There are many varieties of text styles in Russian. One of them is the artistic style of speech, which is used in the literary field. It is characterized by an impact on the reader’s imagination and feelings, the transmission of the author’s own thoughts, the use of rich vocabulary, and the emotional coloring of the text. In what area is it used, and what are its main features?
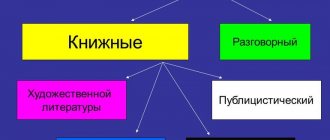
Features of artistic style
Artistic style has a purpose of emotional impact on a person, but it is not the only one. The general picture of the application of this style is described through its functions:
- Figurative-cognitive. Presenting information about the world and society through the emotional component of the text.
- Ideological and aesthetic. Maintaining the system of images through which the writer conveys the idea of the work to the reader awaits a response to the plot's concept.
- Communicative. Expressing the vision of an object through sensory perception. Information from the artistic world is connected with reality.
Application in other forms of art
The artistic style is used in various forms of art, including painting. However, artists do not use it in its pure form, but combine different directions. In addition, in the visual arts there is a tendency to constantly change styles: some flow into others, merge with others and acquire new features.
In the process of painting an oil painting or creating a graphic design, modern European and Asian artists do not limit themselves to traditional means. Often they stylize their works so strongly that they violate cultural norms. This is typical for fashion masters of the current era. Artistic directions in painting:
- baroque;
- classicism (classical);
- Revival;
- Gothic;
- purism;
- cubism;
- naturalism;
- abstract art (abstract);
- urbanism (urbanistic);
- impressionism;
- geometry (geometric).
Within each direction, researchers name prominent representatives. So, in impressionism it is Claude Monet, in cubism it is Pablo Picasso, in urbanism it is Edward Hopper, in naturalism it is José Julio de Souza Pinto.
When talking about style, researchers usually mean 2 meanings: global and narrow. In the first case, we are talking about a set of tools and techniques that involve repeatability. In a narrow sense, style is the individual handwriting of the master, which can be traced in every creation. The situation is similar in architecture, music, theater, cinema and other forms of art.
Signs and characteristic linguistic features of artistic style
To easily identify this style of literature, let’s pay attention to its features:
- Original syllable. Due to the special presentation of the text, the word becomes interesting without contextual meaning, breaking the canonical patterns of text construction.
- High level of text organization. Dividing prose into chapters and parts; in a play - division into scenes, acts, phenomena. In poems, metric is the size of the verse; stanza - the study of the combination of poems, rhyme.
- High level of polysemy. The presence of several interrelated meanings for one word.
- Dialogues. The artistic style is dominated by the speech of characters as a way of describing phenomena and events in the work.
The literary text contains all the richness of the vocabulary of the Russian language. The presentation of the emotionality and imagery inherent in this style is carried out using special means called tropes - linguistic means of expressive speech, words in a figurative meaning. Examples of some tropes:
- Comparison is part of the work, with the help of which the character’s image is complemented.
- Metaphor is the meaning of a word in a figurative sense, based on an analogy with another object or phenomenon.
- An epithet is a definition that makes a word expressive.
- Metonymy is a combination of words in which one object is replaced by another on the basis of spatiotemporal similarity.
- Hyperbole is a stylistic exaggeration of a phenomenon.
- Litota is a stylistic understatement of a phenomenon.
The main features of artistic stylistics of speech
The characteristics of an artistic style of speech have developed over the course of its long development. Its main features allow the text to fulfill its tasks by influencing people's emotions. The linguistic means of a work of art are the main element of this speech, which helps to create a beautiful text that can captivate the reader while reading. Expressive means such as:
- Metaphor.
- Allegory.
- Hyperbola.
- Epithet.
- Comparison.
Also, the main features include the speech polysemy of words, which is quite widely used when writing works. Using this technique, the author gives the text additional meaning. In addition, synonyms are often used, thanks to which it is possible to emphasize the importance of the meaning.
The use of these techniques suggests that when creating his work, the author wants to use the entire breadth of the Russian language. Thus, he can develop his own unique language style, which will distinguish him from other text styles. The writer uses not only purely literary language, but also borrows means from colloquial speech and vernacular.
Features of the artistic style are also expressed in the elevation of emotionality and expressiveness of texts. Many words are used differently in works of different styles. In literary and artistic language, some words denote certain sensory ideas, and in the journalistic style these same words are used to generalize certain concepts. Thus, functional speech styles complement each other perfectly.
Linguistic features of the artistic style of the text include the use of inversion. This is the name of a technique in which the author arranges words in a sentence differently than is usually done. This is necessary in order to give more meaning to a particular word or expression. Writers can change the order of words in different ways, it all depends on the overall intent.
Also in the literary language there may be deviations from structural norms, which are explained by the fact that the author wants to highlight some of his thoughts, ideas, and emphasize the importance of the work. To do this, the writer can afford to violate phonetic, lexical, morphological and other norms.
The features of the artistic style of speech allow us to consider it the most important over all other types of text styles, because it uses the most diverse, rich and vibrant means of the Russian language. It is also characterized by verb speech. It consists in the fact that the author gradually indicates each movement and change of state. This works well to activate the tension of the readers.
If you look at examples of styles of different directions, then identifying the artistic language will definitely not be difficult. After all, a text in an artistic style, in all of the above listed features, is noticeably different from other text styles.
Where is the fiction style used?
The artistic style has absorbed numerous aspects and structures of the Russian language: tropes, polysemy of words, complex grammatical and syntactic structure. Therefore, its general scope of application is enormous. It also includes the main genres of works of art.
The genres of artistic style used are related to one of the genres that express reality in a special way:
- Epic. Shows external unrest, the author’s thoughts (description of storylines).
- Lyrics. Reflects the author’s inner emotions (the experiences of the characters, their feelings and thoughts).
- Drama. The presence of the author in the text is minimal, there is a large number of dialogues between the characters. Such works are often made into theatrical productions. Example - Three sisters A.P. Chekhov.
These genres have subtypes, which can be divided into even more specific varieties. Basic:
Epic genres:
- Epic is a genre of work in which historical events predominate.
- A novel is a large manuscript with a complex plot line. All attention is paid to the life and fate of the characters.
- A short story is a work of smaller volume that describes the life story of a hero.
- A story is a medium-sized manuscript that has the plot features of a novel and a short story.
Lyric genres:
- Ode is a solemn song.
- An epigram is a satirical poem. Example: A. S. Pushkin “Epigram on M. S. Vorontsov.”
- Elegy is a lyrical poem.
- A sonnet is a poetic form of 14 lines, the rhyme of which has a strict construction system. Examples of this genre are common in Shakespeare.
Genres of dramatic works:
- Comedy - the genre is based on a plot that makes fun of social vices.
- Tragedy is a work that describes the tragic fate of heroes, the struggle of characters and relationships.
- Drama – has a dialogue structure with a serious storyline showing the characters and their dramatic relationships with each other or with society.
Examples of texts
This style can be found everywhere. It is present in poems, stories, novels, novellas. Every author has his favorite techniques. For example, some actively use detail, while others saturate the text with epithets. An example of a text with an artistic style of speech, emphasized by detail: “The soldier walked briskly along the white sand, warmed by the scorching rays of the sun. All his clothes were wet, and his skin showed red marks left by the barbed wire. An aching pain permeated his whole body, but he walked, gathering his last strength, because the headquarters was already visible in the distance.”
This passage shows the physical suffering of a soldier, and the author pays attention to details that allow the reader to understand what the character is going through. The second passage is an example of how epithets can be used: “The little mischief maker Yasha was not just a tomboy, but a child with great potential. One only has to remember how masterfully he cleaned out Baba Zina’s garden. As he grew up, he became just as skilled at stealing money from banks. The fraudster managed to act so cleverly that he was never caught in the act.”
Functional style
Functional stylistics explores the differentiation of lit. language according to its historically established varieties (functional-style unities), that is, it studies and describes the system of functional styles and the patterns of its intrastructural organization. It develops general principles of typology, classification and identification of fundamentals. functional varieties (functional style, functional-style sphere) lit. language taken as a theoretical object. research and as a specific historical and cultural reality; reveals them extralinguistic. style-forming factors, their hierarchy and the interaction of styles and functional-style spheres within literature. languages, processes of their functioning and development; the use and principles of organization of speech means within the framework of a certain functional and stylistic unity, basic. parameters of its compositional speech structure; general principles and methods of organizing syntax and vocabulary in texts of a certain functional variety of literature. language.
Styles or directions
Style refers to the idea of this poem and the ways in which this idea is conveyed. The name of the style is strictly tied to the time of its origin. Everything here is similar to architecture, because the building is a poem in stone, don’t you think?
Classicism
Just like classical buildings: rectilinear, strict, monumental. The poem as a whole has a structure where each line is a brick, without which the whole structure will fall apart.
Classicism is necessarily based on antiquity, so it appeared in Europe in the 16th century, and in Russia a little later - in the 18th. Antiquity also determined the genres: ode, fable, comedy and satire. There were others too, but these are the most indicative. The most striking examples: the work of Fonvizin and Lomonosov.
Realism
Writing forever about the lofty would bore even Lomonosov, so realism simply could not help but arise. In Europe, the heyday of realism was the 18th century, in our country it was the 20th, against the backdrop of troubles with the change of power...
Realism shows real life, but in an exaggerated way, exaggerating the desired idea. Here people and their relationships with other people, nature and the world as a whole are brought to the fore.
Often this genre reveals the negative sides of a person. And the scenery is just a way to convey the atmosphere to the reader. Prominent representatives will be Balzac and Bulgakov, and in poetry - Pushkin with his Onegin.
Sentimentalism
While some reveled in human sins, others delved into the topic of feelings. The same 18th century in Europe and only a decade later in Russia. It was conceived as a return of poetry to real life, a departure from sublime odes and abstract fables.
The hero of a sentimental work is usually an ordinary person, and the task of the poem will be to show his feelings and experiences. Here all emotions are often hypertrophied, the response to any event is vivid and memorable. Recognizable examples are Goethe, Karamzin and Zhukovsky.
Romanticism
Here we coincided with Europe - the 18th century, the beginning of the 19th. Odes and fables are, in principle, quite figurative works, and where fantasy is involved, the authors want to express their opinion. And while some were moving away from abstraction altogether, others were actively promoting their worldviews in poetry.
Imagery and interest in traditions, legends and myths are also characteristic here. By the way, science fiction also belongs to romanticism. An example would be Lermontov, all Decembrists. In prose - most of the authors we read at school, contrary to the program: Cooper, Poe, the Brothers Grimm.
Naturalism
All the same late 18th, early 19th centuries. Naturalism is the natural evolution of realism, the inevitable end of this genre. And Darwin, with his “Evolution of Species,” returned people from the sublime to the sinful earth.
Naturalism wants to show that we are ordinary people, with mundane needs and desires. Here people work not for a higher purpose, but to earn money for food. The most prominent authors will be Guy de Maupassant and Zola. In Russia, naturalism has not gained wild popularity, especially among traditionally abstract poetry.
Impressionism
The end of the 19th century, when the painting style of the same name appeared. Here the author’s main task is to convey the significance of each moment, fleeting impressions and move on to another moment through an associative connection, rather than a logical one. In Russia, such an author was Balmont and Fet.
Symbolism
Another legacy of the 19th century. Remember the blue curtains that teachers always ask for the meaning of? So, the hidden meaning of all curtains, bows and other things is only in symbolism. Everything else is the invention of teachers and the earnings of literary scholars.
The general idea of this style is that it is impossible to understand the world with the help of the mind, only intuitively. The authors teach us to understand nature, putting meaning into each symbol in their work. After all, seeing signs is one of the useful skills of a shaman, if you understand my reference. Authors: Blok, Bely, Gippius.
Acmeism
A prominent representative is Akhmatova. A return to the construction of the classics, but without this imagery and moralizing. Just a strict, logical and orderly poem.
There are also styles, it all depends on who classifies and by what criteria. But we dragged on too long, did we manage to get bored?
Genres
If styles are an abstract concept, then genres are more mundane. This means that they logically divide the entire poetic world and there are many of them. Just a few words about the most popular ones.
Oh yeah
Something solemn, sublime and glorifying. “O you who are awaiting...” More pathos to the god of pathos. Add praise to the event, a strict structure and simple wording - and you get the anthem genre.
Ballad
This genre is a little less old than poetry in general. There is a plot that tells about a real or fictional hero and his adventures. For example, about Robin Hood.
Elegy
We see sadness, disappointment, loneliness and a description of the frailty of existence - that means we see elegy.
Song
Probably the most popular genre in all of history. In fact, almost any poem can be sung, but the songs still have a simple rhythm, musicality and choice of words that are easy to sing. And so, any verse sung to music can be called a song. The song about love will already be a romance.
Sonnet
A sonnet is any verse written in the form of “two quatrains and 2 tercets.” There are rules of rhyme and rhythm. And if there are 15 lines in a verse, then this is already a rondo, and the 1st, 9th and 15th lines are repeated here.
Fable
There is imagery, allegory, comedy, necessarily morality, and also a fable - a fairly short work. These are the brightest and most recognizable genres; in fact, there are naturally more of them.
Types of speech
Speech type is a way of presenting information, constructing words and sentences in a logical order.
There are three types of speech:
- narration;
- description;
- reasoning.
Let's consider the features of each type of speech.
Narration
A story about an event or phenomenon. Main features:
- associated with a period of time;
- has a certain sequence of actions;
- consistency of presentation;
- the text answers the questions “what”, “where”, “when”;
- a large number of verbs.
As a result of the narration, the reader becomes clear what happened, where and with whom. The narrative is characterized by the beginning, development and denouement of events. Used in letters, memoirs, memoirs, diary entries.
Description
The purpose of the description is to verbally convey the phenomenon, talk about the qualities of the object, signs, and create a visual or sensory image in the reader. You can describe people, animals, a certain place, event, phenomenon, the internal state of a person and any other phenomenon.
Comprises:
- general characteristics of the subject, general impression;
- signs, details;
- overall assessment of the subject.
Speech is dominated by adjectives, adverbs, and nouns. A minimum of verbs, unlike the narrative, the text is static. Can be used in various styles of speech, most often in artistic and scientific ones. In the latter, accuracy and detail are important, in the artistic - the creation of a certain image in front of the reader, only the most striking moments are described.
Reasoning
Reasoning is thinking, expressing thoughts and ideas, explaining phenomena and properties of an object. The text provides answers to the questions “why” and “why”.
Comprises:
- thesis - an idea that needs to be proven;
- substantiation of the thesis, supporting arguments with examples, evidence;
- summary - results, conclusions.
The purpose of the text is to convince, explain, prove. Reasoning is characterized by rhetorical questions, a sequence of thoughts - “firstly”, “secondly”, “thirdly”, introductory constructions - “meanwhile”, “thus”, “so”, “because”, “ hence".
Often found in scientific and fiction literature, philosophical treatises.
Verse and poem
Any topic needs to start with a short excursion into theory, otherwise you and I will simply speak different languages. A poem is a work of art, complete and logical. For example, Lermontov's poem. A verse is a line of a poem. But in common parlance you can use verse and poem interchangeably, which is what we will do.
Styles, types and other fantastic creatures. Most of us confuse the concepts of style, appearance and God knows what else in these verses, so we analyze each meaning separately.