December 3, 2021 Speech development defects in children (dysarthria) usually have complex causes. This may be disturbances in the speech centers of the brain, problems with the transmission of nerve impulses, or insufficient mobility of the speech organs. The main method that helps children begin to speak normally is speech therapy massage for dysarthria. It can be compared to training in the gym, because the speech organs - and, above all, the tongue - are controlled by the work of the muscles. With the help of the procedure and regular exercises, you can quickly achieve good pronunciation of all sounds, including the most complex ones.
Correction of dysarthria with massage in children
Speech therapy massage for various forms of dysarthria involves mechanical effects on various parts of the face and on the tongue. As a result, pathological symptoms in the peripheral part of the speech apparatus are eliminated, and muscle tone changes.
As a result, in the child, the strength of muscle spasms and their number decreases, and muscle tone normalizes with dysarthria (articulatory and facial muscles). The mobility of the speech organs is restored, blood flow in the soft tissues of the face and brain improves.
These factors help improve the quality of speech: it becomes smooth, expressive, and understandable to others. The baby begins to behave calmer and sleeps better.
Speech therapy massage is prescribed only by a speech therapist after a detailed examination. The specialist assesses the degree of the violation and, depending on this, selects an individual correction scheme.
Signs of erased dysarthria
Typically, dysarthric children are characterized by clumsiness, impaired coordinated movements, and underdevelopment of finger motor skills. They have difficulty mastering the skills of buttoning and lacing, do not know how to hold scissors, and do not like to draw and sculpt. But in my practice over the past two years, I have observed many children aged 5-7 years with good coordination and developed fine motor skills; they love to draw, paint, sculpt, hold a pencil well, and successfully handle shading. Signs of the disease are visible only on the face, and not in everyone. One of the noticeable signs of erased dysarthria: a static, sedentary face, tense lips or, conversely, saggy lips and cheeks, the mouth does not close.
Of particular interest in the erased form of dysarthria is the language. In most cases, the tongue is thick and massive; when stretched, the back of the tongue tenses and gathers into a lump. Due to this, the child has difficulty pronouncing many sounds. When pronouncing hard sounds, soft sounds are heard, since the back of the tongue automatically rises to the sky, as a result, instead of [p] we hear [p'], instead of [b] - [b'], instead of [s] - [s'], instead of [ z] – [z'], etc. The tense back of the tongue closes the hole for the free passage of the air stream, so whistling and hissing sounds have the sound [ts]. When repeating syllables and words, many sounds acquire overtones [l']. For example, tya-tya-tya sounds like aphids-aphids. The tip of the tongue with erased dysarthria is usually not pronounced, that is, it is impossible to determine where the tip is. Often, due to pareticity of the tongue muscles, the child cannot lift it up, lick the upper lip, or reach the upper teeth with the tip. In this regard, the baby does not have hissing sounds and [r].
Many children experience deviation
- deviation of the tongue towards the paralyzed muscle. When you ask a child to pull out his tongue and hold it on his lower lip for a count of five, the tongue shakes, trembles and tries to move to the side. This is a clear sign of dysarthria. Due to hyperkinesis, the pronunciation of a group of whistling, hissing and sonorant sounds is impaired, and prosody also suffers. Speech is inexpressive, slurred, inarticulate, monotonous, often quiet, with a slight crackle in sound, nothing can be understood. They say about such children: “he has porridge in his mouth.”
A distinctive feature of dysarthrics is their unstable psyche. Such children often rush from one extreme to another. Either they are overly touchy, vulnerable, whiny, they react painfully to every little thing, then they become aggressive, rude, refuse to engage, talk, and even throw themselves at others with their fists. Dysarthric children have very low motivation and motivation to learn.
Contraindications
Speech therapy massage for children with dysarthria cannot be performed when the child has:
- rash, swelling of various types on the skin;
- exacerbation of herpes infection;
- colds, viral diseases;
- inflammatory processes of the oral cavity and lips - stomatitis, gingivitis, caries, fungal infection;
- inflammatory processes of nearby organs - conjunctivitis, rhinitis, lymphadenitis, furunculosis;
- cuts, abrasions, hematomas;
- severe chronic diseases - oncological, cardiovascular, hematological, neurological, psychiatric.
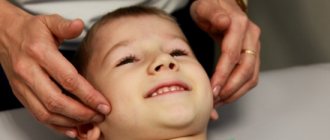
Face massage
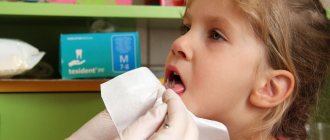
The correct sequence for a relaxing massage is as follows: first, apply to the face and lips, then to the tongue.
Facial massage for dysarthria involves rubbing, kneading, and stroking. Before the procedure, remove jewelry and keep your nails short. The first sessions are short, the duration gradually increases.
The classic version begins with kneading movements in the forehead area. The movements are smooth, from the central part towards the temples. Then stroking from the eyebrows to the hairline with the pads of all fingers.
You cannot press hard on the eyelids: all movements should be light, stroking. The direction is circular, clockwise.
In the cheek area, it is necessary to relax the muscles by stretching them from the mouth towards the temples, and from the cheekbones - downwards, towards the chin. After this, we move to the nose, smoothly rubbing the wings up and down, stroking the nasolabial fold in the direction from the nose to the corners of the lips.
Articulatory lip massage for dysarthria involves kneading with vibration movements, then rubbing from the middle of the lips to the corners. Then they rub the chin and stroke the ears.
When a child has facial asymmetry, different muscle tone on the left and right, pay more attention to the affected side to achieve normalization of muscle tone in dysarthria.
general information
Like any procedure, facial massage for dysarthria in children has its own indications and rules. First of all, this is the qualification of a specialist. The speech therapist must be trained in this area and have completed training courses.
It is advisable that he constantly study the relevant literature and improve his qualifications.
To perform a massage you need a couch or chair. They should be easy to use. If necessary, take flat pillows (they are placed under the back, which leads to muscle relaxation) and bolsters.
The massage therapist's hands must be clean and free of abrasions, calluses, warts, etc. At the first appointment, the child is diagnosed and muscle tone is determined. They can be too tense (hypertonicity) or too relaxed (hypotonicity).
A speech therapist must understand anatomy, physiology, and psychology. Every action must be thought out. Only with this approach can sessions be conducted.
Speech therapy tongue massage
The tongue is the main organ of speech. Therefore, speech therapy massage of the tongue for dysarthria is a necessary element of treatment. Helps fight weakness, limited muscle mobility, paresis and paralysis. Specialists use several techniques in their work. Let's take a closer look at them.
Massage with a toothbrush
A toothbrush, due to its bristles, perfectly warms up the tongue. It can be used both in classes with a speech therapist and for independent speech therapy massage at home. The approximate steps are as follows:
- Place a paper napkin or handkerchief under your tongue to prevent saliva from running off and irritating your skin. When the napkin gets wet, you need to change it;
- the child should relax his tongue as much as he can;
- first perform circular kneading movements along the back of the tongue, the pressure should not be strong;
- stroking over the entire area of the tongue, intermittent movements, as when brushing teeth;
- the baby tenses his tongue, lifting it upward, you massage the lower part of the tongue and the pit under it.
When massaging, be careful not to trigger a gag reflex in the child.
Tongue massage with fingers
Finger speech therapy massage of the tongue for dysarthria allows you to work all muscle groups, including deep ones. Sessions help relieve hypertonicity of facial and articulatory muscles. To carry out the procedure, you need a clean handkerchief, fabric napkins, and special finger pads.
The stages are:
- Relaxation of the tongue muscles;
- Grab your tongue with two fingers, twist it clockwise and counterclockwise, tap on the back;
- Move towards yourself, while grabbing the tip with three fingers: one from above, two from below;
- Now let's deal with the middle part of the tongue. Also grab your tongue and pull it towards you, holding this position for a couple of seconds;
- Grab your tongue and pull it towards you a little. In this position, use the fingers of your other hand to make squeezing movements over the entire surface of the tongue. They squeezed - they let go, they squeezed - they let go;
- Turns around an axis, while the tongue needs to be placed on one edge, hold it for a couple of seconds, then on the other edge;
- It is also necessary to work with the lips - their role in articulation is significant. Tap them with your fingertips, stretch them up and down, and roll them into a tube.
Speech therapy massage for various forms of dysarthria should be performed once or twice a day, for 15 minutes, for a couple of weeks. The speech therapist will tell you the exact duration and quantity: it all depends on the diagnosis and the degree of impairment. Also consider age: small children cannot sit for long, so choose a few exercises one day and do only them. And the next day, do others.
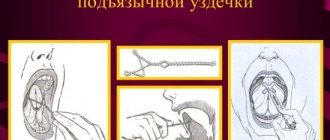
Probe massage
One of the modern correction methods is probe massage for dysarthria. This is one of the new treatment methods that is gradually gaining popularity. It is carried out using special probes developed by E. V. Novikova, Doctor of Pedagogical Sciences.
The standard set consists of 9 tools, each of which is designed for specific purposes. For example, sleds, shaped like sled runners with rounded ends, are designed to stimulate muscles. The “hatchet” in the form of two flattened loops can be used with both increased (light pressure) and decreased tone (strong pressure) of the muscles.
There are variations by other authors, for example, probes with a su-jok effect for additional stimulation of nerve endings and muscles.
After the sessions, children’s speech breathing normalizes, their voice becomes expressive and strong, defects in sound pronunciation are eliminated, and the condition of the central nervous system improves.
Articulatory massage with probes for dysarthria should not be performed on children under six months; at this age there is no such need.
The sequence of a relaxing massage is determined by a speech therapist/speech pathologist, based on the specific situation, the severity of the disease and the age of the patient. The standard tactics are as follows:
- The tool in the form of a small ball needs to be moved over the entire surface of the tongue;
- Piercing the tongue with a pitchfork-shaped probe. Muscle contraction occurs. Then the doctor makes oscillatory and rotational movements with the instrument at various points for five seconds;
- Using a figure eight, press on the organ at several points;
- “Sleds” come in three sizes. They also make pressing movements;
- "Hatchets" are used to slide with little pressure;
- Use a “crosspiece” or “pusher” to press on the tongue, and then remove the probe. The muscles of the tongue contract.
Probe massage for dysarthria is carried out for a long time: usually in courses of 2–3 weeks. Each movement must be repeated 20–30 times. A repeat course is indicated after a month and a half.
Speech therapy massage when working with dysarthric children; article on speech therapy on the topic
Speech therapy massage when working with dysarthric children
In recent years, the number of children suffering from various speech disorders, in particular children with dysarthric disorders, has increased.
Dysarthria is a disorder of the pronunciation organization of speech associated with damage to the central part of the speech motor analyzer and a violation of the innervation of the muscles of the articulatory apparatus. With dysarthria, the mobility of the speech organs (soft palate, tongue, lips) is limited, which makes articulation difficult. For dysarthric children, articulation and breathing exercises alone are not enough to correct sound pronunciation. Speech therapy massage is required.
Speech therapy massage is a unique, unconventional and effective method of correcting sound pronunciation, as it helps to normalize the pronunciation side of speech, improves the condition of the voice, speech breathing, and normalizes the emotional state of a child suffering from speech disorders.
Speech therapy massage not only improves the motor function of lagging brain systems, but also involves nearby brain systems. It is part of the comprehensive rehabilitation of preschool children, as a means of effective correction of speech disorders. Massage has a beneficial physiological effect on the body. Massage improves the secretory function of the skin, activates its lymph and blood circulation. And therefore, it improves her nutrition and increases metabolic processes. The state of the muscular system changes significantly under the influence of massage. First of all, the elasticity of muscle fibers, the strength and volume of their contractile function, muscle performance increase, and their activity is restored after exercise. The differentiated use of various massage techniques makes it possible to reduce tone in case of muscle spasticity, and, on the contrary, increase it in case of flaccid paresis of articulatory muscles. This helps the formation and implementation of active voluntary, coordinated movements of the organs of articulation.
Thus, speech therapy massage has an overall positive effect on the body as a whole, causing beneficial changes in the nervous and muscular systems that play a major role in the speech-motor process.
There are various methods of speech therapy massage. The most popular is massage by E.A. Dyakova. and probe massage by Novikova E.V. There are also known works covering the methodology of speech therapy massage by such specialists as E.F. Arkhipova, I.B. Karelina, O.I. Krupenchuk, T.A. Vorobyova, Yu.V. Makleeva, O.G. Prikhodko and others.
The main objectives of speech therapy massage are:
- normalization of muscle tone of the articulatory apparatus (in more severe cases - a decrease in the degree of manifestation of motor defects of the articulatory muscles: spastic paresis, hyperkinesis, ataxia, synkinesis);
- activation of those muscle groups of the peripheral speech apparatus in which there was insufficient contractility (or inclusion in the process of articulation of new muscle groups that were previously inactive);
— stimulation of proprioceptive sensations;
— preparing conditions for the formation of voluntary, coordinated movements of the organs of articulation;
- reduction of hypersalivation;
- strengthening the pharyngeal reflex;
— afferentation into the speech zones of the cerebral cortex (to stimulate speech development in case of delayed speech formation).
Contraindications for massage are infectious diseases (including ARVI, influenza), skin diseases, herpes on the lip, stomatitis, conjunctivitis. Massage should be used with great caution in children with episyndrome (convulsions), especially if the child cries, screams, breaks out of his hands, his nasolabial “triangle” turns blue or there is a tremor of the chin.
Speech therapy massage is performed in a warm, well-ventilated room. Typically, massage is recommended to be carried out in cycles of 10-15-20 sessions, preferably every day or every other day. After a break of 1-2 months, the cycle can be repeated. Under certain circumstances, when massage cannot be done often and regularly, it can be carried out for a longer time, but less frequently.
The duration of one procedure can vary depending on the age of the child, the severity of the speech-motor disorder, individual characteristics, etc. The initial duration of the first sessions is from 1-2 to 5-6 minutes, and the final duration is from 15 to 20 minutes. At an early age, massage should not exceed 10 minutes, in junior preschool - 15 minutes, in older preschool and school age - 25 minutes.
Body position during speech therapy massage.
Before starting a massage session, the child’s body must be brought into the correct position. Correct posture helps normalize muscle tone (usually relaxation) and makes breathing more free.
For speech therapy massage, the following positions are most optimal:
— in a supine position, a small cushion is placed under the child’s neck, allowing him to slightly raise his shoulders and tilt his head back; arms extended along the body; the legs lie freely or are slightly bent at the knees (you can also place a cushion under the child’s knees);
- child - in a half-sitting position in a chair with a high headrest;
- child - in a half-sitting position in a reclining highchair or a stroller.
Types of speech therapy massage.
There are several types of speech therapy massage. The main ones are:
1. Classic (manual) massage is a massage that uses 4 classic techniques: stroking, rubbing, kneading and vibration. In classical massage, the state of muscle tone is taken into account; accordingly, it is divided into activating and relaxing.
A harmonizing massage is a massage between a relaxing and an energizing massage. It is carried out in case of uneven muscle tone.
2. Acupressure or massage on biologically active points (BAP) is a massage that is a method of reflex therapy. Acupressure involves applying pressure to active points and is also divided into relaxing and toning massage.
3. Mixed massage is a massage that includes several types of massage. For example, a differentiated classic massage can be supplemented with acupressure techniques, which enhances the effect on the body as a whole; or supplemented with individual techniques of instrumental (probe) massage, which enhances the effect on individual muscle groups.
4. Self-massage is a massage that is performed by the child himself. This type of massage is an additional means of influence and can also be relaxing and energizing. This can be either a hand massage or a tongue massage using the teeth (the articulation exercise “Combing the tongue,” when the child forcefully pushes the tongue through closed teeth).
5. ILC - artificial local contrast derma - this is the effect on skin receptors of either cold or heat.
6. Massage of reflexogenic zones is a massage of the feet, hands, scalp, ears, tongue. Massage of reflexogenic zones regenerates organs, improves their blood supply, and promotes relaxation. This alone creates important prerequisites for restoring impaired functions in the body. Experience shows that such a massage can relieve blockade or overstrain.
7. Segmental reflex massage is when the massage is carried out in separate zones, parts, for example, first one half of the face, then the other, or it can be a massage of individual parts of the hands, feet, ears, scalp, tongue. With segmental reflex effects, all the basic techniques of classical massage are used + additionally developed and scientifically proven techniques for various pathologies. With this massage, elements of gymnastics and isotomic (with elements of resistance) exercises can be used to normalize the work of the muscles of the neck, lips, and tongue. The choice of massage techniques, the technique of their application and the dosage of the effect depend on the form and stage of the pathological process. All this is established at the first visit to a specialist.
8. Hardware massage - carried out using vibration, vacuum and other devices.
9. Instrumental massage – massage using speech therapy probes and special devices such as probe substitutes, spatulas, toothbrushes, spoons, etc.
Krupenchuk O.I. has developed an interesting new technique for conducting speech therapy massage using ordinary spoons. This massage has a number of advantages:
- it helps to avoid a negative reaction to probe massage,
- interested parents can easily master it and use it at home,
- The massage movements are quite simple, which allows you to teach children self-massage.
All actions with spoons are performed accompanied by poems, which not only set the rhythm of the movement and determine the sequence of actions, but also describe the movements themselves, which is very useful for children with speech underdevelopment.
And yet, probe massage, according to experts, is the most effective in corrective work with children who have speech disorders.
Probes are speech therapy (French sonde - probe) instruments designed for mechanical impact on the tongue when setting and correcting the pronunciation of certain sounds. Speech therapists have been using a traditional set of probes to produce sounds for many years. E.V. is rightfully considered the first developer of probe massage. Novikova, who in 1998 presented a method for correcting speech disorders and a set of probes for speech therapy massage. E.V. Novikova created her own set of probes and developed a special massage of the tongue, lips, cheeks, cheekbones, and soft palate with their help.
Classic massage techniques.
Speech therapy massage uses the same techniques as regular classical massage. In classical massage there are four main techniques, everything else is their modification. Classic massage makes it possible to purposefully influence the affected areas of the articulatory organs, activating and restoring their activity. Normalization of sound pronunciation is faster.
1. Stroking - the hand slides over the skin or mucous membrane, without moving it, without collecting it into folds, the skin should not turn red. Movement is carried out in various directions (longitudinal, transverse, circular, spiral). Any massage session begins and ends with stroking.
2. Rubbing – displacement, stretching, movement of tissues in different directions. The hand moves the skin, but does not press deeper. It is used with greater pressure (straight, circular, spiral, hatching).
3. Kneading - tissue displacement is carried out with the grip of the massaged area, kneading methods (pressure, squeezing, rubbing, stretching, pinching).
4. Vibration is the transmission of vibrations of the speech therapist’s hand to the tissue being massaged. Vibration comes in two types: intermittent and continuous. Options for receiving vibration are shaking and the percussion technique is tapping (finger shower). The vibration technique is carried out with one or more fingers, while the tissues are given oscillatory movements of varying frequencies and amplitudes. Vibration can be carried out by the surface of all fingers or by the fingertips.
There is another technique, it is borrowed from acupressure and is used in classical massage. This is a firm pressure. This technique, which improves blood circulation, lymph circulation, and metabolic processes, is used at the exit points of bundles of nerve endings. These are the so-called biologically active points. Firmly pressing these places, as a rule, ends any stroking.
The choice of techniques depends on the state of muscle tone, motor capabilities and pathological symptoms.
Before the massage, the main thing to do is to determine the tone of the muscles of the speech apparatus. It can be normal, increased (hypertonicity) or decreased (hypotonicity).
It is best to determine tone in a lying position, when the child’s muscles are as relaxed as possible. Normally, muscles are in a state of some tension. A healthy muscle is soft, elastic, and painless when touched. With hypertonicity, the muscles are denser, more tense, and passive movements are difficult to perform. With hypotonicity, the muscles are flabby and flabby. Accordingly, for hypertonicity, a relaxing massage is necessary, and for hypotonicity, an energizing one. The muscles of the speech apparatus can be affected only on one side. In this case, there is a deviation of the tongue, lips, and jaw to the side. The side to which the tongue or lip deviates is spastic, the opposite side is flaccid.
You need to start the massage from intact (not affected) areas. This requires a thorough examination of the speech apparatus to find out which muscles or muscle groups are affected and to what extent.
Recommendations for performing speech therapy massage.
- Relaxing massage of articulatory muscles.
It is used in case of increased tone (spasticity) in the speech muscles (facial, labial, lingual muscles).
Carrying out facial massage contributes not only to the formation of facial means of communication, but also to the development of the oral sphere, which is necessary for the child’s normal nutrition and subsequent speech development.
Important: Place the child in positions in which pathological tonic reflexes would manifest themselves minimally or not at all.
Relaxation of the neck muscles (passive head movements).
Before starting a relaxing massage of the articulatory muscles, especially in the case of a significant increase in muscle tone of the upper shoulder girdle and neck, it is necessary to relax these muscles.
The position of the child is on the back or half-sitting, the head hangs slightly back:
a) support the child’s neck from behind with one hand, and with the other make circular movements of the head, first clockwise, then counterclockwise;
b) with slow, smooth movements, turn the child’s head in one direction and the other, rock it forward (3-5 times).
Relaxation of the neck muscles causes some relaxation of the root of the tongue. Relaxation of the oral muscles is achieved by lightly stroking and patting the muscles of the face, lips, neck, and tongue. Movements are carried out with both hands in the direction from the periphery to the center. Movements should be light, sliding, slightly pressing, but not stretching the skin. Each movement is repeated 5-8 times.
Relaxation of facial muscles:
- stroking from the middle of the forehead to the temples;
- stroking from the eyebrows to the scalp;
- stroking from the forehead line around the eyes;
- stroking the eyebrows from the bridge of the nose to the sides to the edge of the hair, continuing the eyebrow line;
- stroking from the forehead line down across the entire face along the cheeks, chin and neck;
- stroking from the lower edge of the auricle (from the earlobes) along the cheeks to the wings of the nose;
- light pinching movements along the edge of the lower jaw;
- Pressure massage of the face from the hair roots down.
Relaxation of the labial muscles:
- stroking the upper lip from the corners of the mouth to the center;
- stroking the lower lip from the corners of the mouth to the center;
- stroking the upper lip (movement from top to bottom);
- stroking the lower lip (movement from bottom to top);
- stroking the nasolabial folds from the wings of the nose to the corners of the lips;
- acupressure of the lips (light rotational movements clockwise);
- lightly tapping your lips with your fingers.
In case of asymmetry of the facial muscles, we perform articulation massage with hypercorrection of the affected side, that is, perform a greater number of massage movements on it.
2. Stimulating massage of articulatory muscles.
It is carried out in case of muscle hypotonia in order to strengthen muscle tone.
Techniques: Energetic and fast movements.
Massage movements are carried out from the center to the periphery. Strengthening the facial muscles is carried out by stroking, rubbing, kneading, pinching, vibration. After 4-5 light movements, their strength increases. They become pressing, but not painful. The movements are repeated 8-10 times.
Strengthening facial muscles:
- stroking the forehead from the middle to the temples;
- stroking the forehead from the eyebrows to the hair;
- stroking eyebrows;
- stroking along the eyelids from the inner to the outer corners of the eyes and to the sides;
- stroking the cheeks from the nose to the ears and from the chin to the ears;
- squeezing the chin with rhythmic movements;
- kneading the zygomatic and buccal muscles (spiral movements along the zygomatic and buccal muscles);
- rubbing the cheek muscle (index finger in the mouth, the rest outside);
- pinching cheeks.
Strengthening the labial muscles:
- stroking from the middle of the upper lip to the corners;
- stroking from the middle of the lower lip to the corners;
- stroking the nasolabial folds from the corners of the lips to the wings of the nose;
- tingling lips;
- slight tingling of lips.
3.Massage of the lingual muscles.
Perform the massage lying down before meals or 1.5-2 hours after meals for 5 minutes.
Gum massage begins with movements in a horizontal direction on one side of the gum. This increases salivation, so after 2-4 weakening movements the child should be given the opportunity to swallow saliva. Then a similar massage is carried out on the other side of the gum. Next, the gums are massaged with vertical movements.
The palate is massaged with a finger along the midline, starting from the front with a slight lifting of the soft palate. This movement is repeated 10-15 times. During the massage, the child can pronounce the vowels A and E.
The tongue is massaged from front to back until the gag reflex occurs. This involves stroking, light patting, and vibration for 15 seconds.
Massage to relax the tongue muscles:
- acupressure in the area of the submandibular fossa, which is carried out for 15 seconds, vibrating movements with the index finger under the lower jaw;
— vibration with two index fingers of both hands at the angles of the jaw (15 seconds).
The movements used are straight, spiral, circular, while holding the tongue with the fingers of one hand, and performing massage movements with the fingers of the other. They should be sent:
- From the middle of the tongue to its tip and back.
- From the center of the tongue to the left and right (“herringbone”),
- From the left edge of the tongue to the right and vice versa (across the tongue),
- Rolling your finger over your tongue in different directions
- Pinching and stretching of the edges of the tongue.
- Stroking the tongue from the hyoid frenulum to the tip of the tongue and back.
The study of various methods of speech therapy massage, as well as the study of the experience of using speech therapy by one’s colleagues and personal experience, allows one to be convinced of the indisputable and obvious effectiveness of this non-traditional method of influence for correcting sound pronunciation in preschool children with dysarthria. Massage not only improves pronunciation, but also has a positive effect on the development of phonemic hearing and overall speech development. The correct selection of massage complexes helps to normalize the muscle tone of the organs of articulation, improves their motor skills, which helps improve the pronunciation aspect of speech. The combination of logomassage with traditional speech therapy classes significantly brings closer positive results in correcting sound pronunciation in preschool children.
List of used literature:
1. Belaya K.A., Petrov I.B. Therapeutic and wellness massage. - M.: , 1998.
2. Belyakova L.K. Dyakova E.A. Speech therapy: Stuttering. - M.: V. Sekechev, IOI, 1998. 3. Blyskina I.V. An integrated approach to the correction of speech pathology in children. Speech therapy massage. – SPb.: DETSTVO-PRESS, 2004.
4. Dyakova E.A. Speech therapy massage. - M.: Academy, 2003.
5. Krause E.N. Speech therapy massage and articulation gymnastics: a practical guide. – SPb.: CORONA print, 2004.
6. Lopatina L.V., Serebryakova N.V. Overcoming speech disorders in preschool children. Correction of erased dysarthria. – St. Petersburg Publishing House of the Russian State Pedagogical University named after. A.I. Herzen: Publishing house, “Soyuz”, 2001.
7. Novikova E.V. Probe massage: correction of sound pronunciation: A visual practical aid. - M.: GNOM and D, 2000.
8. Serbina A.F., Voloskova N.N. A set of techniques for massaging speech and facial muscles for dysarthria. Dysarthria, clinical, neurolinguistic, psychological and pedagogical aspects of the problem: Educational and methodological manual. - Stavropol, 1996.
9. Filicheva T.B., Cheveleva N.A., Chirkina G.V. Basics of speech therapy. – M.: Education, 1989.
10. Fomicheva M.F. Teaching children correct pronunciation. M.: Education, 1989.
11. Shafeeva A.A. Speech therapy massage. - M.: V. Sekechev, IOI, 2009.
Is it possible to perform massage at home?
Experts recommend performing speech therapy massage at home. Firstly, this is a guarantee of continuity of treatment, which affects the effectiveness of correction. Secondly, children, especially small ones, are more relaxed in normal circumstances, but with a stranger it can be impossible to even force their mouth to open. Thirdly, at home you can perform a massage at any time: you don’t need to adjust to your schedule or change your routine, which is a stress factor in itself.
Massage your face with your fingers. You can use teaspoons. Instead of probes, when massaging your tongue, you can also use improvised means: spoons or the same toothbrushes. Kneading with your fingers will also help.
It is necessary that you know how to do a relaxing massage for dysarthria. It is important to do all the movements correctly, to know where to press harder and where it is better to use light touches. You can learn through courses. A speech therapist can also show you the basics. If you combine the procedures with a regular massage, the effect will be many times higher. Just keep in mind that it can be relaxing or tonic.
Incorrect technique can cause deterioration: other types of speech disorders may appear, in addition to dysarthria.
Difficult moments
In some cases, massage is not so easy. In various pathologies, an increased gag reflex is observed. In this case, it will not be possible to really influence the muscles.
To reduce sensitivity, some tricks are used. Children are given strong tea for rinsing. Due to tannins, it has an anesthetic effect. Menthol lollipops are given for the same purpose.
In some cases, analyzers are trained. To do this, take the “Small Sleigh” probe and carefully guide it to the permissible line and take it back. This is done five times. Gradually the tool is wound further and further.
To suppress the reflex, it is useful to develop the chewing muscles. To do this, give the child a small syringe to chew. It is placed in the mouth with the wide part and asked to be squeezed slightly.
Some children are afraid of metal probes and may react negatively to them. In this case, they are pre-prepared for manipulation. To do this, they use toys, offer to look at all the tools and test them on objects.
Important rules of logomassage
Articulation massage for dysarthria is undoubtedly an effective method of correction. To benefit and avoid complications, the following conditions must be met:
- All stages of treatment are controlled by a speech therapist: drug treatment, physiotherapy, massage. Therefore, choosing a specialist is one of the fundamental moments in therapy;
- In addition to professional qualities, it is important to establish emotional contact between the speech therapist and the child. This means that a specialist must be able to find a common language with children of different ages. If the child behaves awkwardly and starts throwing tantrums during sessions, there will be no benefit from such procedures, no matter what credentials the speech therapist has;
- The room in which a relaxing massage for dysarthria is performed should be comfortable. It is necessary to ventilate it, remove distracting objects;
- It is better to do the procedures while lying down. But if the child is so uncomfortable, he can sit down;
- The child should be in a good mood, well-fed and happy. Treatment cannot be carried out when he is tired, emotionally overworked or sick. During the massage he should not experience discomfort or pain;
- Your mood is also important. If you are excited and nervous, the baby will feel it and will also begin to worry;
- If you use a spoon or brush, purchase them specifically for massage;
- The sooner you start therapy, the faster you will get results. Therefore, pay attention to the child’s speech, especially if he is at risk: your pregnancy and childbirth were difficult, you were sick during pregnancy, the child had a traumatic brain injury, he was seriously ill for a long time, you have close relatives with speech problems. disorders. The first “bells” are limited mobility of the lips, palate, tongue, difficulties with sucking and swallowing food. Nasal and slurred speech when the child begins to talk. If you notice these symptoms, consult your doctor;
- The procedures will be effective only with an integrated approach. This means that at the same time lessons are held with a speech therapist on sound production, breathing exercises, and the development of fine motor skills.
Be patient. Lead a normal life: let your baby feel that he is no different from the rest, that he is also loved and appreciated. This is an important point that will undoubtedly help him cope with his problems.
Who treats dysarthria
To correct the situation, you need to contact two specialists - a neurologist and a speech pathologist. An accurate assessment of the condition can only be determined after a thorough examination and history taking.
Corrective measures are also carried out in two directions - neurological and speech therapy. An integrated approach includes methods such as:
- Drug therapy.
- Physiotherapy.
- Physiotherapy.
- Speech therapy classes.