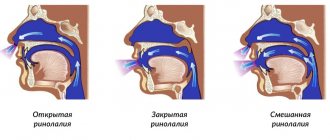
Alalia is a systemic underdevelopment of speech function or its complete absence. The main causes of the disease are considered to be organic lesions of the speech areas of the brain that occurred in the first 2-3 years of life or in utero. The clinical diagnosis of alalia is made by a neurologist and a psychiatrist. In speech therapy, speech pathology caused by congenital or acquired brain defects is called general speech underdevelopment (GSD).
Alalia disease is characterized by:
- agrammatisms;
- distortion of sounds;
- late appearance of speech;
- violation of syllable structure;
- small vocabulary;
- violation of phonemic processes.
A patient with alalia needs to undergo a thorough neurological, psychological and speech therapy examination. The disease occurs in 1.5% of preschool children and 0.5% of schoolchildren.
Comprehensive treatment of underdevelopment of speech function includes:
- taking medications;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- working with a psychologist, neurologist and speech therapist.
Causes of alalia
Alalia disease is provoked by various anomalies of pre-speech ontogenesis.
In the antenatal (intrauterine) period, speech pathologies can be caused by:
- hypoxia;
- prematurity;
- torch syndrome;
- perinatal pathology;
- asphyxia of newborns;
- somatic disease of a pregnant woman.
Doctors note a genetic predisposition to the development of alalia. The history of patients with general speech underdevelopment reveals a chain of hereditary factors that provoke dysfunction of the speech areas of the brain.
Etiopathogenetic factors have a significant influence on the physiological development of the speech apparatus:
- rickets;
- meningitis;
- malnutrition;
- encephalitis;
- endocrinopathies;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- lack of competent child development.
In case of intrauterine, congenital or other organic damage to the brain in the first years of a child’s life, the development of nerve cells (neuroblasts) is inhibited. This pathology leads to neuronal inertia and functional depletion of brain cells. In case of alalia, multiple bilateral nature of deviations in the development of speech function, including compensatory capabilities of the brain, are diagnosed.
Alalia classification
Each area of clinical medicine has its own narrow classification of alalia, which is based on the causes of occurrence, existing pathologies of psychomotor development and the degree of speech underdevelopment.
Modern speech therapy suggests taking as a basis the classification of alalia by V.A. Kovshikov:
- Motor (expressive).
- Sensory (impressive).
- Mixed (sensorimotor).
Expressive alalia
In most cases, motor (experimental) alalia is caused by intrauterine organic damage to the cortical speech-motor analyzer. At the same time, the newborn does not have his own speech, but he perfectly perceives the speech of others. It is necessary to distinguish between efferent and afferent expressive alalia.
Efferent motor alalia is diagnosed with abnormalities of the premotor cortex (posterior part of the inferior frontal gyrus, Broca's area). The pathology manifests itself in kinesthetic articulatory apraxia (distortion of the sound of consonants and vowels). During physiological development, the premotor cortex in a child is responsible for the coordination and sequence of movements, which is very important for the formation of speech. Children with efferent alalia find it difficult to repeat a series of movements; they have difficulty reproducing correct articulation. It is with this problem that the phenomenon of persistence is associated: the inability to reproduce syllables in the required order.
Afferent motor alalia develops as a result of lesions in the postcentral zone (parietal parts of the left hemisphere). In healthy children, the postcentral zone is responsible for analyzing sensations at the time of conversation, and the synthesis of a motor program immediately occurs: open the mouth, lower the jaw, inhale air, raise the tongue. With afferent alalia, the child is not able to independently perform a chain of movements to pronounce sounds, so smearing, rearranging or swallowing of sounds occurs. Simply put, the baby has no idea about the sequence of actions of the articulatory apparatus when speaking, and it is difficult for him to reproduce movements even when repeating after his parents. In case of motor alalia with concomitant developmental pathologies, the child is assigned a disability.
Impressive alalia
The main cause of sensory alalia is damage to the auditory-speech analyzer in the cortical region (posterior third of the superior temporal gyrus, Wernicke's center). Patients with this disease have good hearing and developmental abilities. The main problem of correcting pathology is poor memory for pronunciation and a gap in understanding between the sound and meaning of words. The consequence of such dissonance is a lack of contact with others, a distortion of visual perception and a delay in the overall development of the child’s psyche.
The need for examination for alalia
The goal of all these studies is to exclude hearing loss (it is treated by an ENT specialist) and autism with mental retardation from potential diagnoses. Sensory alalia is not a sign of mental retardation in a child, since such children have normal intelligence. If a specialist nevertheless makes this diagnosis, it is necessary to carefully monitor the child, since alalia manifests itself differently in different situations. It is corrected quite successfully, however, due to the restlessness of children and poor perception of information, this process can take a long time. Here everything depends on the experience of the specialist and the perseverance of the parents, since they are tasked with the daily work of developing their child.
At the slightest sign, we recommend immediately seeking advice from specialists. The faster you identify a violation, the higher the likelihood that the consequences will be minimal and timely correction will help the child. Don’t put off until tomorrow the most important thing – your baby’s health. By doing this you will help both yourself and him to avoid serious problems in the future. In Russia, the diagnostic system is quite well developed. You can contact private specialists or refer kindergartens and schools for free examination to government institutions.
Alalia correction is carried out at the Govorush center.
For more detailed information, you can contact our specialists by phone, +7 (921) 744-18-52, or contact the address: St. Petersburg, Pulkovskaya str., building 2, building 1. st. Zvezdnaya metro station from 9.00 to 20.00. We are always happy to help you.
Alalia symptoms
Symptoms of motor alalia
With expressive alalia, the child is diagnosed with psychological and neurological abnormalities. Symptoms of nervous disorders can manifest themselves in a disorder of motor skills: poor motor skills, clumsiness, lack of coordination of movements. Such children find it difficult to cope with lacing shoes, fastening buttons, self-care, and putting together puzzles.
Characteristic features of the psychological development of patients with motor alalia:
- speech negativism;
- lack of attention;
- small vocabulary;
- low performance;
- poor assimilation of material;
- violation of sound pronunciation;
- deviations of the emotional-volitional sphere;
- hyperactivity or, conversely, inactivity.
It should be noted that there is a strong dissociation between expressive and impressive speech when diagnosed with “motor alalia”. The first speech skills (babbling, googling, sounds, phrases) appear with a delay and a characteristic reduction. The lack of dynamic development of a speech stereotype can be a consequence of stuttering.
Such children have a predominance of nouns in the nominative case in their vocabulary and difficulties in the formation of grammatical word forms. Speech in the motor form of the disease consists of simple short sentences, sometimes incoherent. The child is not able to consistently talk about things, convey events and explain the essence of phenomena. Intellectual development with motor alalia can be completely restored after correction of speech disorders.
Symptoms of sensory alalia
Characteristic symptoms of sensory alalia are:
- disturbances of perception;
- lack of ability to understand the meaning of someone else's speech.
Patients with sensory alalia experience hyperacusis: increased sensitivity to squeaks, rustles, the crunch of snow, the sound of rain, and the rustling of paper. Children are acutely aware of such side sounds and may experience discomfort in their ears and head.
Impaired phonemic hearing in the sensory form of the disease prevents patients from correlating heard words with objects or phenomena. During speech therapy sessions, children with sensory alalia develop logorrhea - incoherent reproduction of all familiar phrases and sounds, while speech is accompanied by gestures and lively facial expressions.
In the severe form of sensory alalia, the patient is diagnosed with a complete lack of speech and understanding of others. Experts practice teaching “lip reading,” which makes it much easier for a child to comprehend speech. Children with sensory alalia are often misdiagnosed as autism, hearing loss, mental retardation, dysarthria.
Separately, sensory underdevelopment of speech function is quite rare. In most cases, sensorimotor alalia is diagnosed. This double pathology indicates the inseparability of the speech-motor and speech-auditory analyzers.
If you experience similar symptoms, consult your doctor
. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Clinical picture and behavioral characteristics
In the absence of verbal communication with children or adults, the child experiences psychological discomfort. Children from a very early age use gestures to express their emotions and desires.
Gradually, they begin to connect speech to this, which becomes more complex as they grow older.
A child with alalia does not have this opportunity; it is difficult for him to explain what he wants from an adult. The degree of difficulty may vary, but there are three levels of underdevelopment of the speech apparatus:
- Complete lack of speech.
- There are initial signs of speech development. The baby has some words or sounds in its reserve and can make words from them, but such a reserve is extremely limited.
- There is an extended speech with fragments of weak development of the speech system. The vocabulary in this case is large, but the words are pronounced in a distorted way, and there are defects in the pronunciation of certain sounds.
These levels are not related to the child's age. At 5 years old he can be at the first level. These impairments inevitably affect oral speech and, later, the ability to write and read.
Children have difficulty remembering letters and numbers. They confuse them, interfere with each other. This further complicates the development of speech ability. The child understands everyday speech. It is simple for him and does not require grammatical rules.
The child can understand simple requests, such as closing the door or taking a book, based on the current situation. He understands that if the door to the room is closed, and his mother suddenly spoke about it, then some manipulations need to be done with it.
Intuitively, the baby will open the door. But whether he understands exactly the meaning of words at this moment depends on the severity of the disease. At difficult stages, he may not understand at all what adults tell him.
Diagnosis of alalia
Patients diagnosed with alalia need to be examined by the following specialists:
- Speech therapist - for perinatal history, identifying features of speech and psychomotor underdevelopment, as well as drawing up a model of lexical and grammatical structure, correction of phonemic processes and impressive speech.
- Neurologist - to identify the source of neuralgic dysfunctions and genetic abnormalities.
- Psychologist - to diagnose auditory-verbal memory, timing of psychomotor development, articulatory motor skills.
- Otolaryngologist - when drawing up a therapeutic treatment plan, it is necessary to exclude damage to the function of the hearing aid.
For additional diagnostics and identification of the degree of brain pathologies, the following is carried out:
- EEG;
- otoscopy;
- audiometry;
- MRI of the brain;
- X-ray of the skull;
- echo-encephalography.
Treatment of patients with alalia
The system of corrective action for sensory, motor and mixed alalia should include a set of procedures with an impact on the pathology itself and accompanying diagnoses. In correctional centers, specialized preschool educational institutions and speech therapy hospitals, medical, psychological and pedagogical therapy is used when treating patients with alalia. Drug treatment is mainly aimed at stimulating the formation of brain structures.
For pathologies of speech centers in the cerebral cortex, experts note the high effectiveness of the following physiotherapeutic procedures:
- DMV;
- IRT;
- hydrotherapy;
- laser therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- electropuncture;
- transcranial electrical stimulation.
When treating alalia, it is important to focus on the development of motor skills, thinking, and memory. The disease is caused by systemic disorders, therefore speech therapy treatment should be based on full coverage of sound-letter formulations and combinations, visualization of concepts, as well as concentration. Speech therapy massage and logorhythmics must be carried out along with speech therapy classes.
It is recommended that children with alalia begin to learn the alphabet, counting and writing as early as possible. Such skills allow you to better develop memory, learn to compose syllables into words and control speech.
In complex therapy of motor alalia, the main work should be aimed at:
- stimulation of speech activity;
- development of coherent speech;
- formation of speech reserve;
- grammatical format of the statement.
With a diagnosis of “sensory alalia,” the emphasis of speech therapy should be focused on developing skills to distinguish speech and non-speech sounds, differentiate words, and understand speech instructions.
It is important to systematically work through:
- correct phonemic awareness;
- acoustic skills;
- associative series.
Treatment of motor and sensory alalia in St. Petersburg, at the Prognoz clinic
- First, a comprehensive neurological examination is carried out using modern equipment, consultation with a neurologist and speech therapist.
- Based on the diagnostic results, experienced specialists create a rehabilitation course.
- Children undergo an intensive course of individual lessons and procedures, lasting 16 days.
Based on the diagnostic results, the following treatment methods can be prescribed:
- training using the Alfred Tomatis method (Besson of Switzerland)
- inTime
- massage
- Neurodynamic gymnastics
- Classes with a speech therapist using verbotonal equipment
- TCMP
- RTMS
- physiotherapy
and other techniques, which you can read about in the “techniques” section
Forecast and prevention of ANR
For motor alalia, the prognosis for recovery is always favorable. The result of therapy for sensory and sensorimotor diseases is uncertain and depends on many factors: the degree of damage to the speech center of the brain, side pathologies, and the presence of psychosomatic disorders. At school age, children with ODD are faced with written language disorders: dyslexia and dysgraphia.
Prevention of alalia includes:
- monitoring the course of pregnancy;
- long-term breastfeeding;
- early diagnosis of congenital pathologies;
- complex physical development of the child.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Possible complications and consequences
If parents do not take a child with alalia to a specialist or do not follow his recommendations, the condition progresses. If we are talking about the motor form of the disease, the baby may encounter problems such as:
- speech negativism (reluctance to speak);
- stuttering;
- dysgraphia and dyslexia (reading and writing disorders).
Any form of speech impairment without correction causes delayed intellectual development, significant difficulties in learning and socialization of the child.