Sensorimotor alalia in children is a severe disorder in which oral speech is significantly difficult or absent. The cause of the defect is damage to the speech centers of the brain, which are responsible for the perception and reproduction of speech. In this article we will look at the causes, treatment and prognosis of sensory-motor alalia, and will tell you how to behave as parents of a child with such a pathology.
Causes of the disease
Sensorimotor alalia develops due to damage to areas of the brain that are responsible for understanding and reproducing speech.
A damaging factor can affect different periods of a child’s development:
- In the prenatal period, infectious diseases in a woman, the threat of miscarriage, polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios, premature rupture of water, entanglement in the umbilical cord, bad habits, taking medications, concomitant diseases, vitamin deficiencies have a negative impact;
- During childbirth, there is an increased risk of birth injuries and hypoxia, in which the brain experiences oxygen deficiency or is damaged. The use of forceps and rapid labor are dangerous;
- After childbirth and the first years of the baby’s life, brain damage can occur as a result of injuries, encephalitis and meningitis, and severe concomitant diseases.
Relationships with parents play an important role in the development of sensorimotor alalia. It has been proven that children whose parents are distant towards their baby ignore his needs for love, communication, care, and lag behind their peers in development. This also applies to speech development.
Sensory alalia is one of the speech disorders in childhood, which is difficult to diagnose and correct. Special literature refers to the term “sensory alalia” as a sharp limitation or lack of understanding of speech by children whose hearing acuity and intellectual capabilities are sufficiently well developed. Despite the preserved abilities for the development of active speech and fairly good hearing, children with sensory alalia are characterized by the presence between the sound of words and their meaning, and, consequently, impairments in understanding the speech of others. Such children do not understand speech, do not use it, and this leads to accompanying disorders - difficulties in contact, distortion of visual perception and lack of communication with others, delayed intellectual development, etc. Such a child may be given an incorrect diagnosis: autism, hearing loss, mental retardation, etc., and accordingly, completely inadequate correction is offered.
The insufficiency of a unified judgment about the nature and nature of speech pathology of this form leads to diagnostic errors, creating enormous difficulties in pedagogical practice.
Conducted by S.I. Kaydanova and Traugott N.N. Research suggests that sensory alalia manifests a special state of the auditory analyzers, characterized by weakness of inhibitory and excitatory processes, as well as mild generalization (irregular perception of sounds that are accessible to children’s physical hearing).
The main distinctive feature of hearing function in sensory alalia is the ease of occurrence of extreme inhibition due to high functional exhaustion. It is difficult to answer the question of why such exhaustion of the auditory analyzers manifests itself; among the versions one can name the inferiority of the functionality of the peripheral section or the central section of the auditory analyzer. There is evidence that indicates the presence of sensory alalia leading to hearing loss - damage to the peripheral part of the auditory analyzers.
With sensory alalia, an unusual speech hearing defect manifests itself in the fact that the child is inattentive to sounds; sometimes he hears a quiet sound, sometimes he does not react at all to the sound stimulus, he learns individual words with great difficulty and with difficulty retains them in memory, his passive vocabulary is slowly enriched, a gap appears between the named object and the understanding of the word denoting it. Also, with sensory alalia, there is a reduced ability to distinguish the sound of phonemes from surrounding speech, a lack of ability to distinguish correlating phonemes by ear, etc. The child has poor hearing ability to differentiate individual phonemes that are similar in acoustic parameters; when the teacher’s (speaker’s) voice is raised, sound discrimination does not improve significantly; phoneme discrimination improves in the process of learning to read and write and speak, that is, in the process that develops phonemic hearing.
In the works of Traugott N.N. It is said that children with sensory alalia may have high speech activity. And in fact, it is often difficult to stop the flow of speech and achieve listening to the speech of others (in many cases, echolalia is noted). The child listens with pleasure to his voice, his speech and his intonation. Alalik’s speech has an expressive intonation, is richly modulated, he accompanies it with lively gestures and facial expressions and literally “hampers” the understanding of both his own speech and the speech of those around him.
When it comes to a child’s impairment of auditory attention, he does not use his hearing at all or uses it in rare conditions of overmotivation (listens and hears), if he really needs to hear and understand something. As we said earlier, such disorders are quite typical for children with sensory alalia (however, not only for them).
To summarize, it can be noted that children suffering from sensory alalia have impairments not in the very ability to develop speech, but mainly or exclusively in the ability to learn speech from the ear. This factor determines the specifics of correctional activities with a child from this category, as well as with a child with a pronounced sensory component.
If we talk about the auditory-verbal development of such children, the prognosis depends on numerous factors. What matters is the nature and severity of sensory impairments, the level of hearing loss, as well as the severity of violations of higher analysis and synthesis of the auditory analyzer, the ability to imitate speech sounds, characterological and personal aspects, characteristics of intelligence, conditions of education, development and correction.
To understand the nature of auditory-speech characteristics in a child suffering from sensory alalia, it is advisable to differentiate the symptoms that are characteristic of sensory alalia with hearing loss that manifests itself in the pre-speech period.
The importance of normal hearing in the formation of a child’s speech is undeniable; for this reason, in any cases of speech development disorders, first of all, a thorough study of the child’s auditory functions is required. We also emphasize the need for pure-tone audiometry, because a hearing analysis based only on testing whispered and spoken speech can lead to an erroneous conclusion about the presence of central disorders such as alalia in the baby.
It also happens that children suffering from sensory alalia are diagnosed not only with hearing loss, but also with intellectual impairment. And indeed, at first glance, the clinical picture of sensory alalia gives grounds for this. In addition, at certain stages of development, a child with impaired intelligence may be diagnosed with sensory alalia.
Consequently, the sensory component, expressed to varying degrees, can become complications of various disorders of functional and organic (intellectual impairment, hearing loss) origin, and here children with intellectual and hearing impairments constitute the main risk group.
Due to the fact that the main manifestation of sensory alalia is a violation of the synthesis of the auditory-speech analyzer and the processes of higher analysis, the main correction goal should be compensation for this disrupted link.
But, since we cannot develop the suffering function directly, we should form a new functional system using all the intact analyzers by creating additional supports.
The work to overcome sensory alalia, thus, uses motor and visual analyzers, kinesthetic sensations, tactile-vibrational perception, smell, taste, and, naturally, hearing, dosed in the form of a damaged link.
Correctional activities with children who suffer from sensory alalia should include elements of various correctional programs, for example, much is borrowed and adapted from systems of working with children with hearing impairments, as well as from neuropsychological techniques.
Three stages of work:
— The preparatory stage - it includes creating motivation for classes, and then communication needs (the child is included in a group of children).
Due to the fact that speech is considered as a rhythmic space-time structure, these three components are included in these classes. Here we develop general sensory skills, auditory, visual, kinesthetic and tactile-vibrational perception, touch and smell. This way we get the opportunity to develop all the basic skills and functions that precede and accompany speech development in ontogenesis in a normally developing child.
Work on sequence, series, color, quantitative element and other elementary concepts, which will subsequently form the basis of writing, reading and counting, is carried out before working on the elements of global reading with articulatory support and sound analysis.
2 – Main stage – represents work on phase speech, as well as its grammatical design. At the first couple of stages, work on auditory perception is carried out only in music classes, as well as in a group.
3 – Final stage – we work on auditory perception, automation and differentiation of sounds, we also work on complex grammatical structures.
At all of these stages (of course, in different ways), motor and visual supports are actively used, and vocabulary work is also carried out.
The experience of specialists suggests that these methodological techniques, which are aimed at developing the processes of higher analysis, as well as the synthesis of an auditory-speech analyzer and the creation of a new functional system using all types of intact analyzers, make it possible, in case of sensory alalia, to successfully compensate for auditory-speech process disorders.
In addition, this comprehensive approach is also effective for other types of speech and hearing disorders (dyslalia, dysarthria, complex disorders, etc.).
Symptoms of sensorimotor alalia in children
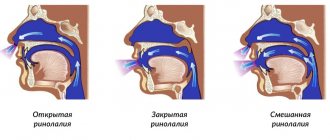
The clinical picture is characterized by severe speech disorder. If with motor alalia pronunciation suffers, sensory alalia affects the understanding of speech and its analysis, then with sensorimotor alalia both components are affected. The disorder may also affect the association center, the area of the brain that controls the construction of phrases and sentences.
Let's look at these violations in more detail:
- Expressive language disorder is the inability to produce sounds. At the same time, there are no hearing impairments, and there is also no pathology of the articulation organs. The child pronounces the first word only at the age of 3–4 years. In conversation he uses onomatopoeia, gestures, and babble. Replaces sounds or skips them, repeats words uncontrollably, but cannot repeat words when asked, purposefully. Uses mostly nouns;
- Impressive speech disorder is characterized by a lack of understanding of speech addressed to him. Although the child hears sounds and words perfectly, he cannot analyze them and respond adequately. In some cases, there is no reaction even to one’s own name. At the same time, he unconsciously repeats words and syllables, but at the request of an adult he cannot do this. Logorrhea is characteristic - verbosity, but speech is inarticulate, consisting of individual interjections and babbling words.
In an unfamiliar environment, sensorimotor alalia becomes more pronounced. For example, if at home a child reacts to his mother’s words, answers them correctly or reacts accordingly, then elsewhere he understands absolutely nothing and does not react.
Vocabulary is limited. The baby does not know how to inflect words and confuses cases, numbers, and genders. Grammar, writing, and reading suffer. Due to difficulties with speech perception, it is difficult for them to assimilate school material.
Such children are characterized by impulsiveness and an unstable emotional background. Because of this, they cannot communicate with other people, they have no friends. They usually stay apart from the team. This later leads to psychological problems.
With severe sensorimotor alalia, neurological disorders and symptoms are associated:
- Difficulties with coordination and fine motor skills;
- Clumsiness;
- Cognitive disorders - impaired memory, attention, concentration;
- Restlessness, fussiness, or vice versa, lethargy and slowness;
- Stuttering;
- Enuresis;
- Sleep and appetite disorders.
Severity
Depending on the depth of brain damage, signs of sensorimotor alalia in children can be of varying degrees of severity:
- a mild degree is characterized by minor violations - a change in the sequence of sounds in a word, the use of only simple phrases of 2 - 3 words. It is possible to understand what a child is talking about;
- with sensorimotor alalia of moderate severity, understanding the speech of the baby is difficult, there are problems with pronouncing sounds, constructing even simple phrases;
- a severe degree is accompanied by a lack of reaction to someone else’s speech and the absence or difficulty of one’s own speech.
Construction of lessons
With sensory alalia, speech therapy is aimed at training a number of reactions. It is necessary to train not only phonetic hearing itself, but also motor skills, memory, and attention. The training system should be built comprehensively.
Another point is environmental control. Any sound source has an impact on the patient, so it is important to arrange quiet modes. It is also better to reduce the number of sound stimuli for the patient so that he can better learn to isolate the necessary sounds. Reducing sound stimuli is also used during classes. The main task of speech therapy work for sensory alalia is to teach the patient to understand speech in various situations and to form competent speech independently.
Exercises can be done in the format of various games. Children love games and this will help them remember the lesson better.
Diagnosis of sensorimotor alalia in children
The diagnosis of sensorimotor alalia is made on the basis of an examination with the participation of a neurologist, speech therapist, otolaryngologist, psychologist, and pediatrician. If necessary, consultations with other specialists are prescribed. The purpose of diagnosis is to identify the exact cause of the defect and exclude other health problems that may be accompanied by speech disorders: autism, hearing loss, mental disorders.
To clarify the diagnosis and identify signs of brain damage, exclude space-occupying formations, and vascular problems, a small patient is referred to electroencephalography, vascular Doppler, MRI or CT.
Motor alalia
This form of disorder is a consequence of motor disorders in the child’s body. Accompanied by a poor vocabulary. A child with this type of alalia finds it difficult to express his thoughts, form phrases and use words correctly.
Children with motor alalia have normal mobility of the organs responsible for speech. However, it is difficult for a child, for example, to lift his tongue up if adults ask him to do so. He cannot repeat the words he heard. Such children have mental and neurological disorders due to the disease.
More often, children with motor alalia have difficulty in physical activity, but in some cases the child may demonstrate increased activity, which is associated with the location of the lesion in the brain.
Treatment of sensorimotor alalia in children
Therapy for children diagnosed with sensorimotor alalia should be comprehensive, based on the individual characteristics of the disease in a particular child. It is also necessary to be systematic and attend classes regularly.
Treatment consists of medical, speech therapy, and psychological assistance.
The medical component of therapy consists of prescribing medications that stimulate brain metabolism and restore connections between neurons. Nootropics, multivitamins and other groups of drugs are used as needed. The course includes physiotherapeutic techniques (laser therapy, acupuncture, electrophonophoresis, electrical stimulation, magnetic therapy), massage.
Possible mental disorders
Motor alalia is accompanied by various deviations that affect various areas of the child’s interaction with the outside world. A child with such a disorder reacts violently to everything, often cries and becomes hysterical, and does not want to have any contact with others. He also has:
- thought processes occur more slowly;
- memory is impaired;
- there is a deterioration in concentration;
- visuospatial impairments are present.
Such children study worse, it is more difficult for them to remember any facts, as they are often distracted and cannot concentrate.
Corrective classes for child speech development
The basis for correcting speech disorders with signs of sensorimotor alalia in children is working with a speech therapist or speech pathologist. Group classes are possible, but at the initial stage it is better to study individually.
The specialist helps step by step:
- at the first stage, teaches how to correctly perceive and reproduce sounds and words;
- The second stage of therapy is aimed at constructing words and short phrases and developing dialogue skills. At the same time, the set of words in the lexicon is enriched;
- The third stage of correctional work consists of developing monologue speech and consolidating grammar.
Classes are conducted in a playful way, using toys and pictures. Usually the baby undergoes therapy on an outpatient basis. But in more complex cases, hospitalization in specialized hospitals is indicated.
It is useful to develop fine motor skills. Drawing, classes with construction sets, mosaics, modeling, and appliques are suitable for these purposes. Alternative methods include hydrotherapy (hydromassage, swimming pool, therapeutic baths), and treatment with animals (dolphin therapy, hippotherapy).
A psychologist also works with the child. Under his control, the baby learns communication skills and control of the emotional and volitional sphere.
Dependence of teaching methods on the form of sensory alalia
Corrective speech therapy work on sensory alalia requires taking into account the form of the disease. To begin with, it is important to examine the patient to understand the severity of the disease. Classes should include a set of exercises and tasks.
It is necessary to distinguish between the mild form of sensory alalia and the severe one. In a mild form, the patient understands individual words and phrases, but is unable to use them independently or highlight them in a spoken sentence.
The rough form of alalia leads to impairment of the intellect and psyche. The child loses the ability to understand words spoken by others. To work with a rough form, it is worth hiring a specialist.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis depends on the age at which sensorimotor alalia is diagnosed in children and the timing of initiation of therapy. If the diagnosis is made in preschool age, the child receives adequate treatment, regularly works with a speech therapist and psychologist, then it is possible to stop the progression of the disease and teach the patient communication skills. Articulation is normalized. Subsequently, he is socialized and can study in a regular school.
The participation of parents in the correction of sensorimotor alalia and their understanding of the complexity of the situation is very important. Unfortunately, such violations do not go away on their own. A good result requires patience, desire and effort on the part of both parents and baby. Try to motivate the baby, encourage, praise for success. Follow your speech therapist's recommendations.
If you trigger sensorimotor alalia, then stuttering, mental retardation, and nervous tics may occur. This will worsen the already difficult prognosis and negatively affect the future life of the child.
Prevention consists of clear pregnancy planning. The expectant mother should eat a balanced diet, get enough rest, and see a doctor regularly. During childbirth and the first years of the baby’s life, you should carefully monitor its development, prevent injuries and promptly treat infectious and other diseases.
If you find symptoms of sensorimotor alalia, contact a specialist so that they can examine you and identify the cause of this condition.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out in several directions.
Speech therapy exercises. Can be carried out individually or within a special school. Positive results are achieved only by systematic, long-term training.
Under the guidance of a speech therapist, the child gradually masters the pronunciation of individual syllables and words and recognizes speech by its sound. With the help of various pictures, the skills of linking them with specific words are acquired.
When certain progress has been made, the child is already able to name one or another object shown in the picture. Gradually, the baby masters the correct endings of words, cases and declensions.
Additionally, classes are conducted that develop fine motor skills using drawing, modeling, cutting, and construction toys.
The success of treatment largely depends on home exercises. Exercises conducted with a speech therapist should be constantly reinforced with the direct participation of parents.
Speech therapy massage. Considered an effective addition to exercise. It develops individual muscles of the oral cavity responsible for correct pronunciation. The procedure is performed manually or using a special probe. Additionally, speech muscles are developed with the help of specific exercises designed specifically for these purposes.
Physiotherapeutic procedures. They are prescribed in the form of specific courses, depending on the child’s condition. They can be supplemented with hydrotherapy, magnetotherapy, laser therapy and other procedures.
Reflexology. Its essence is to stimulate the necessary areas of the brain with electrical impulses. This leads to the formation of new neural connections that facilitate learning. Applies to children over 9 years of age.
Drug therapy. Includes the use of drugs that stimulate blood flow to the brain. Additionally, vitamins B12 and B15 are prescribed. Much attention is paid to a balanced diet.
Clinical picture, behavioral features
To be able to express their desires and emotions, children learn to communicate with adults using gestures. Later they begin to connect speech to this process, which gradually becomes more complex and improved.
However, children with alalia do not demonstrate such developmental success. They are unable to communicate with adults using speech. There are three degrees of underdevelopment of the speech apparatus:
- The child knows many words, but when pronouncing them, he greatly distorts them due to the poor development of the speech system.
- The child knows a list of simple words and demonstrates initial speech development skills.
- The child has no speech at all.
These levels have no relationship with age and depend solely on the severity and form of the disorder.
Home therapy
Alalia therapy should not be limited only to classes with specialized specialists. Parents should try to help their baby. To quickly get rid of the disease, you can use special methods that have been developed for more effective treatment:
- Ask your child to point to objects more often, while saying their names.
- Play a game: name the object, and let the child find it and show it. You can use both ordinary household items and multi-colored figures or any toys.
- Talk to your child more often, and try to keep the speech not fast, understandable, and correct.
- Teach letters with your child, after he remembers a new one, ask him to name words that begin with this letter.
Children's books with many bright illustrations can help develop speech skills. Read them to your child more often, explain what is shown in the picture, tell fascinating stories about the characters.