Many children have problems with diction. Incorrect pronunciation of sounds can become entrenched and then it will be much more difficult to teach the child to pronounce words clearly and clearly. For this reason, at an older age, many psychological complexes develop; it is difficult for a person to read, express his thoughts out loud, he withdraws and reduces communication with the surrounding society to a minimum. That is why, from the age of 4-5, children are referred for consultation to a speech therapist. The specialist determines whether there are problems with pronouncing sounds and teaches the child to speak correctly. How to make an appointment with a speech therapist at a children's clinic will be discussed below.
Who is a pediatric speech therapist?
A specialist with a higher pedagogical education who knows effective methods for correcting speech development defects in children under 14 years of age is a children's speech therapist. For children with minor speech impairments, classes with a specialist in this profile, available in most kindergartens, may be sufficient. Children with serious speech disorders are referred to a speech therapist at a children's clinic for individual lessons. Such communication with a specialist includes special exercises for training the muscles of the cheeks and tongue, saying tongue twisters, learning songs and much more. Good specialists often have their own effective methods that allow them to achieve excellent results.
Important: if the child has speech problems, classes should be systematic, all recommendations of a specialist should be followed by studying with the child at home, involving all family members in this process
Individual lessons with a child conducted by an experienced specialist are mandatory for severe speech disorders, which include:
- aphasia, when speech is absent due to organic lesions of the cerebral cortex;
- alalia, absence of speech while maintaining normal hearing and intelligence;
- severe degrees of logoneurosis (stuttering), the main causes of which remain psychological problems (experienced stress, parental divorce, lack of attention).
In addition, the baby may be diagnosed with:
- GSD (general speech underdevelopment);
- dysarthria (impaired speech clarity, tempo, intonation, voice problems);
- dyslalia (the child cannot pronounce a sound or group of sounds correctly).
If a problem is identified, it is necessary to help the child in a timely manner.
After all, the absence of speech leads to inevitable delays in mental development, which worsen as the child grows up, and even if the child
speaks, there are long coherent phrases in his speech, the baby can please you with a story about his day or events during a walk and pronounces only some of the sounds incorrectly; classes with a speech therapist can correct the situation. It is better to do this before school; problems with speech make it difficult to perceive new information and lead to a decrease in academic performance.
Logomag
From the Regulations on Speech Therapist, we learn the definition of the profession of speech therapist. Logopedist is a specialist with a higher pedagogical defectology education in the specialty of speech therapy, proficient in methods of neuropsychological examination of patients with speech disorders and other higher mental functions, individual and group rehabilitation training, theoretical and practical knowledge in the field of defectology, provided for by the training program in accordance with the requirements of the qualification characteristics and received a certificate in speech therapy.
Conducts diagnostic examinations of patients with speech disorders and other higher mental functions. Together with the doctor, he develops individual programs for medical and pedagogical rehabilitation of patients with speech disorders and other higher mental functions (aphasia, dysarthria, agnosia, apraxia, dyslexia, dysgraphia, stuttering, delayed speech development, etc.).
The first link of speech therapy assistance is speech therapy centers in children's clinics. Currently, more than 180 speech therapists work in Moscow clinics. Every children's clinic in Moscow has a speech therapy room. The main tasks of a polyclinic speech therapist are:
- initial reception of the population;
- advisory assistance to relatives of children with speech disorders;
- conducting individual and group lessons with children;
- medical examination of the child population;
- participation in staffing specialized kindergartens and schools;
- referral of children for treatment to specialized hospitals, sanatoriums, and central centers.
Speech therapy rooms are organized at a rate of at least one per 100 thousand adult population and at least one per 10 thousand child population.
In the office for the adult population, the following positions are established: speech therapist - 1; medical psychologist - 1; social work specialist - 1; nurse - 1.
3.3. In the office for the children's population, the following positions are established: speech therapist - 1; medical psychologist - 1; nurse - 1.
“Regulations on the work of speech therapy rooms at children's clinics and children's departments of general clinics” was approved by the Deputy People's Commissar of Health of the USSR M. Kazantseva on December 26, 1940. The Regulations indicate the organization for children-speech therapists of “special speech therapy rooms at children's clinics, where with children special classes are being conducted to correct speech disorders,” recommendations are provided on regulating the duties of a polyclinic speech therapist, organizing initial appointments and classes, as well as explanatory work among parents and teaching staff of kindergartens and schools served by the clinic.
The speech therapy service of the Department of Health, including children's clinics, is headed by the Organizational and Methodological Department (OMO) for children's speech therapy (headed by Nina Mikhailovna Klyuvaeva) and its chief specialist (Tamara Pavlovna Rabotnikova, speech therapist at Children's Hospital No. 6). OMO in speech therapy belongs to the structure of the city dispensary DPB No. 6
Tasks and functions of OMO:
- analysis and generalization of the speech therapist’s activities, making proposals for its improvement,
- offers modern technologies for implementation,
- analysis of speech therapist’s annual statistical reports,
- is in charge of advanced training issues,
- makes recommendations for improving the content of the speech therapist’s office,
- organizes and conducts scientific and practical conferences,
- participates in the work of certification commissions for assigning categories;
- controls the implementation of legislative acts and letters of direction.
There is a provision for a senior polyclinic speech therapist in the district. (Regulations on the senior freelance speech therapist of the district health department of the city of Moscow. Recommended by the chief specialist in children's speech therapy and the organizational and methodological department for children's speech therapy of the Moscow Department of Health).
In accordance with this provision, a speech therapist at a children's clinic who has the highest qualification category and work experience in the clinic for at least 5 years, with experience and knowledge of organizational and methodological work, is appointed to the position of senior speech therapist of the district. The main task of the senior speech therapist of the district is to: provide organizational, methodological and advisory assistance to speech therapists of health care facilities of the district (if necessary, with on-site visits).
The senior speech therapist of the district carries out scheduled and unscheduled inspections of the work of speech therapists in the district's clinics (based on the results of the inspection, he applies for incentives or penalties for speech therapists at the district's health care facilities); maintains operational records of the availability of specialists (children's speech therapists) in the district's clinics.
It is the senior speech therapist of the district who analyzes and summarizes statistical and reporting materials on the activities of the speech therapy rooms of health care facilities in the district, and submits analytical reports on the reporting data to the district health department and the city OMO for children’s speech therapy.
The speech therapist is administratively subordinate to the chief physician of the clinic.
The main areas of work of a speech therapist in a children's clinic:
— pedagogical work to correct speech defects, carried out in systematic and advisory classes;
— medical examination of children, both organized and unorganized;
— participation in the staffing of speech therapy institutions in the healthcare and education systems;
— registration of speech therapy characteristics for each child;
— carrying out speech therapy sanitary and educational work: conversations with parents, work with pediatricians and kindergarten teachers, issuing speech therapy bulletins, producing visual speech therapy aids.
The size and equipment of the speech therapy room should allow for the initial reception of the population, as well as individual and group (for 3-4 children at a time) classes in the presence of parents.
The regulations on the speech therapist of the healthcare system, developed by the OMO on speech therapy, contain a list of the necessary equipment for the speech therapy room: desk; children's table; wardrobe; manual cabinet (bookcase); ordinary chairs (5 pcs.); children's chairs (5 pcs.); wall mirror; a set of picture material for examining all components of a child’s speech; a set of picture material for correcting speech defects, automating and introducing acquired skills into speech; metal speech therapy probes; wooden spatulas; colored pencils, felt-tip pens; handouts for parents, photocopied in sufficient quantities to consolidate the material covered at home; sterile wipes, cotton wool, alcohol for disinfection of used instruments; hand mirrors (5 pcs.); a set of educational board games; a set of toys for examination and activities.
The administration of the clinic pays the cost of benefits upon presentation by the speech therapist of a sales receipt and credits the paid benefits to the balance of the clinic.
The speech therapist's work schedule is approved by the chief physician of the clinic at the rate of 18 working hours per week with a five-day working week at one rate.
4 hours a week are allocated for the initial appointment, 10 hours per week for systematic and advisory classes with children, 4 hours for medical examinations. The timing of medical examinations is established in agreement with the administration of the clinic. Upon completion of medical examination in kindergartens, the freed 4 hours, in agreement with the administration, are allocated for the initial appointment, professional appointment at the clinic or classes with children.
Organization of initial reception.
The initial appointment is carried out at strictly established hours, convenient for the population, by appointment. Both morning and evening appointments are possible (on a certain working day or one hour of each working day).
When a speech therapist works at 0.5 rate, all classes and the initial appointment are held in the afternoon, while 2-3 hours are allocated for the initial appointment.
The initial appointment with a speech therapist is aimed at examining the children’s speech and deciding on the time and form of speech therapy assistance. Children are referred to an initial appointment with a speech therapist by pediatricians, psychiatrists, otolaryngologists, as well as kindergarten teachers and school teachers.
During the appointment, the speech therapist is obliged to: find out the purpose of coming to the speech therapist (speech complaints, medical examination, examination for placement in a preschool institution, etc.); collect brief anamnestic information about the early development of the child; conduct an examination of the child’s speech; make an entry in the outpatient card; if necessary, provide the necessary advice; determine the type of speech therapy help if the child needs it.
The speech therapist conducts the initial appointment based on the basic principles of speech therapy: systematicity, complexity, development, ontogenetic principle.
The study of speech understanding includes: understanding contextual speech; understanding of the simplest questions and questions of indirect cases; understanding prepositions; understanding of logical-grammatical structures and inverted phrases. In some cases, understanding of grammatical categorical changes is examined.
Vocabulary research is carried out in the form of a survey based on pictures arranged in logical-thematic groups. It is advisable to present both rarely occurring and frequent words. Knowledge of generalization words is tested, and the volume of parts of speech in the child’s dictionary is determined.
The study of syllabic structure is carried out using albums containing pictures, the names of which reflect different syllabic complexity. Perseverations, elision, permutations, addition of syllabic vowels, anticipation, and addition of syllables are recorded.
The study of the grammatical system includes: the use of prepositions, changing words by case, various types of word formation, coordination of various parts of speech.
Studies of coherent speech: the child is asked to compose a story based on a series of plot pictures, as well as to retell the text told by a speech therapist.
Sound pronunciation status: Sound pronunciation is checked during all of the above tests. You can also check the child’s pronunciation of a particular sound using pictures or in conjugate-reflected form.
The structure of the articulatory apparatus: only deviations from the norm are recorded.
Features of the child’s speech behavior: speech contact, features of entering into speech, highlighting the most difficult speech situation, desire to correct the defect; and also features of general behavior are noted (contact, activity, excitability).
If stuttering is present, the following parameters are described: degree of severity; place of occurrence of speech spasm; breathing features; type of seizure; the presence of speech tricks.
In the presence of rhinolalia, the following parameters are recorded: the presence of scars after uranium, cheiloplasty, the degree of closure of the soft palate, the degree of mobility of the organs of the articulatory apparatus.
If dysgraphia or dyslexia is present: the child’s workbooks are examined and the written short dictation is checked.
Organization of dispensing.
The speech therapist is one of the specialists who, in accordance with the orders of the Department, takes part in the targeted medical examination of the child population. This means that every child living in the territory under the jurisdiction of this clinic must be repeatedly examined by a speech therapist. Such examinations are carried out by children aged 4 and 5 years old in general and schoolchildren selectively, at the direction of school teachers. At the age of 6, children are examined when applying for a special medical form for admission to school.
For a complete medical examination of the child population, the speech therapist of the clinic goes around the kindergartens of his microdistrict, examining the speech of all children in middle, senior and pre-school groups, as well as selectively, at the suggestion of teachers of younger groups.
The speech therapist must include information about the examination of children’s speech in the medical records and medical examination log. The entry in the journal must be certified by the signature of a representative of the kindergarten (nurse or manager).
The speech therapist is obliged to inform educators about identified speech defects and notify parents. Each child is invited to the clinic for a more detailed examination and speech therapy assistance. For this purpose, the speech therapist posts lists of children with speech impairments on the information board for parents.
When conducting a targeted medical examination of the child population, the speech therapist of the clinic must visit all kindergartens in his microdistrict.
At the end of each month, he must submit to the administration of the clinic a plan of exits for medical examinations in kindergartens in the next month with an exact indication of the kindergarten number, date and time of his visit.
Medical examination of children who do not attend childcare centers is carried out by a speech therapist in the clinic during the initial appointment hours, upon the referral of a pediatrician.
Organization of activities with children.
A speech therapist is obliged to provide assistance to every child who needs it, regardless of the severity of the defect, from birth to transfer to an adult clinic. Cases of refusal of assistance during initial treatment are unacceptable. The type of assistance and the institution that is optimally suitable in each specific case are determined by the speech therapist.
A child with identified speech pathology can be enrolled in classes at the clinic, which are conducted systematically (1 to 3 times a week) or consultatively. The frequency of consultation sessions is determined by the speech therapist. Children with various types of speech pathology (dyslalia, dysarthria, delayed speech development, rhinolalia, stuttering, dyslexia, dysgraphia) are enrolled in systematic classes.
As a rule, children under 3 years of age or children referred by a speech therapist to a commission in speech therapy kindergartens are enrolled in a consultative form of classes, if more than 3-4 months remain before admission there.
During a consultation session, the speech therapist explains to parents the state of the child’s speech at the moment, sets the immediate task and shows how to accomplish it. If necessary, handouts are provided (memos, descriptions of speech therapy techniques, exercises, text material for memorization, etc.). During classes, the child can be transferred from one form of classes to another.
The presence of a queue for classes with a speech therapist at the clinic should be excluded.
To provide speech therapy assistance, the child can be sent to the appropriate children's institution for a medical and pedagogical commission for staffing specialized kindergartens and speech therapy groups, for consultation at other treatment and preventive institutions. For a more detailed diagnosis of the disorder and search for the optimal type of help, you should use the advice of other clinic specialists (otolaryngologist, neurologist, psychiatrist, psychologist).
It is not recommended to enroll children with hearing loss, significant visual impairments and underdevelopment of cognitive activity in classes with a speech therapist in a clinic.
All work in the clinic is carried out in the presence of parents. The task of a speech therapist is not only to teach a child certain speech skills, but also to involve parents in this process, to interest them in the child’s condition, to force them to take a closer look at his characteristics, and to make them good assistants in their work. It is especially valuable when certain methods of speech therapy work are carried out by parents (for example, methods of producing sounds).
Records management.
The speech therapist is required to maintain reporting and accounting documentation according to established templates. All logs must be filled out in neat, legible handwriting, each entry must be numbered and contain the necessary information. Abbreviations that interfere with the understanding of the recording are not allowed.
1. Outpatient card of the patient
An outpatient card of the established form is created for each child in the clinic. When attending an initial appointment with a speech therapist, the parent must have this card with them. The speech therapist, having examined the child’s speech, puts his stamp and makes a record containing: the date of admission; brief anamnestic information about the child’s early speech development; a brief description of the understanding of the addressed speech; a brief description of your own speech; speech diagnosis (written down in full, without abbreviations); recommendations for classes.
If a child is enrolled in systematic classes at the clinic, a corresponding note is made in the outpatient card at the first lesson and periodically during the work, as well as at the end of the work, indicating the effectiveness.
2. Initial appointment log
The log is kept for a calendar year and, upon completion, is retained for 3 years. It serves as the basis for drawing up an annual report submitted to the administration of the clinic and the organizational and methodological department. The journal includes: serial number; patient's first and last name; medical policy number; date of birth; address; speech diagnosis; recommendations.
3. Journal of clinical examination in kindergartens
The journal contains the following data: kindergarten number; date of visit; list of examined children; addresses and telephone numbers of children with identified speech pathology; preliminary speech diagnoses; signature of the kindergarten representative.
4. Individual speech cards
For each child accepted for systematic or advisory classes at the clinic, the speech therapist creates an individual free sample card, which must contain the following entries: the child’s first and last name; home address and telephone number; detailed description of speech during the initial examination: understanding of addressed speech, state of expressive speech, state of the articulatory apparatus; speech diagnosis; plan for working with the child; systematic ongoing records of work done and its effectiveness.
The frequency of ongoing recordings depends on the child's level of progress in activities. In the consultative form of work, at each lesson the following is made: a final note about the state of speech at the end of the course; performance evaluation and further recommendations.
Upon completion of work, the child’s individual card should be kept for at least 2 years.
5. Journal of speech therapy sessions
The journal, filled out in free form, contains: a schedule of classes indicating the child’s last name, day of the week and time at which classes are scheduled; date of the lesson and note of the child’s presence.
6. Annual progress report
The report is submitted to the administration of the clinic and the organizational and methodological department for children's speech therapy. A copy submitted to the organizational and methodological department must be signed by the chief physician of the clinic and the speech therapist. The report outline is shown below.
A. Clinic number, district.
B. States: number of positions by state; busy; individuals.
B. Education: higher specialized; higher non-specialized.
D. Work experience as a speech therapist: from 0 to 5 years; from 5 to 10 years; from 10 to 20 years; over 20 years.
D. Category: second; first; highest.
E. Children aged: 2 years were examined during medical examination; 3 years; 4 years; 5 years; 6 years; others; Total; pathologies were identified.
G. Examined at an appointment at the clinic: no pathology; with physiological disorders; delayed speech development (general speech underdevelopment); dysarthria; dyslalia; stuttering; others; everything inspected.
3. Sent: to classes at the clinic; to speech therapy kindergartens and groups; specialized institutions (sanatoriums, rehabilitation treatment centers); speech schools; other medical and preventive institutions.
I. Effectiveness of speech therapy sessions: discharged with recovery and significant improvement; discharged with improvement; discharged without improvement.
Working with parents.
The task of a speech therapist is to inform parents about the modern requirements of teachers and psychologists for the development of a child, to explain the true state of his speech development, to teach them some techniques of speech therapy work, making them accomplices in the correction process.
To solve these problems, there are various methods: lectures and conversations, individual consultations, visual propaganda (stands and posters), multiplied handouts on topics intended for each specific case.
The speech therapist at the clinic should place an express test on the information stand, with the help of which parents can independently determine how their child’s speech is developing, whether they urgently need to see a speech therapist, or whether the child is developing safely and they will undergo medical examination in due time.
This is very important, since often parents of non-speaking children believe that visiting a speech therapist is not necessary, because their child does not speak anything yet. They calmly wait for speech to appear until they are 3 years old. But subsequently this leads to the fact that speech delay becomes an insurmountable obstacle to the further development of speech and, as a consequence, leads to failure at school.
True, it should be noted that there is a category of parents who, on the contrary, are in an excessive hurry, making excessive demands on their children, which also negatively affects the development of their speech. The express test makes it possible to adequately look at the development of a child’s speech. The questionnaires are built according to the questionnaire type. They are filled out by parents or the person raising the child. The person completing the form needs to enter basic information about the child (last name, first name, date of birth and gender), and he emphasizes the rest by choosing the answer options. Some items provide short additions to test questions. This makes filling out surveys simple and takes little time to complete. At the end of the questionnaire there is a section called “Additional Speech Pathologist Notes” for recording diagnosis or other important information.
Standards of work for speech therapists in healthcare institutions of the Russian Federation
Estimated workload standards for speech therapists are established:
1. For adults:
1.1. When working individually with patients with severe disorders (aphasia, dysarthria, dyslexia, dysgraphia, logoneurosis, dysphonia, etc.) - 1.5 visits per hour.
When working with patients at home - 1 visit per hour.
1.2. When conducting group speech therapy sessions with patients with aphasia, dysarthria, dyslexia, dysgraphia, dysphonia - 6-8 visits per hour; with patients suffering from logoneurosis (stuttering, etc.) - 8-10 visits per 1.5 hours.
2. For children:
2.1. For individual work (including examination and consultation) for severe disorders (alalia, general speech underdevelopment, aphasia, dysarthria, dyslexia, dysgraphia, stuttering, mutism, rhinolalia) - 1.5 visits per hour.
2.2. For individual work with mild speech disorders (dyslalia, etc.) - 4 visits per hour.
2.3. When conducting group speech therapy sessions with patients with severe speech disorders - 6-8 visits per hour, with mild speech disorders - 8-10 visits per hour.
Examination by a speech therapist
1 Examination of children with speech underdevelopment 30 Consultations with a psychiatrist, otorhinolaryngologist
2 With delayed speech development 30 Consultations with a psychiatrist, otorhinolaryngologist
3 With dyslalia and FFN 20 Consultations with an otolaryngologist
4 Stuttering 30
5 With dysarthria 20
Psychiatrist consultation
6 With rhinolalia 30
7 With dysgraphia 40
When to contact a pediatric speech therapist
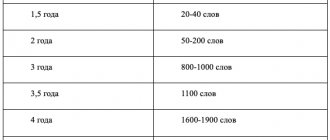
Of course, each child is individual, everyone develops differently, but normally a one-year-old baby should understand some simple phrases addressed to him, show the location of the eyes, nose and mouth, and understand the meaning of the word “impossible.”
At two years old, a baby normally knows more than 20 words, speaks simple phrases, responds to messages “Let’s go for a walk” by starting to get dressed or pointing to clothes for a walk, brings a certain toy upon request, and is able to listen to a short fairy tale.
By the age of 3, a child already has a fairly extensive vocabulary, asks a lot of questions, and tries to share his impressions with his parents.
Today, the norms have changed somewhat, many three-year-olds are just beginning to speak in sentences, and the number of words spoken has decreased significantly.
However, if a child has not started talking by the age of three, avoids communicating with peers on the playground, and cannot interact with loved ones, this is a serious reason to turn to specialists.
In this case, a consultation with a neurologist is necessary, a hearing test should be performed and a speech therapist should be consulted.
A comprehensive examination of the baby will identify the problem and begin treatment. Even if your family or close friends have examples where a child was silent for up to 3 years or more, and then spoke successfully, this is not a reason to postpone a visit to specialists.
How does a speech therapy kindergarten differ from a regular kindergarten?
There is an opinion that a speech therapy group is a certain “stigma” in a child’s personal file. Is it really?
First, let's figure out what a speech therapy group is?
Correctional groups are divided into speech (speech therapy) and groups of children with mental retardation (delayed psycho-speech development).
In speech therapy groups, they introduce sounds that were not there and correct incorrectly pronounced ones (correction of speech defects), enrich the vocabulary, develop phonemic awareness, coherent speech, and teach correct grammatical formatting. In the senior and preparatory groups they prepare for learning to read and write.
In the ZPR groups there are both a speech therapist and a defectologist (in addition to teachers who have the necessary qualifications). Also, a speech center can work in a kindergarten - in this case, a speech therapist individually works with children with impaired pronunciation according to a certain schedule.
But in any case, a speech therapy group in our time is not a punishment, but, most likely, a reward, because it has become more difficult to get there, and the general underdevelopment of speech is easier to correct in the garden, where all the work is aimed at eliminating this problem.
Perhaps it is no longer a secret to anyone that in speech therapy kindergartens the preparation of children, no offense to anyone, is sometimes much stronger than in mass kindergartens. Because children from speech therapy groups come to school with a much better vocabulary than children from a regular kindergarten. They know more, they have a wider vocabulary, and many skills are better developed, starting with graphic skills, sound-letter analysis and ending with stories based on pictures. Generalizing concepts are better formed. That is, children come from speech therapy kindergartens even more prepared.
Some parents are very attracted by all this splendor, and they dream of enrolling their children in a speech kindergarten. Others are afraid of speech therapy kindergartens, believing that a child who finds himself among poorly speaking peers will begin to speak even worse than before.
These are misconceptions. A child with speech therapy problems does not begin to speak worse because he communicates with other children with similar disorders. The only exceptions are those cases when a child with pronunciation problems ends up in a group of children who stutter. Indeed, there are cases where a child develops stuttering “by imitation.” But specialists, as a rule, avoid such mistakes.
So, for one reason or another, you think that your child definitely needs a specialized speech therapy group. What do you need to do to get into a speech therapy garden?
The speech therapy kindergarten accepts children mainly 4-5 years of age, since correction of speech disorders is especially important for them in order to successfully prepare for school. From the age of 3 you can join a group for children with delayed psycho-speech development (DSD).
How to make an appointment
You can make an appointment with a speech therapist in a children's clinic at the reception of the medical institution during a personal visit, by telephone, by calling and specifying the appointment schedule. In addition, registration is carried out on the website of the selected clinic. Often, parents are referred to see a speech therapist by a pediatrician on the recommendation of a specialist from a preschool institution.
Unfortunately, it is not yet possible to sign up with a speech therapist through the State Services portal.
If the appointment is made at the medical institution at the place of registration of the child, the doctor’s appointment will be free; if the parents looked for a specialist on their own, the price of the visit may vary significantly among different doctors.
How to find a good speech therapist and where to look?
More and more children need speech therapy help. But a professional should work with the child. How to find such a professional and what qualities should he have? The truth is that a person's professionalism can only be determined by another professional in the same field . Those. You personally, if you are not a speech therapist yourself, will not be 100% able to determine whether the person in front of you is a professional. This is worth remembering when listening to “good reviews from friends.” If they are not speech therapists, then their reviews, to put it mildly, mean nothing. And on the Internet, everyone buys as many reviews about themselves as they want.
And yet there are indirect signs that will help you cope with this task.
Contact with the child . Even if a speech therapist is a doctor of science at least three times, if emotional contact is not established, you will achieve results much more slowly. Of course, we should not forget that children are all different and there are some who find it difficult to meet new people. In this case, it is worth observing several classes in order to determine as accurately as possible whether the teacher is suitable for the child. Also take a closer look at the speech therapist yourself: how he behaves. A competent specialist must have correct, beautiful speech, and the ability to correctly construct sentences. Qualification. Unfortunately, even a higher education diploma will not give you a 100% guarantee of a highly qualified specialist. But it wouldn’t hurt to inquire about the availability of such a diploma. You can also ask to see the speech therapist’s portfolio.
To provide effective assistance, the material and technical base is important. At your first meeting, pay attention to the number of teaching aids in the office.
The most reliable way to confirm your qualifications is the network structure of the company you are applying to. No one checks a single specialist either when applying for a job, or the classes he conducts (whether a private trader, a speech therapist in a kindergarten or in some “developer-diversified specialist”, etc. But here it should be remembered that the quality of classes at home in times worse than in a specialized office. Otherwise, what are millions of employees doing in offices when all the work could be done at home? That's right: refrigerator, TV, sofa, Internet... And if an adult cannot motivate himself at home, how to deal with it to kid?
And yet, what price is optimal? Here you think about what you want to get for your money. Soft sofas for those waiting, free WiFi, coffee, TV and large rooms - the price will be high, because... All this is not free and you pay for it.
Group classes, private classes at home, speech therapist in the garden, classes via Skype - the price will be low. But the effect of the classes will be even lower.
We decided to look for a “golden mean”, but at the same time completely exclude low-effective options, and also work without unnecessary frills for those waiting. Yes, this reduces our profit, but due to the large flow of people who are willing to pay for a specific solution to problems in the shortest possible time and due to the large number of our centers, we offer one of the lowest prices for individual (most effective) classes.
And yet, even with such a low price as ours, it is worth thinking through and planning the family budget in advance, taking into account the fact that classes with a speech therapist will most likely take place at least twice a week (the frequency depends primarily on your capabilities - time and financial; the more often you practice, the faster the result will be). And if you quit classes “halfway”, there is a high probability that your child’s speech will return to its previous state, and all the money you spent will go “down the drain.” A common question parents ask is “How long will it take to see a speech therapist?” After all, knowing the price, you also want to know the period during which the family budget will incur additional expenses. For a detailed answer to this question, see the link in the article of the same name. Here we will say briefly: you should be wary if the speech therapist gives a very clear forecast regarding the timing. Please take into account that the teacher has not known the child for so long, and during the diagnosis, children are often nervous; accordingly, the teacher will not be able to see the full picture of behavioral reactions. But how a child will behave in class - complete tasks, or shirk them, be capricious - is one of the important components of success. Also, the teacher does not know whether you will personally study at home with the child and monitor his speech, without which the time required for producing sounds will increase significantly.
Where to look?
There are many options, both cheap or even free (budget kindergarten, clinic) and not so (speech therapist within a multifunctional development center, private classes at home, speech therapy centers). We will not take into account the “human factor” or any specific companies; we hope that you will come across the best people and companies in the country. Let us consider only the structural disadvantages and objective advantages of each of them.
In state budgetary organizations (kindergarten, clinic, GPPC, etc. options):
Pros:
1.Free or inexpensive.
2. If this is a speech therapist in a kindergarten, there is no need to take the child anywhere separately, everyone is in one building.
Cons (for more details, see the article “Will a speech therapist help in kindergarten?”):
1. Complete lack of control over the professionalism of the speech therapist.
2. The speech therapist has no motivation to work with your child; no one checks him on this matter.
3. You have no idea what is being done in class.
4. Very short-term classes (in a regular kindergarten - 10 minutes, in a correctional kindergarten - 20 minutes)
5. Very long queues. In order to get to a speech therapist at all, they will often require a certificate, wait another year, “don’t come before 5 years old,” etc. Many parents face this.
6. A huge flow of children. The norm for a speech therapist at a school, for example, to which several kindergartens have been added, is 1000 children. Do you think he will be able to study with this amount two or three times a week for at least 10 minutes? If he receives all these children for 9 hours without breaks, breaks, lunches and rest, then it will take 11.8 minutes for each. According to reporting, he is engaged, we are talking about reality.
Private speech therapist (tutor) at home.
Pros:
1. Tutors who come to your home are very convenient. There is no need to take your child to a specialist; the speech therapist will come himself and bring with him some of the teaching aids.
2. They couldn’t even come up with a second advantage. Think for yourself.
Minuses:
1. Complete lack of control over the professionalism of the speech therapist.
2. The speech therapist does not have the motivation to quickly correct your child’s speech. The longer this happens, the more he will earn. And no one controls him on this or any other matter.
3. You have no idea whether your child is being treated CORRECTLY or not. No one checks such a speech therapist.
4. The speech therapist will only be able to bring a couple of aids with him. If something doesn’t work out for your child, then the speech therapist will not replace benefits, which is wasted time and your money down the drain. But no speech therapist will carry 2-3 cabinets with manuals to your home.
5. My home is my castle. And also toys, favorite places, a refrigerator with “goodies”, cartoons, etc. Very often, children do not want to study normally at home, they are capricious, inventing that they feel bad, want to sleep, are tired, etc. And the teacher will not be forced to engage in the educational process, but to play the role of an “animator” who must entertain the child. The child will get used to such “entertaining education”, come to school, and there will be 30 children per teacher in the class. “Have fun” to the fullest.
Speech therapist in a private clinic.
Pros:
1. A medical license inspires confidence.
2. The proper level of pathos: waiting room, reception, sweets, etc.
Minuses:
1. Prices are two to five times higher than market prices.
2. “Multiprofessionalism”: one specialist receives a bunch of diplomas for completing accelerated courses and can treat anything, as long as they pay well. For example, we personally met the services of a speech therapist at the ophthalmology center. Don't see the connection? Bring money, they'll come up with a connection for you.
3. They will probably ask you to take a dozen more tests from them in order to definitely determine the diagnosis.
4. Do you personally feel comfortable in the hospital (if you are not a doctor, of course)? Here. And the child begins to think that he is sick, since he goes to the clinic. We think it would be more correct if he thought he was healthy and just went to classes.
Speech therapist at a development center somewhere nearby.
Pros:
1. Often close to home.
2. Low prices, especially for group lessons.
3. Here you can sign up for several classes in a row: mental arithmetic, drawing, chess, etc.
Minuses:
1. Complete lack of control over the professionalism of the speech therapist. There is no senior speech therapist above the speech therapist who would check him when applying for a job and during the work itself.
2. A speech therapist most often has 2-3 small shifts per week when he conducts classes. This is clearly not enough for a person to even eat normally, not to mention other needs. Therefore, he either runs around several such centers and conducts classes, or in the same center he does mental arithmetic, drawing, modeling, etc. Could such a “one-man orchestra” be a specialist in each field?
3. Inconvenient schedule, most often 2-3 times a week in a limited time.
4. The center makes money in group classes, but you personally lose . Example: 5 children in a group, 500 rubles. per lesson. The center earned 2500 rubles. in 40 minutes, and your child received: 40/5 = 8 minutes of teacher attention for 500 rubles. Those. the effectiveness will be as many times worse as the number of children attending such classes. It’s as if they wanted to save money and signed themselves up for a group operation, for example, with a surgeon who also works as a medical assistant, a nurse and a watchman. The effect will be approximately the same.
Specialized speech therapy center.
Pros: 1. Most likely, only professionals who have passed all stages of interviews work here; 2. A special educational environment has been created in the classrooms to facilitate the development of speech skills by your child; 3. Specialists deal ONLY with speech therapy, i.e. You receive the highest level of professionalism.
4. Surely there is control over the conduct of classes. Please note whether cameras are installed in the office. If yes, then there is definitely control.
Minuses:
1. There are not many such centers even in Moscow; they will not always be near your home.
2. Although we said that we would not take into account the “human factor,” due to the small number of disadvantages, we decided to voice this one too - the position of the management of such centers. If it is aimed only at “earning money” from clients, at the very first diagnosis you will be bombarded with professional terms, asked for a subscription for a month in advance, given an incomprehensible price list with different cost of classes, depending on what you did during this class (and you have no idea, There was a lesson on alalia, or on dislalia, but the price will be different!), etc.
If the management of the center thinks not only about profit, but also about children: everything will be simpler, clearer, more convenient, and more loyal.
Good luck with your choice!
How is the appointment going?
At the first speech therapy appointment, the doctor interviews the mother in detail, asks questions about the course of pregnancy and childbirth, the presence of diseases in the baby, the presence of a hereditary predisposition to the presence of speech problems, and makes a general impression about the situation in the family.
Often, speech problems in a baby arise due to a lack of communication in the family, when there is no close contact with the parents, in cases where, while fulfilling their responsibilities for caring for the baby, they do not communicate enough with the baby, do not teach him to pronounce words and sounds, or speak too much quickly and the child’s brain does not have time to assimilate the information received.
Having collected all the data about the family, the specialist begins to communicate with the baby using certain techniques. At the appointment, it is important to establish emotional contact with the baby, and the time of the first appointment rarely exceeds 35 minutes.
After talking with the child, the specialist makes a speech therapy conclusion and tells the mother in detail about the baby’s speech problems and ways to eliminate them.
You should not be alarmed if a speech therapist discovers violations, but a frivolous attitude to his recommendations can result in big troubles.
Speech therapists in Moscow
Who is a speech therapist?
Speech problems occur in almost every child. Many babies are unable to make specific sounds. Most often, these problems disappear as they grow older, but the help of a specialist in eliminating such phenomena is still necessary. It is the speech therapist who deals with the correction of such disorders.
What does a specialist do?
The task of a speech therapist is not only to teach the child to say “tiger” instead of “tigl”, but also to understand the causes of the problem that has arisen. If the disorder occurs due to some serious illness, then the help of a doctor may also be required. Often, a speech therapist helps a child prepare for school and learn to interact with society. Poor speech can cause a child to develop serious psychological complexes, so it is imperative to visit a specialist.
A speech therapist works not only with children. It helps restore normal speech to adults as well. Similar problems often occur after head injuries or strokes. Competent interaction between the attending physician and the speech therapist allows a person who has suffered from the disease to minimize the consequences and, if possible, regain normal ability to speak. Sometimes completely healthy adults, for whom speech defects may prevent them from building a career (for example, politicians), resort to the services of a speech therapist.
When should you contact a professional?
It is simply impossible not to notice speech problems in your baby. Some of them can be eliminated at home. However, not all parents have sufficient knowledge and the right amount of time. And even if these important factors are present, it is not always possible to solve the problem. Therefore, speech defects need to be eliminated as early as possible. Speech therapists work both in regular clinics and in private institutions, as well as kindergartens. In educational institutions, specialists themselves check children and, if necessary, can recommend parents to undergo a course of treatment.
How to become a speech therapist?
You can become a speech therapist at almost any pedagogical university. Medical education is not mandatory, but it is worth remembering that in your work you will inevitably have to meet with children suffering from some kind of deviation, so knowledge of the basics of defectology will be necessary. If a future speech therapist plans to work in a hospital, then he will need to understand the basics of neurology in order to understand the causes of the development of specific speech disorders.
To get a job as a speech therapist in Moscow, it is best to graduate from one of the leading universities, for example, Moscow State Pedagogical University or Moscow State Pedagogical University. There are specialized defectology faculties here, which have been training highly qualified specialists for many decades.
Famous Moscow specialists
The beginning of the development of speech therapy in Russia can be considered the first experiments in deaf pedagogy in the 17th century. It was then that scientists first realized the importance of correcting speech disorders. It took more than 200 years for speech therapy to become a separate discipline, and yet it was only in the 30s of the twentieth century that a truly serious attitude towards this area began to take shape. S.S. played a major role in the development of Russian speech therapy. Lyapidevsky. For a long time he worked at the Research Institute of Defectology, and then headed the department at Moscow State Pedagogical Institute. IN AND. Lenin. D.I. worked with him. Azbukin, Doctor of Science, academician. She taught at Moscow universities and L.S. Volkova, through whose efforts higher defectology education was actively developing.
How much does an appointment cost?
The cost of an appointment depends on the qualifications of the chosen specialist; in Moscow it starts from 1000 rubles for an initial appointment; in the regions, prices are slightly lower.
In children's clinics at the child's place of residence, if indicated, admission and subsequent classes are provided free of charge.
The frequency of classes is selected individually, taking into account the identified violations. Clinics often conduct group classes, selecting children with similar problems. Groups are formed taking into account the age and development of the child.
LiveInternetLiveInternet
Approved at a meeting of the activist group of defectologists in Moscow based on the decision of the board of the Moscow Education Committee dated February 24, 2000 https://www.logopedplus.ru/articles/zakon/zakon21/
Explanatory note 1. The work of a speech therapist teacher in a kindergarten that does not have specialized groups is aimed at correcting children’s speech defects. Along with corrective measures, a speech therapist teacher carries out preventive work in a preschool institution to prevent speech disorders in children. 2. A speech therapist works 5 days a week (total number of work hours - 20). The work schedule can be drawn up depending on the employment of children both in the 1st and 2nd half of the day. 3. The job responsibilities of a speech therapist teacher should only include work with children with speech pathology. 4. Children of preparatory and senior groups with simple and complex dyslalia, phonetic-phonemic disorders are selected for speech therapy classes. 5. Speech therapy examination of children in a preschool institution is primarily carried out in children 5-6 years old, other children are examined throughout the year. 6. Children suffering from stuttering, general speech underdevelopment and mental retardation should be sent to special institutions. In case of refusal to transfer a child with complex speech pathology, the speech therapist teacher is not responsible for the complete elimination of the defect. 7. The number of children studying simultaneously at the speech center should be 20-25 children throughout the year. 8. The total duration of speech therapy sessions is directly dependent on the individual characteristics of the children. As necessary, the speech therapist removes children from speech therapy classes and replaces them with others. 9. Speech correction work is carried out 5 times a week, individual or subgroup in nature. The speech therapist teacher works directly with children for all 4 hours of his working time. 10. The speech therapist teacher takes children to his classes from any of the teachers’ classes. 11. In a preschool institution, all the necessary conditions must be created for conducting speech therapy classes; there must be an isolated speech therapy room (for room equipment, see the “Program for teaching children with underdevelopment of the phonetic structure of speech”, compiled by G.A. Kashe and T.E. Filicheva ). 12. Documentation of a speech therapist teacher in a kindergarten that does not have specialized groups: - a log of the speech status of all children; - a list of children in need of speech therapy assistance, indicating the age and nature of the speech disorder; - individual notebooks for children’s activities; — class attendance log; - a speech card for each child taken to classes, indicating the date of entry and end of classes; — a plan of activities aimed at preventing speech disorders in children (consultations, seminars for educators, other preschool specialists, parents on working on the sound culture of speech). 13. An indicator of the work of a speech therapist in kindergarten is the state of sound pronunciation of children graduating to school. 14. A speech therapist teacher in a kindergarten is obliged to participate in all methodological events held in the district and improve his qualifications. 15. Certification of a speech therapist teacher for qualification category II must be carried out with the participation of a senior speech therapist in charge of the municipal territory. Since the speech therapist teacher works in a preschool educational institution, the beginning and end of the school year, the time allocated for examining children, the teaching load (20 astronomical hours per week, 4 hours per day) correspond to the established standards for speech therapist teachers in correctional (speech therapy) groups of preschool educational institutions. The speech therapist teacher works directly with children for all 4 hours of his working time. Distribution of working time The first three weeks are allocated for the complete formation of groups and subgroups of children who will study with a speech therapist in the current school year. A speech therapist works 5 days a week (the total number of hours of work per week is 20). The speech therapist teacher works directly with children for all 4 hours of his working time. The work schedule can be drawn up depending on the employment of children both in the first and second half of the day. A speech therapist teacher has the right to take students (pupils) for correctional work from any classes conducted by teachers in a group. The workload of a speech therapist teacher at 1.0 rate provides for simultaneous speech correction work for 12 to 16 children, 20 to 25 children during the year. Children with simple and complex dyslalia are accepted; in difficult cases, the speech therapist is obliged to recommend that parents attend a special speech group. In case of refusal to transfer a child with complex speech pathology, the speech therapist teacher is not responsible for eliminating the defect. Children are enrolled in groups on the basis of the following documents: - characteristics and directions of the speech therapist at the clinic; - opinions of doctors: otolaryngologist, psychoneurologist and dentist. Children diagnosed with FND are employed for up to 6 months, children diagnosed with FND - for 1 year. As speech deficiencies are corrected, the speech therapist removes children from the list and replaces them with others. Children with speech disorders of senior preschool age are selected for speech therapy classes. The child must receive individual correctional assistance at least 3 times a week. The duration of individual lessons depends on the speech diagnosis, the age of the child, the individual developmental characteristics of the child, and his psychophysical status. The time allotted for an individual lesson with a child increases if the speech therapist himself takes the child from the group and takes him to the group after the end of the lesson. The speech therapist teacher plans subgroup lessons if there are children of the same age with similar speech diagnoses (at least 6 children). The duration of a subgroup lesson should not exceed the time provided for by the physiological characteristics of the age (the program of training and education in kindergarten, the instructional and methodological letter “On the hygienic requirements for the maximum load on preschool children in organized forms of education”). The teacher-speech therapist plans speech therapy work in accordance with educational programs that meet the requirements of the state educational standard, and is responsible for their implementation not in full. Along with corrective measures, she carries out preventive work in preschool educational institutions to prevent speech disorders in children. A speech therapist teacher works with teachers of a preschool educational institution on the problem of speech development of preschool children (consultations, seminars, workshops and other forms and types of work), parents (legal representatives) attending his classes. An indicator of the work of a speech therapist is the state of the sound pronunciation of children graduating to school. Certification of a speech therapist teacher for qualification category II must be carried out with the participation of a senior speech therapist from the CMC. Equipment for a speech therapy room The speech therapy teacher’s work schedule should be posted on the door of the speech therapy room. The following equipment should be available in the speech therapy room. 1. Tables according to the number of children studying in one subgroup. 2. Sufficient cabinets or shelves for visual aids, educational material and teaching literature. 3. Wall mirror 50x100 cm for individual work on sound pronunciation; it should hang near a window with special lighting. 4. Mirrors 9x12 cm according to the number of children simultaneously engaged in pronunciation correction in a subgroup lesson. 5. A table near the wall mirror for individual work with the child and two chairs - for the child and for the speech therapist. 6. A set of speech therapy probes, ethyl alcohol for processing the probes. 7. Technical training aids. 8. Wall-mounted cash register letters. 9. Visual material used in examining children’s speech, placed in a separate box or envelopes. 10. Visual material on speech development, systematized and placed in special boxes. 11. Teaching aids in the form of cards, cards with individual tasks, an album for working on sound pronunciation. 12. Various speech games. 13. Methodological literature. 14. Towel, soap and paper napkins. The speech therapy room should be aesthetically designed and decorated with indoor plants. It is not recommended to hang paintings, prints, drawings and tables on the walls that are not related to the correctional process, as they distract the attention of children during classes and create an unnecessary diversity of the environment. Documentation and its maintenance To take into account the correctional process carried out by the speech therapist, the following types of documentation are offered: 1. A log of children's attendance at speech therapy classes. 2. Journal of examination of the speech of children attending a preschool educational institution (from 3 to 7 years). 3. Register of children in need of correctional (speech therapy) assistance. 4. Speech card for each child with a long-term work plan to correct identified speech disorders, progress results every six months, indicating the start and end dates of classes. 5. Plan of activities aimed at preventing speech disorders in children (consultations, seminars for educators, other preschool specialists, parents or their substitutes on working on the sound culture of speech). 6. Calendar plan for subgroup and individual lessons with children. 7. Notebooks-diaries for individual lessons on correcting children’s speech. 8. Class schedule certified by the head of the preschool educational institution. 9. The work schedule of the speech therapist, approved by the head of the preschool educational institution, agreed with the administration of the institution. 10. Card index listing the equipment, educational and visual aids located in the speech therapy room. 11. Copies of reports on the effectiveness of correctional (speech therapy) work for the academic year (at least for the last three years). 12. Follow-up data on children who completed a course of correctional classes through interaction with primary school teachers and kindergarten teachers over the past three years. Job description of a speech therapist teacher 1. General provisions 1. A speech therapist teacher is appointed and dismissed by the head of the educational institution. 2. A speech therapist teacher must have a higher education in defectology and improve his qualifications. 3. A speech therapist teacher in his work: - is guided by: • the Constitution of the Russian Federation; • laws of the Russian Federation; • decisions of the government of the Russian Federation and educational authorities on educational issues; • Convention on the Rights of the Child; • Charter of a preschool educational institution; • instructions for protecting the life and health of preschool children; • this job description; — must know: • developmental and special pedagogy and psychology; • anatomical, physiological and clinical foundations of defectology; • methods and techniques for preventing and correcting disorders in the speech development of students; • normative and methodological documents on issues of professional and practical activity; • program methodological literature on working with students (pupils) who have disorders in speech development; • the latest achievements of defectological science; • labor rules and regulations; safety and fire protection. 2. Functions 1. Carry out work aimed at preventing and maximizing correction of specific speech disorders and other deviations in the development of mental processes (memory, thinking, attention, etc.). 2. Develops an action plan aimed at preventing speech disorders in children (pupils) (consultations, seminars for educators, other preschool specialists, parents (persons replacing them) on working on the sound culture of speech). 3. Job responsibilities 1. Examines and determines the structure and severity of speech disorders of various origins in students (pupils) aged 3 to 7 years. 2. Completes groups for classes taking into account speech impairments of students (pupils). 3. Conducts subgroup and individual classes to correct deviations in speech development and restore impaired functions. 4. Works closely with teachers and other specialists of the educational institution, and attends classes. 5. Consults teaching staff and parents (persons replacing them) on the use of special methods and techniques to assist children with speech development disorders. 6. Maintains the necessary documentation. 7. Promotes the formation of a general personal culture, socialization, conscious choice and mastery of professional programs. 8. Uses a variety of forms, methods, techniques and means of teaching and correction within the framework of state standards. 9. Provides a level of training for students (pupils) that meets the requirements of the state educational standard, and is responsible for their implementation in full. 10. Implements educational programs of a preschool educational institution. 11. Respects the rights and freedoms of students (pupils) contained in the Russian Law “On Education”, the Convention on the Rights of the Child. 12. Systematically improves his professional qualifications. 13. Participates in the activities of methodological associations and other forms of methodological work to exchange experience in his educational institution, district, district, city. 14. Works according to a schedule based on a 20-hour work week, approved by the head of the educational institution, agreed with the trade union organization. 15. Communicates with parents. 16. Ensures the protection of life and health of students (pupils) during the educational process. 17. Complies with labor protection, safety and fire protection rules and regulations. 18. Carries out dynamic observation of children who have completed a course of correctional classes through interaction with primary school teachers, speech therapists at schools, and preschool teachers. 4. Rights 1. A speech therapist teacher has all social rights provided for by Russian legislation. 2. A speech therapist teacher has the right to be present at any classes conducted with preschoolers. 3. Improve your skills. 4. Pass certification in accordance with the “Regulations on the procedure for certification of pedagogical and managerial employees of state and municipal educational institutions” dated June 26, 2000 No. 1908. 5. Has a vacation of 56 calendar days (48 working days). 5. Responsibility 1. The speech therapist teacher is responsible for organizing propaedeutic and correctional work in an educational institution. 2. For non-fulfillment or improper execution without good reason of the Charter and Internal Labor Regulations of an educational institution, for violation of official duties established by this Instruction, other local regulations, legal orders of educational authorities, orders and orders of the head of an educational institution, he shall be subject to disciplinary punishment up to dismissal from position. 3. For violation of instructions for protecting the life and health of children, sanitary and hygienic rules for organizing the educational process, a speech therapist teacher is brought to administrative responsibility in the manner and in cases provided for by law.
Safety instructions for a speech therapist teacher Introductory part 1. A speech therapist teacher must know and follow instructions on protecting the life and health of children, safety precautions, and strictly observe labor and production discipline. 2. Study and improve safe work practices. 3. Achieve the fastest elimination of deficiencies in work that cause accidents. 4. Strictly follow the instructions on the rules for the safe use of electrical equipment, sanitary rules, fire safety rules and personal hygiene rules. Before starting work, you must: 1. Wash your hands thoroughly. 2. Prepare everything necessary for work. 3. Sterilize speech therapy probes: - by boiling in a sterilizer; - treatment with ethyl alcohol. During work it is necessary: 1. To comply with the doctor’s requirements related to the protection and promotion of children’s health. 2. Maintain speech therapy probes in accordance with sanitary and epidemiological requirements. 3. Use disposable wooden spatulas. 4. Inform the doctor about your observations of the children’s health. 5. Maintain the necessary documentation. 6. Make sure that children do not have sharp metal objects in their hands during classes. 7. Store medicines, disinfectants, matches in a closed cabinet, out of the reach of children. 8. It is prohibited to lengthen the duration of classes with children and shorten the breaks between them. 9. It is prohibited to leave children unattended. Author's note. The above provision regulates the work of a speech therapist teacher at a preschool speech center. It: — determines the hourly workload per week and the distribution of the speech therapist’s working time during the day; — the possibility of conducting speech therapy classes in the first and second half of the day is indicated; — the duration of individual and subgroup speech therapy sessions is indicated. The document also talks about the need for a speech therapist to work on the prevention of speech disorders and filling out documentation, but, unfortunately, the document does not provide time for performing these types of work.
How to choose a good children's speech therapist
Usually, mothers give each other the contact details of a good speech therapist, because by communicating on the playground, parents often make new acquaintances. You can look for a good specialist on the appropriate website for your region. There is detailed information about the qualifications of the speech therapist supported by customer reviews. As a last resort, if there is evidence, the child is given a referral to a specialized kindergarten. To do this, you must pass a special psychological-medical-pedagogical commission (PMPC).
The arrival of a baby in a family is not only a holiday; raising and nurturing a child requires enormous effort from parents. Try to spend as much time as possible with your baby, communicate with him, talk, patiently teach him the simplest things. Do not give a child under 3 years old a smartphone, try not to give in to the temptation to turn on the TV and go about your business, if necessary, do not delay a visit to a specialist and let your “whys” open up this huge colorful world.
Conditions for receiving services on the site
Registration for a consultation or opinion from the Central Psychological-Medical-Pedagogical Commission (CPMPC) to confirm the right of a child with disabilities, including disabled children, to special conditions of education and upbringing in educational organizations, special conditions during state final certification.
The service is available to parents (legal representatives) and employees of educational organizations.
To undergo examination and counseling, the child’s presence at the Center for Medical Education is mandatory (except for the service: counseling for employees of educational organizations). A child under 18 years of age comes to the commission accompanied by a parent (legal representative).
To pass the commission, you must issue a medical report on your health status and recommendations for organizing the educational process.
Before submitting an application for the provision of services, you must check the relevance of the information posted in your personal account about you and your child (including documents) and, if necessary, correct them.
To obtain a consultation, a medical report on your health status is not required.
Applications are accepted throughout the entire calendar year. If you have any questions about the procedure for passing the Moscow Center for Medical Examinations, you can contact us by phone.
Who can apply for the service
Parents (legal representatives) of students:
under the age of 18, if it is necessary to create special conditions for training and education in an educational organization;
- to determine special conditions when conducting state final certification (SFA);
- for examination of students who will be 8 years old by September 1 of the next academic year, if for medical reasons they are recommended to begin studying at the level of primary general education after 8 years of age;
- for consulting on issues of education, training and correction of developmental disorders, students with disabilities and (or) deviant (socially dangerous) behavior.
Employees of educational organizations:
- for consulting on issues of education, training and correction of developmental disorders, students with disabilities and (or) deviant (socially dangerous) behavior.
Cost of service and payment procedure
For free
List of required documents
Documents required for passing the Moscow Center for Medical Education and Training in order to prepare recommendations for the creation of special conditions for training and education in educational organizations:
- medical report (Appendix 3 to the order of the Moscow Department of Health dated April 1, 2013 No. 297) on the state of health and recommendations for organizing the educational process in state educational organizations of the city of Moscow for persons with disabilities - original;
A child under 18 years of age comes to the commission accompanied by a parent (legal representative). To organize special educational conditions, create special conditions for children 8 years old on September 1 of the next school year, the following are provided:
- medical report (Appendix 3 to the order of the Moscow Department of Health dated April 1, 2013 No. 297) on the state of health and recommendations for organizing the educational process in state educational organizations of the city of Moscow for persons with disabilities - original;
- for disabled children, persons with disabilities, a certificate from the Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise (MSE) and an individual rehabilitation or habilitation program (IPRA) - copies with presentation of the originals or duly certified copies;
- student’s birth certificate - a copy with presentation of the original or a duly certified copy;
- student’s passport (if available) - a copy with presentation of the original or a duly certified copy;
- passport of the parent (legal representative) of the student - a copy with presentation of the original or a duly certified copy;
- previous conclusion(s) of the commission on the results of a previously conducted examination of the child (if available) - a copy;
- conclusion(s) of the psychological, medical and pedagogical council of the educational organization or specialist (specialists) providing psychological, medical and pedagogical support to students in the educational organization (for students of educational organizations) (if available) - a copy;
- referral to the Moscow Center for Medical Education from an educational organization, an organization providing social services, a medical organization, or another organization (if any) - original;
- characteristics of a student issued by an educational organization (for students of educational organizations) - original, certified by the seal of the educational organization;
- tests/written works in Russian (native) language, mathematics - copies certified in the prescribed manner, results of the child’s independent productive activity - original.
A child under 18 years of age comes to the commission accompanied by a parent (legal representative). Documents required to pass the Moscow Center for Medical Examination before the state final certification (GIA-9, GIA-11):
- medical report (Appendix 3 to the order of the Moscow Department of Health dated April 1, 2013 No. 297) on the state of health and recommendations on the organization of the educational process in state educational organizations of the city of Moscow for persons with disabilities with recommendations on the creation of special conditions when passing the state final certification in the current academic year - original;
- for disabled children, persons with disabilities, a certificate from the Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise (MSE) and an individual rehabilitation or habilitation program (IPRA) - copies with presentation of the originals or duly certified copies;
- student’s birth certificate - a copy with presentation of the original or a duly certified copy;
- student’s passport (if available) - a copy with presentation of the original or a duly certified copy;
- passport of the parent (legal representative) of the student - a copy with presentation of the original or a duly certified copy;
- previous conclusion(s) of the commission on the conditions of study (if available) - a copy;
- characteristics of a student issued by an educational organization (for students of educational organizations) - original, certified by the seal of the educational organization.
To organize an exam at home, you must additionally provide the following documents:
- medical report (Appendix 3 to the order of the Moscow Department of Health dated April 1, 2013 No. 297) with recommendations on the creation of special conditions when passing the state final certification in the current academic year at home - if it is necessary to pass the State Examination at home - the original;
- medical reports (Appendix 3 to the order of the Moscow Department of Health dated April 1, 2013 No. 297) with recommendations on home education for the last 3 years (if available) - copies certified in the prescribed manner;
- orders for transfer to home study for the last 3 years (if available) - copies certified in the prescribed manner.
A child under 18 years of age comes to the commission accompanied by a parent (legal representative). To advise parents (legal representatives) of students, specialists from the Moscow Center for Medical Education and Training provide:
- a detailed extract from the history of the child’s development with the conclusions of doctors observing the child in a medical organization at the place of residence (registration) or a medical report (Appendix 3 to the order of the Moscow Department of Health dated April 1, 2013 No. 297) on the state of health and recommendations for organizing educational process in state educational organizations of the city of Moscow for persons with disabilities - original;
- student’s birth certificate - a copy with presentation of the original or a duly certified copy;
- student’s passport (if available) - a copy with presentation of the original or a duly certified copy;
- passport of the parent (legal representative) of the student - a copy with presentation of the original or a duly certified copy;
- previous conclusion(s) of the commission on the results of a previously conducted examination of the child (if available) - a copy;
- conclusion(s) of the psychological, medical and pedagogical council of the educational organization or specialist (specialists) providing psychological, medical and pedagogical support to students in the educational organization (for students of educational organizations) (if available) - a copy;
- referral to the Moscow Center for Medical Education from an educational organization, an organization providing social services, a medical organization, or another organization (if any) - original;
- characteristics of a student issued by an educational organization (for students of educational organizations) - original, certified by the seal of the educational organization;
- written work in the Russian (native) language, mathematics, results of the child’s independent productive activity.
A child under 18 years of age comes to the commission accompanied by a parent (legal representative). To provide consultations to employees of educational organizations by specialists from the Moscow Center for Medical Education and Training, no documents are required.
Duration and result of service provision
Receiving information about the readiness of the conclusion of the Moscow Center for Medical Inspectorate or the provision of consulting services. The result is sent in the form of an electronic notification to the Personal Account on the Official Portal of the Mayor and the Government of Moscow and by email no later than 5 working days from the date of the reception.