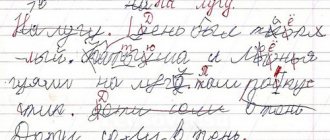Dysgraphia is a pathology associated with writing, which is characterized by the same type of regularly repeated errors with developed intelligence and hearing. This disease is often accompanied by dyslexia (deviations in the reading process).
The causes of the disease can be both biological - difficult pregnancy and childbirth, hereditary diseases, injuries, and psychological and social. For example, if the child has received little attention, there is pedagogical neglect, the child learned to write too early, and so on.
Dysgraphia - what are its causes?
Dysgraphia can develop as a result of damage to the part of the brain responsible for mastering writing skills, as well as visual perception, which leads to impairment of memory and visual analysis abilities.
Dysgraphia can be caused by some abnormality in hand function, muscle tone (too much muscle tension), especially in the fingers and wrist, as well as established poor writing habits.
Dysgraphia can be associated with the child’s psychomotor disorders, hyperactivity and neurosis. There is also the so-called vague dysgraphia, which can be caused by neglect of the child’s education or mental development disorders. Then it becomes noticeable that mental development is not going as it should.
Dysgraphia in primary schoolchildren very often accompanies diseases such as ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder), Tourette syndrome and autism.
Very often, parents of children suffering from dysgraphia themselves face this problem. If signs of the disease are noticed at an older age, this is most likely due to neuralgia.
Dysgraphia in younger schoolchildren photo
Mechanism of occurrence, causes
Writing is a process that requires the coordinated work of the visual, auditory, speech and motor systems. By the time the child masters the basics of writing, he should have mastered oral speech well. If the lateralization of brain functions is not carried out as needed, then a disorder such as dysgraphia develops. Usually these processes are normalized by the time the child begins school.
If the delay in lateralization causes disturbances in a part of the brain, the child develops dysgraphia, which requires correction. Otherwise, the deviation may affect the child’s thinking, memory, and perception.
Causes of occurrence in children
Dysgraphia can be caused by birth trauma. The development of such deviations is provoked by various infectious diseases and improper upbringing. Also, experts do not exclude such a factor as genetic predisposition.
Dysgraphia in children may be accompanied by other concomitant diseases that were previously diagnosed.
Causes of occurrence in adults
In adults, imperfections in written speech can be caused by both internal and external factors. Main reasons for deviation:
- presence of a tumor in the brain;
- low saturation;
- stroke;
- previous brain surgery;
- poor social conditions.
Social factors include insufficient upbringing in childhood, incorrect speech of people around, and lack of communication with others.
With dysgraphia, errors in the process of writing are persistent, despite the fact that the person knows well all the rules of writing words.
Dysgraphia - characteristic symptoms
Often, due to the large number of students in a class, not every teacher can determine that one of the children has dysgraphia. Teachers assume that illegible and unattractive handwriting is the result of a student's lack of concentration and effort. Dysgraphia is primarily defined by an illegible writing style with the following characteristics:
- inaccurate or incorrect spelling of letters,
- too much tilt from the vertical,
- letters of varying size within the same word,
- confusing letters,
- hesitant, shaky writing;
- diacritics and punctuation marks are lost,
- writing between the lines.
If it is noticeable that in addition to unsightly and illegible handwriting, a child has symptoms such as improper squeezing of the pen, fatigue when writing quickly and an aversion to drawing, one can fairly safely suspect dysgraphia.
In children, symptoms of dysgraphia in grades 1, 3 and 4 manifest themselves in the form of illegible handwriting, missing words, incomplete sentences, some letters bent to the right, others to the left. There are also problems with spelling words. A child very often focuses on the fact of writing a word, but does not understand what he is writing.
Teens and adults have difficulty expressing and communicating thoughts on paper, as well as with grammar and syntax. Writing is much more difficult for them than speaking. There is also a big discrepancy between what a person writes and what he actually knows.
What mistakes does a child with optical dysgraphia make?
Children with optical writing disorders most often have difficulty transferring letters onto paper in the correct form. They distort the appearance of letter characters or write them in mirror images. Schoolchildren cannot write letters correctly, so they unintentionally add extra loops or details to them, or lose the necessary components of the characters.
Experts say that most often optical-type dysgraphics make the following specific errors:
- Substitution of letters consisting of identical elements in different quantities (hooks, circles, etc.). Most often in writing these are the letters sh-i, r-y, m-l, t-p. for example: neck - eeya, rag - pyapka, coin - loneta.
- Replacing letters with similar spellings that have different locations of individual symbol elements. In written form, these are letters such as b-u, v-d, sh-t. for example: booth - fishing rod, cleaning - buorka, schoolboy - tkolnik, fork - dilka.
- Loss and failure to complete the components of letters. Most often, hooks are lost in the capital characters y and d, ticks in the letters b, a, etc. for example: Anton - Λton.
- Writing letters in their mirror image. The characters are written correctly, but in the wrong direction. Very often this type of mistake is made by left-handed people. For example: Ekaterina - Zkaterina.
It is extremely important to remember that the student does not make such mistakes intentionally, and the reason here does not lie in his laziness, reluctance or irresponsibility. Most often, the child takes learning extremely seriously, however, neither his efforts nor the extra time devoted to writing bring the desired result.
What types of dysgraphia are there?
Generally, there are three types of dysgraphia, which each have their own symptoms.
- Spatial dysgraphia. A child with this type of dysgraphia does not have spelling errors in written text. Difficulties arise when copying or rewriting other texts. In addition, difficulties with drawing are noticeable.
- Dysgraphia dyslexia . It is characterized by the fact that the text of a person who suffers from this disease is full of spelling errors. Usually the sounds at the end of a word become dull; the child “writes as he hears.” There are no problems with rewriting and copying other texts. Drawing is also easy.
- Motor dysgraphia. A child suffering from a movement disorder mainly has problems with writing texts. The lack of coordination of movements is clearly expressed, and the copied text contains many errors.
Diagnosis of dysgraphia
The diagnosis of dysgraphia is made by a speech therapist after communicating with the child and a series of written tests. The student is asked to write a dictation, rewrite text printed and handwritten, read, and make a written description of the picture. In addition to the speech therapist, it is necessary to show the child to other specialists: an ENT specialist, an ophthalmologist, a neurologist.
Based on the conclusions of doctors and written tests, a conclusion is made and the type and severity of dysgraphia is determined.
Treatment: examples of written exercises
There are three ways to treat dysgraphia.
- You can change the form of the letter. If a child struggles with movement disorders, they can write on the computer and transfer their knowledge orally.
- One form of treatment for dysgraphia may also be to change the demands placed on the person affected by this problem.
- The last solution for dysgraphia can be special exercises for the hands, eyes and focus, and to perform them you will need not only a pen and a sheet of paper, but also crayons, paints, markers, and colored paper. In this way, exercise turns into a game.
Treatment of dysgraphia should be carried out using a special set of tasks developed by a psychologist or teacher. These tasks should be selected individually, taking into account the child’s predispositions and capabilities. Some of them:
- drawing “lazy eights” - you need to move your hands in the air, freely drawing big eights,
- correcting and thickening the contours of the image with felt-tip pens, following the line of the drawing,
- tracing the template this could be a template cut out of cardboard with simple shapes at the beginning. You can also ask your child to trace his or her arm or leg on paper.
- drawing with large free movements on paper or other media using a brush, marker, or chalk.
- covering with color one selected part of a sheet of a certain shape, you can ask the child to paint, for example, a square in the corner of the page,
- precise drawing of lines, preferably in checkered notebooks, where the child will find more guidelines when drawing,
- copying a picture, this option can be easier by drawing a grid on the picture and on a blank sheet of paper (it will help you find guidelines for redrawing),
- connecting points with solid lines,
- rewriting letters in lines,
- linking images with corresponding titles. You can draw various objects on a piece of paper and write their names under them, then the child must connect them and then color the pictures.
Dysgraphia is one of the conditions that can be associated with bad memories of school times. It is important to quickly diagnose the problem and begin treatment as soon as possible. If symptoms of dysgraphia are observed in a child, it is necessary to begin occupational therapy with a teacher or psychologist.
dysgraphia with speech therapist
Dysgraphia
- Specially selected speech material is also used to practice problem areas in writing and exercises for correction:
1. Clap or tap out the word syllable by syllable and name their number.
2. Be able to identify vowel sounds in a word, learn the basic rule of syllabic division: there are as many syllables in a word as there are vowel sounds.
3. Be able to isolate a vowel sound from a syllable and word. Determine the vowel sound and its place in the word (beginning, middle, end of the word).
4. Name the vowels in the word.
5. Write down only the vowels of the given word.
6. Select vowel sounds and find the corresponding letters.
7. Repeat the word syllable by syllable. Count the number of syllables.
8. Determine the number of syllables in the named words. Raise the corresponding number.
9. Write down the words in two columns (split the pictures into 2 groups) depending on the number of syllables.
10. Select the first syllable from the names of the pictures and write it down.
11. Combine syllables in a word, sentence, read the resulting word or sentence (for example: “beehive”, “house”, “car”, “moon”, “toad”). After highlighting the first syllables, the sentence is obtained: There is a puddle near the house.
12. Identify the missing syllable in a word using a picture:
__buzz, ut__, lod__, ka__, ka__dash.
13. Compose a word from syllables given in disorder (nok, tsyn, las, toch, forest, ka).
14. Find words in a sentence with a certain number of syllables.
Game “Guess who I'm calling?”
Goal: developing the ability to select words with a given number of syllables.
The teacher invites those children whose names consist of as many syllables to stand up as he claps.
For example: the teacher claps 3 times, the students count, then stand up (Se-ryo-zha, A-ri-na).
Game “Changes”.
Goals: development of the ability to compose words; accumulation of syllable images in memory.
Equipment: cards with syllables (4–6) for each player.
The teacher names two syllables, the children find cards with these syllables and first compose one word, then, rearranging the syllables, another: sos, na; tea. CA; spring; kA, mouse; jar; la, ska”ni, tka; ra. But; Which.
Game “Chain”.
Goal: developing the ability to select words based on one given syllable.
One of the students writes a word on the board syllable by syllable, the next one selects a word that begins with the next syllable of the given word (ok-no, no-ra, ra-ma).
Game “If I meet a word on the road, I’ll break it into syllables.”
Goal: development of syllable skills, attention, speed of thinking.
The teacher throws a ball to the children and names one-, two- and three-syllable words. The child who catches the ball determines the number of syllables, names them and passes the ball back. You can invite children to pronounce the word syllable by syllable while simultaneously hitting the word with a ball.
Game "Name of a fairy-tale character"
Goal: improving the skills of syllabic analysis and synthesis.
Objectives: develop phonemic hearing; Exercise students in the ability to divide words into syllables.
Equipment: cards with a set of words.
Fairy tale character name
Dysgraphia and left-handedness
Very often, dysgraphia is diagnosed in left-handed people or people who use both hands. This is due to lateralization, i.e. the predominance of the right or left hand, including the dominant hand, this process occurs in the nervous system. It is worth remembering that left-handedness or two-handedness are not synonymous with dysgraphia.
Often left-handed people are known for their slender and beautiful handwriting. One of the interesting facts about dysgraphia is that left-handed children who are forced to write with their right hand can master it very quickly.
Methods for correcting dysgraphia
The method of correction depends on the severity of the child’s written language impairment. In addition, the method of treating the deviation is influenced by the degree of neglect, as well as the characteristics of the patient. Correction is a long and complex process that requires persistence on the part of teachers and parents, patience, endurance and a positive attitude of the patient. If you follow all the necessary recommendations, dysgraphia can be completely cured. It is better if the disorder is diagnosed at an earlier age, since the course of correction for older schoolchildren is longer due to the presence in most cases of additional speech and writing disorders. In this case, the time required for rehabilitation will take more. There is also a high risk that the violation cannot be eliminated completely.
It is impossible to get rid of dysgraphia on your own. This process requires the participation of many highly specialized specialists, for example, a psychologist, a neuropsychologist. However, the main work falls on the speech therapist, who will have to select a rehabilitation program appropriate to the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient. The specialist individually selects the necessary sound pronunciation exercises. Classes are aimed at improving motor skills, developing the patient’s lexical and grammatical structure, as well as improving phonemic speech recognition.
Methods for correcting dysgraphia, which are among the most effective:
- Exercises through which the patient learns to correctly understand sounds, words, and letters.
- Tasks aimed at training memory, improving thinking, and developing perception.
- Exercises necessary for the patient to learn to correctly recognize letters that are similar in appearance.
- Proper production of sounds, work on speech automation.
- Educational games to improve sound analysis.
In some cases, specialists include drug treatment, physiotherapy, massage, and exercise therapy in the rehabilitation course. This often applies to patients whose dysgraphia was caused by organic causes. It is important to know that drug treatment should be prescribed exclusively by a qualified specialist.
Speech therapy correction
Auditory differentiation of sounds is what needs to be achieved initially when treating dysgraphia. If a child cannot distinguish sounds, then further exercises will not be effective. The rehabilitation period is determined individually and depends on many factors. Classes with a speech therapist are possible both in a group with other children and individually. It depends on the wishes of the child and his parents.
During classes, the speech therapist gives the child verbal and visual exercises, as well as practical lessons, during which correctional work takes place.
Exercises you can do at home
Since it is impossible to get rid of dysgraphia on your own, experts, in addition to basic classes, recommend doing additional exercises at home to consolidate the results obtained with a speech therapist.
Exercises that can be done at home should also be agreed upon with a speech therapist. It is important that parents supervise the technique and regularity of classes. The simplest but most effective exercises that you can do at home with your parents include:
- Labyrinth. The child draws a line on a piece of paper, moving only his hand. You cannot make breaks or change the position of the sheet.
- Search for objects or pictures. The child searches for and paints the objects found.
- Exercises aimed at developing attention. The child must read the text and look for missing letters or words, writing them in the right places.
- Improved articulation. The child learns songs, rhymes, and tongue twisters.
- Logorhythmics.
To get a positive result as quickly as possible, home exercises should be performed regularly. This will significantly shorten the rehabilitation period.
Dysgraphia and ugly writing
It happens that a child has ugly handwriting, but the features attributed to dysgraphia do not appear. We are talking in particular about slanted, overlapping or large letters, as well as the difficulties of combining them.
Children or adults who do not have signs of dysgraphia and have unsightly handwriting can improve their skills. Calligraphy master classes have become very popular lately. If you have decided not to send your child to such classes, then you should study with him at home. Exercise will definitely bring beneficial effects.
To improve a parent's or child's writing skills, it is important to use professional and trusted sources.
Is it possible to eliminate dysgraphia in a child?
Dysgraphia is a defect that can be corrected. Children with this pathology successfully develop, grow up and achieve success. This can be confirmed by famous people who were diagnosed with dysgraphia in childhood, including Albert Einstein, Walt Disney, Marilyn Monroe, Vladimir Mayakovsky and many others.
The key task of the parents of such a child is to attract a competent speech therapist-defectologist to solve this problem. A correction course is developed after determining the type of dysgraphia and the severity of the pathology. The speech therapist creates exercises that allow you to compensate for defects in the pronunciation of sounds, correct speech, form the recognition of sounds and letters, develop motor skills and other mental functions of the child.