Children under the age of 5-6 years should be able to independently pronounce all existing sounds. If this does not happen, parents need to independently train their child’s pronunciation at home or seek help from specialists in case of particularly obvious deviations from the norm. Setting and automating the sounds “R” and “R” is the most difficult task compared to the rest of the pronunciation of letters of the Russian alphabet.
Types of violations
In speech therapy
There are different types of deviations
in children
in the pronunciation of the sound “R”:
- Lack of phoneme. When reproducing a letter, an incorrect placement of the articulatory apparatus is observed. The sound can be completely devoid of the necessary movements of the speech organs and can be formed by lengthening a similar vowel letter. Or have guttural
trembling sound. - Pararotacism. Replacing the phoneme “P” with consonants.
- Rotacism. Sound distortion is divided into subtypes:
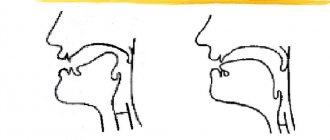
- Velar
.
The child does not use language during production. Vibration occurs due to the soft palate. The pronunciation is similar to the French way
of pronouncing "R". - Uvular
. Vibration by means of a small tongue (uvula). - Nasal.
The sound “R” is pronounced together with “G”. - Lateral .
Combination of "R" and "L". The sound is like "squelching". - Buccal .
Rare subspecies. Vibration of the cheeks during pronunciation is observed. - Kuchersky.
Both lips vibrate. - Bilabial.
"P" is similar to the English "W". - One-hit.
There is no vibration. The tongue touches the alveoli once.
4. Mixing sounds . Mostly “R” on “L” and “R” on “L”.
Expert opinion
Margarita Sergeevna S.
Speech pathologist and speech pathologist with 15 years of experience working in various speech correction centers with children of different ages.
To understand which type of incorrect pronunciation is observed in a child, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination of all organs of the speech apparatus.
Important: to understand and
correct deficiencies in the pronunciation of the hard or soft sound “R”, you must ask the child to reproduce the phoneme. First separately, then in a syllable and word . Based on the form in which the error is heard, direct training activities in exactly that direction.
Drawing up a correction program
It depends on the form of the sound pronunciation disorder. For example, a child may have no vibrant in his speech at all, or he may replace it with other sounds or mix them. Rotacisms, that is, distortions, are also common. There are 8 types of rotacisms. Therefore, the speech therapist selects a step-by-step production of the sound “r” individually for each little patient. However, there is a list of exercises that are suitable for any form of vibrant pronunciation disorder.
“Imitation” technique for simple cases
The staging exercise involves auditory perception of sound. The little student is offered examples of phonemes, for example, the roar of a motor, thunder. And he, sitting in front of the mirror, repeats what he heard.
Causes
To know why the baby is not succeeding
pronounce a sound,
how
and
where to start
correctional work, you need to have an idea of the possible reasons:
Deviation occurs due to cardiovascular diseases, respiratory
Incorrect speech breathing.
system, adenoids, advanced forms of rhinitis. A speech therapist can regulate the breathing rhythm during speech.- Hearing. Poor hearing has a direct impact on the development of coherent speech.
If pronunciation defects are present before the age of 5, this indicates problems with phonemic hearing. The baby does not recognize sounds, so it reproduces them poorly. - Poor development of the articulatory apparatus. In order for the sound to be pronounced correctly, it is necessary to develop the speech organs. There are special exercises for this ( articulation gymnastics
).
They help the child understand how the organs are located
during the pronunciation of the phoneme. - With a short bridle. The defect limits the movement and position of the tongue
when the child speaks.
To eliminate the deviation, use a step-by-step
set of exercises or remove the problem using the surgical
method
. - With throaty pronunciation. This reproduction of the phoneme “P” is usually called burr. The defect is characterized by a complex process of establishing the correct
reproduction of the letter.
To correct throat
pronunciation, articulatory gymnastics are used and the baby is taught to pronounce the sound again in a completely different way. - Muscle tone disorders. The defect is called dysarthria here. To prepare for sound reproduction, speech therapy massage
. Exercises are carried out only by a specialist using special tools. In order not to harm the child, they first determine what state the muscles are in (tone or weak mobility). Afterwards an individual course of therapy is carried out.
Advice: Among the reasons, the desire to imitate loved ones plays an important role. The baby can repeat incorrectly pronounced sounds, syllables, and words after adults. Therefore, it is important that the people around him speak unmistakably in front of the child, then he (she) will begin to try to speak without defects.
Classification
Replacement (substitution) and confusion (interchange) of speech sounds are phonemic (sensory, phonological) defects, usually caused by incompleteness or disruption of the development of phonemic hearing.
Substitutions are classified into the same groups as distortions of sounds, only the prefix “para-” is added to the name of the latter: 1. Parasigmatisms
(from the Greek letter “sigma”) - replacements for whistling and hissing words:
- labial-dental - voiced [Z] and [Zh] are replaced by [V], unvoiced [S] and [Sh] - by [F] (“sleigh” - “fani”, “green” - “veleny”);
- prizubny - replacing [S] and [W] with [T], and [Z] and [Z] with [D] (“elephant” - “tlon”, “teeth” - “oaks”);
- hissing ‒ instead of [S] it is pronounced [Ш], instead of [Z] ‒ [Zh] (“sledge” - “shanki”, “bunny” - “zhaika”)
- whistling ‒ instead of [Ш] [S] is used, instead of [Z] ‒ [Z] (“washer” - “sayba”, “belly” - “yawn”).
2. Paralambdacisms
(from the letter of the Greek alphabet “lambda”) - replacing the sound [L] (“paw”) with [U] (“uapa”), [V] (“vapa”), [Y] (“yapa”), [L ′] (“blunder”), [P] (“rapa”), [Y] (“yapa”), [D] (“dapa”).
3. Pararotacisms
(from the Greek letter “rho”) - replacing the sound [P] (“hand”) with [P′] (“ryuk”), [L] and [L′] (“bow,” “luka”), [Y ] (“yuka”), [G] (“guka”), [D] (“duka”), [V] (wuka).
4. Paraiotacisms
(from the Greek “iota”) - replacing the sound [Y] with [L′] (“shirt” - “fry”).
5. Replacement of back-lingual sounds
(from the Greek letters “kappa”, “gamma”, “chi”): parakappacisms - [K] on [T] (“Kolya” - “Tolya”), paragammatisms – [G] on [D] (“head” - “dolova”), parachitisms - [X] on [T] (“tail” - “twist”).
Also in practical speech therapy, sound substitutions include voicing defects (replacement of voiced phonemes with paired voiceless ones - “kushi” instead of “geese”) and softening defects (replacement of soft consonants with their hard pairs - “tota” instead of “aunt”). Close to replacement is the mixing of sounds, i.e., mutual substitutability, confusion of phonemes.
A set of exercises for the speech organs
Articulation gymnastics is needed here for the preparatory stage
before sounding.
It is carried out in a playful way
to interest the child as much as possible.
Don't miss: What is SSD (speech development delay)?
Tasks to improve lip mobility
- Smile. Stretch your lips in a smile so that the upper and lower rows of teeth are visible. Maintain the position for 5 seconds.
- Pipe. Pull your lips forward, making them a ring.
- Doors. Open your mouth wide. At the same time, stretch your lips into a smile.
Tongue mobility tasks
We brush our teeth. Imitating a toothbrush, clean the upper and lower rows of teeth in turn.- Horse. Click the tip of your tongue against the roof of your mouth.
- Machine gun. Open your mouth wide. Tap behind the upper teeth with the tip of your tongue. At the same time, pronounce the sound “D” out loud, gradually accelerating the pace.
Exercises help with weak tongue
, making it more mobile.
Expert opinion
Margarita Sergeevna S.
Speech pathologist and speech pathologist with 15 years of experience working in various speech correction centers with children of different ages.
Not the entire range of tasks for the mobility of speech organs is presented here. Best ways
are selected for
individual lessons for preschoolers
and they are given
homework
to work in a relaxed atmosphere with loved ones.
Gymnastics for lips
The complex includes 3 exercises:
- "Let's smile!" The baby smiles, showing all his teeth. The duration of the approach is 5 seconds.
- "Tube". There are 2 variations of this exercise. The student stretches out his lips, imitating a tube, silently “reproduces” the sound “u” or closes his teeth and slightly stretches his lips forward so that a square is formed.
- "The doors are opening." The baby slowly opens his mouth so that there is a distance of 10 mm between the teeth of both jaws.
Then he smiles, showing his teeth.
Methods for setting the phoneme P
The methods for forming the sound R are varied. You can use one of the proposed ones, or you can use several at the same time. Detailed plan with stages
The work is compiled by a specialist, taking into account the baby’s needs and capabilities.
Main methods:
- Imitation . This is done using a mirror. The child and the adult sit in front of the mirror. A relative or specialist clearly demonstrates how the speech organs are positioned when producing sound. The baby must repeat what is shown, checking the correctness by looking at his reflection.
- Staging using the letter "D". The baby opens his mouth slightly. He touches the sky with his tongue and quickly says the letter “Ddddd”. Then he repeats it with a strong exhalation. This produces the vibration necessary for the sound “R”.
- Staging using the letter “Z”. The baby is asked to reproduce the letter “Z”. The tongue is raised up and the tip is moved along the protrusions on the palate near the upper teeth, while the phoneme is sounded. The sound “Sr” comes to the ear.
- Mechanical method. The method is performed using the motor exercise
. The child is asked to pronounce the sound “D” for a long time. At this time, use a clean index finger or a special spatula to move the tongue under the bottom from side to side. As soon as the sound Drrrrr begins to be heard after class... it is necessary to consolidate the result. Teach your child to pronounce words with the letter “R”, tongue twisters, rhymes, etc. - In a lying position. Suitable for children with large tongues. Before the procedure, a special massage is performed. The speech therapist sits down on the edge of the couch. The baby puts his head on his/her lap. In this position, he should pronounce the sound “Za”. The specialist, holding the child’s chin, moves the tongue with the instrument, creating vibration.
Important:
how quickly positive changes in work will occur. It all depends on the regular completion of tasks and the characteristics of the baby. Some kids get it a couple of days after training. Other kids master the skill within a few months.
Bogomolova method
A.I. Bogomolova in 1979 proposed a method for generating vibration for saying “R”. The teeth are open to a distance of 2 fingers. The tongue is pressed against the palate, stretching the frenulum as much as possible. The teacher moves the edges of the tongue towards the palate with his fingers, while the frenulum is free.
The child takes a deep breath and blows it out sharply, using his voice. The combination “TZ” is formed. Repeat the exercise, gradually increasing the air pressure. The sound combination “TLE” will change to “TR”. After fixing the short “TR”, they practice the rolling “TR” with the help of fingers, and then without them.
How to make the sound L
After completing the preparatory stage, they move on to the main exercises.
Staging L is carried out:
- by imitation;
- on inspiration;
- by mechanical means.
When the child begins to pronounce the letter correctly, it is necessary to consolidate this skill and bring it to automaticity. First, the child needs to be taught a soft sound, then a hard one.
By imitation
The most common method of learning is through imitation of an adult. First, the parent or speech therapist shows how to properly position the tongue and lips.
To make it clearer to the child, you can first explain to him in words:
- The language needs to be made broad.
- The tip is pressed against the upper front teeth or gums.
- The middle of the tongue is bent downwards, and the root is raised.
- Do not raise the side parts so that air can pass between them and the cheeks.
To check for correctness, touch the cheeks while the child says L. If everything is done correctly, the cheek muscles vibrate slightly.
It is better to practice in front of a mirror. First, the adult says it correctly himself several times, then asks the child to repeat it.
Automation of the sound “L” in phrases.
On inspiration
Exercises to develop correct articulation are combined with breathing exercises. It is advisable to put L while inhaling.
Before starting the workout, do several breathing movements:
- Inhale quickly - 1 second.
- Exhale smoothly and slowly - up to 5 seconds.
Then you can complicate the exercise and present it in the form of a game. The ratio of inhalation and exhalation should be maintained.
The complex for each child is selected individually and may include the following exercises:
- Blow on the pinwheel and watch it spin.
- "Stop a running horse." Inhale, lips relax. The air is exhaled to make a “prrrrr” sound.
- The child lies on his back on a flat surface (floor or hard couch). The hand is placed on the stomach. Inhale and inflate your stomach. The hand should feel how, as you inhale, “the ball inflates”, and as you exhale, it “deflates.”
- You can ask your child to close his eyes and guess the smell of fruits or other objects. As you inhale, you need to smell the fruit, drawing in air through your nose. As you exhale, pronounce the name of the object.
With mechanical assistance
To set the sound correctly, you can use mechanical devices:
- spatula;
- special probes;
- wooden ice cream stick;
- handle of a spoon, etc.
If there are no suitable objects at home, you can help the child with your fingers. The main task of such work is to fix the organ or muscle in the correct position.
Using improvised means, do the following exercises:
- A wooden stick is placed across the tongue. In this way, space is created between the upper molars and the sides of the tongue. The correct passage of air through the oral cavity is formed.
- Setting a hard sound from a soft one is done using the thumb. To do this, place the fingertip in the hollow under the chin. Lightly press on this area, and the sound reflexively becomes hard.
- You can learn to pronounce a hard phoneme by pressing the back of your hand to the bottom of your chin.
- If the child is overly tense, you can relax the facial muscles a little by massaging them with your fingertips.
- To correct bilabial lambdacism, the corners of the lips are stretched to a smile position and held in this state with the index fingers.
You can relieve tension by smacking your lips, exhaling through your mouth full through closed teeth - “oof”, snorting.
Words for practicing the sound “L”.
Diagnostics
If there are sound substitutions in the speech of a child or adult, the diagnosis is based on anamnesis and objective data. The speech therapist conducts a detailed study of speech function, and medical specialists (audiologist, orthodontist) conduct a detailed study of the state of the auditory analyzer and the dental-jaw system:
- Oral speech examination.
It is performed in accordance with algorithms adopted for various speech pathologies (dyslalia, rhinolalia, dysarthria, aphasia). All replaceable and mixed sounds are identified, and the type of defect in the sound side of speech is determined. At this stage, it is necessary to determine what results in sound substitutions: disturbances in speech or physical hearing, articulation difficulties. - Study of the auditory analyzer.
To exclude hearing loss as a cause of sound replacement, an examination of auditory function is necessary. In order to determine the degree of hearing loss, audiometry, acoustic impedance measurements, and auditory EP studies are performed. - Orthodontic diagnostics.
In case of improper closure of the dentition, teleradiography is performed, diagnostic impressions are taken, and photographs of the face and teeth are taken. Based on these data, subsequent treatment is planned.
What mistakes can there be when trying to pronounce L?
If a child tries to pronounce the sound L, the following errors are possible:
- The tongue goes deep into the oral cavity, its tip does not come into contact with the upper teeth or gums. Instead of the desired sound, the child produces Y (“boat” - “yodka”).
- A sharp breath at the moment when you need to say the right sound. If the muscles of the cheeks are involved in the process, the phoneme F is obtained.
- The air flow passes into the nose, so it turns out to be N.
Sometimes the child is first given R and then L. In such a situation, the second sound can replace the first (“rune” instead of “moon”)