Collocations (22)
- namely
- moreover
- a large number of
- doesn't matter
- for this
- Good morning
- Based on this
- as if
- as is known
- usually
- Besides
- Besides
- did not have
- My pleasure
- no need
- Not only
- although
- Besides
- because
- first of all
- more likely
- more often
On this page you can find the most popular words ending with "o" (at the end of the word - O). The list is sorted alphabetically. You can add your options in the comments. If you click on a word, its synonyms and meanings will open.
See also: words containing O.
- The search took 0.005 seconds. Remember how often you look for something to replace a word with? Bookmark sinonim.org to quickly search for synonyms, antonyms, associations and sentences (press Ctrl+D).
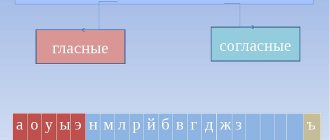
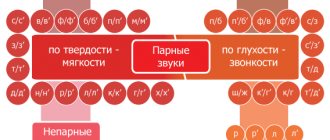
1.8. Vowel sounds in stressed and unstressed positions
As noted (see paragraph 1.5. Speech sounds and letters), in the Russian language there are 6 main (that is, those pronounced under stress) vowel sounds :
| A | ABOUT | E | U | Y | AND |
which are indicated on the letter by 10 letters :
| A | I | ABOUT | Yo | E | E | U | YU | Y | AND |
1. The use of vowels as part of a word has some features in the Russian language:
- The vowel [s] at the beginning of words, as a rule, does not appear; initial [s] is possible in rare borrowed proper nouns.
Oyya, Ynykgan.
- The sound [s] is used only after hard consonants.
Smoke [smoke], rear [rear].
- The sound [and] is used only after soft consonants.
Physicist [f'iz'ik].
- The spelling of the letter and after zh, sh, ts (these sounds are always hard) is not determined by pronunciation: the letter combinations zhi, shi, qi are pronounced as [zhy], [shi], [tsy].
- The vowel [s] is pronounced in place of the letter and also at the beginning of the word after a preposition for a hard consonant (the preposition does not have its own stress and is adjacent to the subsequent word).
From iris - [from-y]ris.
- The vowel [e] is used in most cases after soft consonants.
Children [d'et'i], weight [v'es].
But there are digressions here. The sound [e] is combined with hard consonants:
- after [g], [w], [ts];
Gesture [gest], six [shes't'], prices [tsen].
- in some foreign words;
Test [test], pace [temp].
- in some compound words.
HPP, VTEK.
2. A characteristic feature of Russian pronunciation is the different sound of vowels under and without stress.
- A vowel in a stressed position is in a strong position , that is, it is pronounced most clearly and with the greatest force. A vowel in an unstressed position is in a weak position , that is, it is pronounced with less force and less clearly.
3. In an unstressed position (in a weak position), all vowel sounds are pronounced with less force, but some of them retain their qualitative characteristics, while others do not:
- The vowel sounds [i], [ы], [у] (letters i, ы, у, yu) do not change the sound quality in an unstressed position;
Mil [m'il] - sweet [m'ila], lived [zhyl] - lived [zhyla], jester [jester] - (no) jester [jester].
The exception is the sound [and]: at the beginning of a word, if in the flow of speech the word merges with the previous word ending in a hard consonant, the sound [s] is in place;
In exile [in exile]. - The vowels [a], [o], [e] (letters a, i, o, e, e, e) change the sound quality in an unstressed position.
4. Russian literary pronunciation is usually called “akay” and “hiccuping”.
- In the pre-stressed syllable after hard consonants in place of the vowels [a], [o], [e] (in the position after hard ones, this sound is rarely found in the Russian language), a sound close to [a] usually sounds. In the school version of the transcription it is usually denoted as [a], although this sound is not so open, therefore in linguistics a special sign [Λ] is used to denote it.
My [moj] - my [mΛja] or [maja], gave [gave] - gave [dΛla] or [gave].
- In the pre-stressed syllable after soft consonants in place of the vowels [a], [o], [e], a sound close to [i] sounds. In the school version of the transcription it is usually denoted as [i], although this sound sounds more like [i] with the overtone [e] - [ie].
Wed: took [v'al] - took [v'iela] or [v'ila], carried [n'os] - carried [n'iesla] or [n'isla], white [b'el] - white [b'iela] or [b'ila].
- It is with these features of Russian pronunciation that the need to check unstressed vowels is connected with the help of related words in which this vowel is stressed, that is, in a strong position.
- The position of the vowel in the first pre-stressed syllable is called I weak position : the force of exhalation when pronouncing a pre-stressed syllable is approximately one and a half times less than when pronouncing a stressed syllable.
| So, in the first weak position in place of [a], [o], [e] after hard consonants there is a sound close to [a] - [Λ], after soft consonants there is a sound close to [i] - [ie] . |
5. An exception may be some words with vowels [a], [o], [e] in the first weak position after hissing [zh], [sh] and after the sound [ts]:
- after hard [zh], [sh], [ts] before a soft consonant, in place of [a] there is usually a sound intermediate between [s] and [e] (indicated [ые]);
To feel sorry for [zhyel'et'], horses [lyshyed'ej], twenty [dvatsyet'i].
- in place of the letter e after [zh], [sh], [ts] there is a sound intermediate between [s] and [e], - [ye];
Wife [zhyena], sixth [shyestoj], price [tsyena].
- after hard [zh], [sh] in place of [a] there is a sound close to [a] – [Λ], as well as after other hard consonant sounds.
Ball [ball] – balls [shΛry].
6. In other unstressed syllables (second, third pre-stressed syllables, unstressed syllables) the vowels [a], [o], [e] sound even weaker and unclear.
- The position of the vowel in other unstressed syllables (not in the first pre-stressed) is usually called weak position II : the force of exhalation when pronouncing such syllables is three times less compared to a stressed syllable.
- In the school course, these sounds are not specifically discussed.
- In linguistics, such sounds are usually called reduced, that is, “weakened.” To designate them, the following signs are most often used: “er” [ъ] – after hard consonants, “er” [ь] – after soft consonants. (This resource uses a simplified version of vowel transcription, that is, the pronunciation features of vowels [o], [a], [e] in closed and open overstressed syllables are not taken into account, the difference in pronunciation [o], [a], [e] in overstressed syllables syllable, etc.)
For example:
after hard consonants: brownie [d'mavój], fish [ryb'], roof [krysh'], entirely [ts'l'ikom];
after soft consonants: private [r'davoj], field [pol'j], watchmaker [ch'sΛfsch'ik].
7. The exception is the II weak position of vowels at the absolute beginning of the word [a], [o]. In place of these vowels at the beginning of the word, there is not a reduced “er” [ъ], but a sound close to [a] – [Λ], as in the first weak position after hard consonants.
Cucumber [Λgur'ets]; monkey [Λb'iez'janʹ].
Analysis algorithm when transcribing a word
| 1. | Break the word into syllables and add stress. Regret - so-zha-le-ni-e. |
| 2. | Underline the stressed vowel with two lines. Regret. A stressed vowel does not change its sound. Just keep in mind that the letters e, e, yu, i can mean:
|
| 3. | Place the number of the weak position above the unstressed vowels: first pre-stressed syllable – I weak position; the remaining unstressed syllables are II weak position. CoII-zhaI-le-niII-eII. If among these vowels there are sounds [i], [ы], [у] (letters i, ы, у, yu), then emphasize them with one feature: they do not change their sound in an unstressed position. SoII-zhaI-le-niII-eII – in an overstressed syllable the vowel [i] does not sound. |
| 4. | Determine which vowel sounds sound in weak position I (first pre-stressed syllable) in place of the letters e, e, o, a:
SoII-zhaI-le-niII-eII – in the syllable zha the vowel sounds [е]. Please note that if the letters e, i denote two sounds: a consonant [j] + a vowel [e], [a], then these vowels also change according to the general rules: j is a soft consonant, which means that after it the letters e, i the sound [ee] will sound. Announced - oII-byaI-vil-syaII - the first pre-stressed syllable byaI will sound like [b'jie]. |
| 5. | Determine which vowel sounds sound in the second weak position (any unstressed syllable, except the first pre-stressed one) in place of the letters e, e, o, a:
Please note that if the letters e, i denote two sounds: a consonant [j] + a vowel [e], [a], then these vowels also change according to the general rules: j is a soft consonant, which means that after it the letters e, i the sound [ь] will sound. SoII-zhaI-le-niII-eII – the syllable с with a hard consonant sounds like [съ]; the syllable e ([j] + vowel) sounds like [ь]; oII-byaI-vil-syaII - o at the absolute beginning of the word will sound like [Λ], the syllable sya with a soft consonant will sound like [s'ь]. |
Exercises for the topic “1.8. Vowel sounds in stressed and unstressed positions"
►
How vowel sounds are formed
“The sounds of voices flow, we read them as we sing.
Letters are called vowels, we can find them in every word.”
Vowel sounds in Russian are formed when a stream of air during exhalation passes freely through the larynx, in which the vocal cords are located. When they are tense, the air causes them to move, to tremble. This is how the sound we hear is created. The vowel sound contains a voice (hence the name - “vowels”, that is, created by the voice). Therefore, you can pull them out, sing: - a-a-a-a-a-a; - oo-oo-oo-oo-oo.
Why are they different? The formation of sounds [i], [s], [o], [u] and others depends on the position of the tongue and lips during articulation.
To pronounce the sounds [o] and [u], you need to stretch your lips forward. Therefore, these sounds are called labialized, rounded. In addition, vowel sounds, depending on the position of the tongue during exhalation and sound formation, are divided into:
- sounds of the front row (the tongue is in the front) - [i], [e];
- sounds from the back row (the tongue is tucked into the back of the mouth) – [o], [u];
- sounds of the middle row (the tongue occupies an intermediate position) - [a], [s].
The second characteristic is lift: high, medium or low rise of the tongue while pronouncing a sound:
- the tongue is raised as far as possible to the palate - sounds [i], [s], [u];
- middle position of the tongue – sounds [e], [o];
- lower – [a].
Letter O pictures for children coloring book
Letter O pictures for preschool children: 3-4 years old, 4-5 years old, 5-6 years old, 6-7 years old and primary school age: 1st, 2nd, 3rd grade. The coloring book includes a drawing of the letter O and pictures of animals and objects that begin with this letter. By coloring pictures, children remember the letter faster.





![Pronounce (read) syllables with the sound [L_]](https://ls-kstovo.ru/wp-content/uploads/proiznosit-chitat-slogi-so-zvukom-l_-330x140.jpg)
