4.6
Average rating: 4.6
Total ratings received: 760.
4.6
Average rating: 4.6
Total ratings received: 760.
The branch of the science of language, called stylistics, studies functional styles of speech. What it is and how they differ, we will tell you in this article.
The material was prepared jointly with the highest category teacher Lyubov Alexandrovna Koroshchup.
Experience as a teacher of Russian language and literature - 30 years.
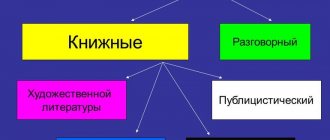
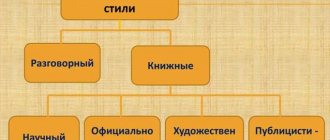
What styles are there?
Depending on the communicative task, when creating texts, we use one or another style. It is he who determines what lexical and syntactic means we need.
Because the choice of style depends on the function that the text is intended to perform, styles are called functional. Usually in the modern Russian language the following types of functional speech styles are distinguished: scientific, official business, colloquial, journalistic and the style of fiction (fiction).
Not all scientists believe that it is right to distinguish an artistic style, because it combines the features of all styles.
Definition and characteristics
Speech styles are varieties of literary language, distinguished in accordance with the role (function) they perform in communication. They are used in various spheres of public life - everyday conversations, scientific works, fiction, journalistic addresses, and so on.
Each of the functional styles of the Russian language consists of both neutral and specific expressive means . Their features depend on the following factors:
- sphere of communication - everyday, political, professional, social and others;
- the goal is to briefly and succinctly convey information, awaken certain emotions, call to action and motivation, establish contact, and so on;
- method - contact, non-contact, mass, personal.
Differences in styles appear at all levels - from intonation and stress placement to the nature of grammatical and syntactic structures, spelling, and vocabulary. In practice, they often mix and interact, especially in oral communication. Incorrect use of stylistic features can create ambiguity or misinterpretation of speech, which is why it is important to avoid this. Substyles are also distinguished. They are used in specific areas of texts, mainly scientific ones.
Styles are used in different genres. They mean types of texts - from a fiction novel or poem to a scientific report, article, official order, interview. Each of them must meet certain requirements for the means of expression and the method of their organization.
Scientific style
Scientific style is sometimes called “encyclopedia style.” Typical genres for it are:
- Research Article;
- monograph;
- thesis;
- popular science article;
- lecture, etc.
This style is characterized by the use of terms, accuracy, and adherence to a certain structure of reasoning. Texts in this style contain specific facts, figures, quotes, and links to other scientific works.
Like other styles, scientific has a number of substyles, which have different main features. Thus, popular science text is characterized by greater freedom and entertainment, and fewer terms. The recipients of texts in a scientific style are scientists, students, schoolchildren, people interested in science. The goal is the transmission of accurate scientific facts and training.
Functional speech styles in Russian: features
In the process of language development, the process of distribution of its communication units occurs according to the area where they are most often used. This is how speech styles arise.
Thus, in colloquial speech, people can use slang, short and incomplete sentences, the content of which is clear from the context or circumstances under which communication occurs. In conversation, speech is emotionally charged. It can use colloquial words, dialectisms, etc.
Photo: medium.com: UGC
These linguistic means will never appear in, for example, a scientific or official business style, and vice versa. It would be funny if a young man, declaring his love, used bureaucratic cliches, and a researcher, instead of terminology, used colorful metaphors to describe the phenomenon of nuclear fission.
Speech styles in the Russian language are strictly differentiated. Each of them solves clearly defined communication problems, is used in a specific environment, and has its own addressee. According to these requirements, vocabulary is selected and certain grammatical and syntactic units and forms are used.
In fact, a speech style is a set of communicative units, strictly regulated by the goals of communication. With their help you can create:
- laws and regulations;
- poems and novels;
- encyclopedias and dictionaries;
- articles in the media, interviews, advertising.
One of them (colloquial) is used in oral speech to solve everyday issues.
Each of these styles implements a specific language function:
- cognitive (epistemological);
- informational;
- aesthetic;
- descriptive.
Photo: kuroku77777.blogspot.com: UGC
Speech styles are easy to recognize. The main thing is to know their features:
- Artistic style is the style of literature (novels and stories, poetic works, drama).
He is distinguished by his emotionality and expressiveness. The main task is to create an artistic image, to evoke an aesthetic experience. Therefore, the artistic style uses both generally accepted vocabulary (recorded in dictionaries) and marked vocabulary (barbarisms, dialectisms, jargon and argot, slang). Both scientific terms and colloquial forms of speech are found here.
- Journalistic style is the style of a public information system—the media.
The main task of the linguistic means that are used in this style is to inform about some event, influence the consciousness of the reader or listener, form public opinion, and encourage individuals and society to take action.
The means used by journalism are synthetic: to implement certain tasks and depending on the genre, journalists can operate with scientific terms and artistic metaphors, clerical clichés and colloquial forms.
- Scientific style - the style of textbooks, monographs, scientific articles.
His means are distinguished by rationalism, logic, clarity, rigor and regulated meanings. Scientific style is dominated by terms.
- Official business style is the style of bureaucracy: legislative acts, diplomatic correspondence, office work.
Its means are used both in oral and written speech. Speech clichés and clerical cliches reign here. All words are used in their literal meaning.
- Conversational style is a style of live oral communication.
This form of communication is mainly dialogical. It is characterized by spontaneity and improvisation. Therefore, this style is characterized by pauses, repeated questions, and short, emotionally charged sentences. Specific grammatical forms are used: condensates (for example, utility room meaning 'utility room') synonyms-doublets (for example, navigator - 'seafarer').
Each style of speech in the Russian language is used in a specific area. They differ in the topics they cover, genres, phraseology, grammatical and syntactic forms.
Formal business style
This is the “document style”. It is characterized by extreme unification of linguistic means, a large number of language clichés (standard formulas), and special vocabulary - clericalism.
In an official business style, clericalisms are appropriate as specific vocabulary (a kind of term); but no other style uses them.
The addressee of the text in this style is an official, a clerk. The goal is to convey official factual information in a condensed form. Genres : statement, memo, report, etc.
Official or business
The official style of speech is used in managerial, administrative, legal and diplomatic spheres of human activity. It is used in documents and contracts, legislative regulations, business and some specific genres of literature, such as autobiography. There are 5 main substyles:
- legislative;
- business correspondence;
- clerical;
- diplomatic.
The style differs from others in that its features and rules of application are enshrined in official manuals and GOSTs for the purpose of standardization and unification. Therefore, it develops slowly and is little subject to change, regardless of time, location, cultural and other characteristics of the population. Distinctive features of the style:
- standardization;
- language that leaves no room for ambiguity or misinterpretation;
- conciseness;
- a combination of neutral, bookish and special vocabulary, the use of professional terminology;
- use of official speech stamps;
- the presence of archaisms (outdated words), absence of slang and neologisms;
- unambiguity of information, confirmed by references to its sources (articles in codes, clauses of the contract, and so on);
- abundance of verbal nouns (application, confirmation) used to reduce volume;
- direct word order;
- sentences with complex grammatical construction, use of participial and participial phrases;
- a large number of enumerations, homogeneous members of the sentence;
- use of passive designs (accepts board instead of accepts board);
- speech without any expressiveness, emotional or figurative coloring;
- narrative nature of the presentation;
- abundance of details and clarifications.
In colloquial speech, business style is rarely used and under specific circumstances. It can be found in courts, at diplomatic negotiations, in communication between entrepreneurs and business partners. The rules of formal speech in oral communication are less strict than in written documents.
Conversational style
Unlike other styles, texts in a conversational style are created mainly orally, although they are also possible in written form (for example, personal letters). This style presupposes freedom in choosing means of expression (but this does not mean that the colloquial style is swearing; we are talking about the style of a literary language, and swearing lies beyond it), simplified syntax, and the use of non-verbal means of expression (gestures, intonation).
The addressee is the interlocutor. The most important form is dialogue. The goal is the emotional transmission of information, usually of personal rather than universal significance.
Journalistic texts
The task of this functional style of literary language is not only to convey information to the reader or listener, but also to have a certain psychological impact on him and to arouse public interest . It is divided into five substyles:
- newspaper and journalistic - informational articles, notes and reports, interviews;
- propaganda - leaflets, posters, appeals;
- political-ideological - official substyle used in party resolutions;
- mass political - used at rallies, public speeches and other public events of a similar nature.
In the classification table, the journalistic style occupies an intermediate place between official and artistic everyday styles. From the former he adopted standardization and rigor, from the latter - expressiveness and emotionality. Other features of this style:
- information saturation;
- simplicity and accessibility of presentation, targeting the general public;
- elements of appeal, declarativeness;
- a combination of imagery and brevity in the expression of thoughts;
- constant use of emotional amplifiers;
- commitment to a certain position or idea, value judgments;
- motivational words and phrases;
- the presence of speech cliches characteristic of business and newspaper language;
- use of socio-political terminology, including labels (pseudo-democrats, fascists);
- first person presentation;
- addressing the reader directly;
- use of rhetorical questions and exclamatory sentences;
- reverse order of parts of speech in sentences;
- minimal use of negative words;
- an attempt to play on the reader’s feelings, an attempt to hurt his emotions.
Journalistic texts must interact with the reader and motivate him to action. Therefore, all information posted must be understandable and accessible to a wide audience.
Choosing the right speaking style is important to convey information completely and accurately to readers. The use of syntactic and morphological structures, intonation, speech stamps, artistic means and other language tools is necessary to fulfill the main task of the text.
Journalistic style
This is “newspaper style”. It is used both orally (oratory) and in writing. This style is characterized by tropes, wordplay, rhetorical figures, and a desire for a biting, effective phrase. Addressee – any person; the message is often directed at the “target audience” and tailored to it at the lexical and syntactic levels. Genres : journalistic article, oratorical speech, speech during a discussion, etc. The goal is to convince you that you are right.
Characteristics and features of conversational style
The characteristic features include :
- Oral form of speech.
- Informality and ease.
- Emotionality (in the form of a live reaction to people’s words and actions).
- Specificity.
- Simplicity and ordinariness of content.
- Use of colloquial vocabulary with a colloquial flavor.
In addition to the above characteristics, the conversational style of speech has a number of features and distinctive features :
- Most often it is implemented in the form of dialogue.
- Language material is not pre-selected.
- Facial expressions, gestures, and the surrounding environment are of great importance.
- Words are used in a figurative sense, there are incomplete sentences, addresses, interjections and particles, repetitions of words.
- The use of emotional words and expressions (nightmare, horror, victory, this is wonderful, etc.).
- Disorganized and fragmented speech (“A kilogram of apples, please.”).
- Intonation plays a special role: raising or lowering the tone, stretching vowels, pauses, changing the tempo of speech.
- Colloquial style vocabulary consists of common words (work, read, book, metro) and colloquial words (potato, giggle, butuz, scribble, hype).
- There are slang words (to fill up a place), colloquial words (dreary, sleepy, crazy) and slang words (teacher), professionalisms (non-cash, cash, turn on the meter), dialecticisms (pitching - duck, kuren - hut).
- Terminological, abstract vocabulary, as well as book words are almost not used.
- Law of economy of speech means. Very often, instead of two words, one is used: condensed milk - condensed milk, sick leave - sick leave; stable combinations are simplified: maternity leave - maternity leave.
- The conversational style is rich in phraseological units: sewn with white thread, touch a nerve, just a stone's throw away.
- To enhance emotionality, doubling of words is used, sometimes with exaggeration: big-very big, black-black water, quiet-quiet.
- Lots of pronouns (I, you, we) and verbs.
- Participles and gerunds almost never occur.
Art style
This is a style of fiction. Rather, it is a contamination (combination) of styles, since creating an image may require a variety of linguistic materials. A work of art may also contain elements that lie outside the literary language: dialectisms, jargon, curse words, etc.
The addressee is the reader. Genres : novel, story, short story, drama, ballad, etc. The goal is to create an artistic image. For this purpose, tropes are usually used - figurative means of language. These are metaphors, comparisons, epithets, etc.
Examples of texts in different styles
To better understand what the text of each style looks like, let’s give some visual examples.
Scientific
Here is a short text from a physics textbook:
Example of scientific style
Here we see special vocabulary:
- "electrical circuit";
- "voltage source";
- “current consumer”;
- "resistor";
- "conductor";
- "voltage";
- "load".
The sentences are complex. There is an introductory construction “by the way.”
Official business
An example of an official business style - instructions for filling out a car purchase and sale agreement:
Example of formal business style
The vocabulary of this text is dry, without epithets and bright emotional coloring. The audience is narrow - the participants in the transaction or the person who will fill out the document. The agreement is also drawn up in an official business style.
Art
The description of the oak tree in Leo Tolstoy's famous novel War and Peace is a striking example of artistic, or literary, style:
Example of artistic style
The text contains many epithets and adjectives, comparison, metaphor, allegory. The oak is compared to an old man, and the branches are compared to gnarled fingers.
Journalistic
An example of journalism - a description of a completed project on a news portal:
An example of journalistic style
The text is emotional, evaluative, inviting. The author's point of view is visible. Addressed to a wide audience of readers. Raises the topical topic of waste recycling. All these are signs of a journalistic style.
Colloquial
As an example of colloquial speech formatted into text, we give a description of the well-known keyboard simulator Stamina. The author made the instructions in the form of a blog, communicates with readers in simple colloquial language with humor, slang and a bright emotional coloring of speech:
Conversational style example
Test on the topic
- /10
Question 1 of 10How many functional styles are usually distinguished in the Russian language?
Start test
Hall of Fame
To get here, take the test.
- Marufjon Ganiev
10/10
- Nikita Gavrilin
8/10
- Sergey Pisarenko
7/10
- Andrey Romanov
7/10