricative consonants or another type of sound. Another distinctive feature of sonorant sounds is that they do not always have a voiceless pair. And as a clear example, we can cite the sound “l”, which can only be voiced. But in some other languages, such as Tibetan or Burmese, on the contrary, it is paired, requiring other actions during voiceless pronunciation.
Paired consonants at the end and middle of a word
If a voiced consonant ends up at the end or before a voiceless consonant in the middle of a word, then this position is weak for it. When pronouncing at the end of a word, a phonetic process of deafening a voiced consonant inevitably occurs. Let's listen to how the final consonants sound in words:
- crab [n]
- cover [f]
- boot [k]
- city [t]
- youth [w]
- failure [s].
Definition Stunning is the replacement of a voiced consonant at the end or in the middle of a word with a paired voiceless consonant.
In the middle of words, a voiceless consonant affects the previous voiced one and changes the quality of its sound. The voiced one becomes like it and when pronouncing the word becomes deaf. Let's make sure of this:
- box [n]
- witchcraft [f]
- gingerbread [w]
- guess [t].
Similarly, doubts may arise about the spelling of words with final voiceless consonants:
- response (“k” or “g”)
- eralash (“w” or “w”)
- voice (“s” or “z”).
Voiceless consonants, when placed in front of voiced ones, also change their sound. There is a phonetic process of voicing of voiceless consonants:
- request [z']
- beat off [d]
- unload [z].
Definition Voicing is the replacement of a voiced consonant with a paired unvoiced consonant at the end or in the middle of a word before the unvoiced one.
As you can see, the sound of paired consonants and the spelling of the corresponding letters in a word do not match.Additional materialSee more examples with paired consonants.
Acoustic characteristic
To characterize a sound in terms of acoustics is to characterize the way it sounds. This can be done by its sonority, strength and height.
Sonority allows you to separate vocal and non-vocal sounds. All noisy consonants are nonvocalic. Vocal sounds include all vowels and sonorant consonants.
In terms of strength, sounds can be consonant or non-consonant. All consonants are consonant, i.e. weak, and non-consonant, i.e. strong - all vowels.
From the position of height, the sound can be high or low, respectively. High are the front vowels, front-lingual and middle-lingual consonants. All other vowels and consonants are low sounds.
Concept of articulation
Articulation is the process of producing sounds. The human speech apparatus, with the help of which sounds are formed, is represented by a fairly large set of organs. These include the lungs, larynx, vocal cords, nasal cavity, hard and soft palate, mandible, lips and tongue. The stream of exhaled air leaves the lungs and passes through the gap formed by the vocal cords in the larynx. When the vocal cords are tense and vibrating, a voice (tone) is formed. It serves as the basis for vowels, voiced and sonorant consonants. If the vocal cords are relaxed, the voice does not form, and noise occurs, which underlies noisy consonants.
Further differentiation of sounds occurs in the oral cavity, depending on what obstacle the air stream encounters on its path.
Difficulties in Russian
What about the sonants that cause the greatest difficulty in pronunciation for Russian-speaking people? The consonants [th], [m] and [n] do not cause any particular problems. But incorrect articulation of [l] and [r] occurs in almost every third child.
Note!
- The articulation of Russian [l] is different from the articulation of this sonant in other language systems.
- Russian [r], unlike English, is hard and has clearer articulation.
During the development of the speech apparatus, these phonemes are the most difficult for a child. If you do not seek help from a speech therapist at an early age and start a problem, it will be much more difficult to correct it in adulthood. As a rule, adults who have such a defect no longer undertake to correct it.
Characteristics of vowels
The main feature of vowel sounds is that when they are formed, a stream of air, having formed a tone in the vocal cords, no longer encounters any obstacles in the oral cavity. That is, they consist of only tone (voice) without added noise.
The vowels are the sounds a, o, u, i, ы, e. The articulation of each vowel sound depends only on the position of the active organs of speech (lips, tongue, soft palate and lower jaw).
The functional feature of vowel sounds is that they form a syllable, i.e. play a syllabic role.
Paired consonants. Examples of differentiating words
Deafness and voicedness are able to distinguish words by meaning. For example:
- (soup) thick - (above the river) bush;
- (telegraph) pole - (Alexandria) pillar;
- bark (oak) – (high) mountain;
- (unbearable) heat – (surface) of the ball;
- (bouquet) of roses - (boy) grew up;
- (new) house – (thick) volume.
In weak positions, at the end of words, for example, as in the example of “roses” and “ros”, verification is required to avoid semantic confusion. Paired consonants in Russian require careful attention.
Production of sounds
The speech apparatus is used to produce sounds. It includes the larynx with vocal cords, oral and nasal cavities, tongue, lips, teeth, palate. All these organs are used to enable a person to pronounce words. Different sounds are formed due to the fact that obstacles appear in the path of exhaled air: teeth, lips, tongue, and therefore the sounds are different. Try to exhale air while squeezing your lips tightly - you get the sound [m].
Please note that the air does not come out through the mouth, because the lips have created a barrier, but through the nose. Let's try to make one more sound. We exhale the air, but at the same time we compress and unclench our lips. What happens? [b].
When producing each sound, the speech apparatus uses certain air barriers. In ordinary speech, we do not pay attention to whether the air passes freely or not, because the brain gives a signal which letters need to be pronounced at the moment, everything happens as if by itself. But upon closer examination, you will notice that each sound is formed in its own way.