A child begins to pronounce whistling sounds correctly at about 3-4 years of age. But some children have problems with articulation. If measures are not taken promptly, speech dysfunction will persist for life. To create whistling sounds, a set of special exercises is usually prescribed. They are performed both in classes with a speech therapist and at home.
The importance of making a whistling sound
Speech defects that develop in childhood can lead to communication difficulties in adulthood. Therefore, the production of whistling sounds must be carried out in a timely manner. The earlier a deviation is detected, the greater the chances of its successful elimination. Typically, defects become noticeable when the child enters the middle group of kindergarten. Speech therapists distinguish two types of disorders:
- parasigmatism;
- sigmatism.
With sigmatism, the child’s pronunciation of the sound “s” in soft and hard forms is distorted. With parasigmatism, its replacement occurs. Deviations in spoken language can have a negative impact on the functioning of the nervous system. This subsequently leads to low self-esteem and communication disorders. Against the background of incorrect pronunciation, the following develops:
- Dyslalia is a disease characterized by difficulty pronouncing certain sounds.
- Dysgraphia is a deviation accompanied by the replacement and rearrangement of letters during writing.
- Dyslexia is a reading problem caused by the inability to combine letters into a single text.
Preparatory activities
Before performing exercises aimed at developing conversational speech, breathing training is carried out.
She teaches how to blow a stream of air from the lungs. To make the training more interesting for the child, it is recommended to use a small cotton wool or ball. The most common exercises that develop breathing include the following tasks:
- It is necessary to prepare an empty small bottle. Its neck should be brought to the lower lip. A stream of air is directed into the bubble. If the baby does everything correctly, a characteristic sound appears. This exercise is called “storm”.
- The palms need to be placed on the stomach. Then a deep breath is taken through the nose, after which the breath is held for a couple of seconds. Exit is through the mouth. The purpose of the exercise is to teach the child to control the air stream. The task is called "accordion".
- The “breeze” exercise is performed by stretching out the lips with a tube. A deep breath is taken through the nose. Then a palm is placed to the lips, and a stream of air is released through the mouth.
How to set sound mechanically
Speech development can also be carried out mechanically. In this situation, it is recommended to actively use special simple exercises:
- “Depict” a wide smile on your face, with your tongue in an interdental position. An important condition is not to touch the upper row of teeth. After some time, the mouth muscles relax, then the exercise is repeated again.
- The next step is to blow on the tip of the tongue, which should be protruding from the oral cavity. To feel the air stream, you should place your palm to your lips.
- While the child is blowing air, you need to press on the tongue with a toothpick. This will help form a groove through which the air stream is directed.
- At the next stage, the jaws close, but the toothpick remains between them. It helps fix the tongue in the desired position. The passage of an air stream will cause a whistle.
- While playing the whistling sound, you need to press a toothpick on different parts of the tongue, identifying in which position the “s” will sound correctly.
- After the child manages to pronounce the desired sound, the exercise is performed without using a toothpick.
Mechanical assistance
If the tongue is not held behind the teeth, but jumps out, then mechanical support is needed. You can hold the child’s tongue in the slide pose using:
- finger (pre-washed)
- massage or special staging probe
- toothpicks (break off the sharp edge)
- matches (not sulfur head)
- cotton swab
while practicing gymnastics at the same time:
- tube with tongue
- pancake
- brushing the lower teeth
- comb your tongue
- roll the reel
- fence - tube with lips
breathing exercises:
- blow the cotton wool off your tongue between your lips
- between teeth
- downhill
- match from the hill
voice
- pull out the sounds I, A, E in the slide position
tongue and lip massage
Then all these skills worked out separately are combined, holding the child’s tongue and blowing away the cotton wool. He holds the slide, pulls out “iiiiii”, then adds “ssssss” - sometimes whistling ones are better placed in reverse syllables - AS, IS, ES, YS, you can use US and OS, but at the same time you need to clearly make a “pipe-fence” with your lips. If first “ssss” and then “iii”, then it will be Sb, which is also not scary, then it’s not difficult to make a hard sound from it, pressing the back of the tongue with a probe.
Staging from other sounds
The correct pronunciation of “s” can be formed from other sounds. In this case we will talk about the sounds “ts” and “sh”. Initially, the child should reproduce “sh” in a drawn-out manner. Then the tongue gradually moves towards the teeth, without leaving the palate. "Sh" will gradually transform into a fuzzy whistling sound. To get a “s” out of it, you need to clench your teeth. After this, the child must repeat the attempt to replace one sound with another.
The production of whistling consonant sounds from “ts” is less common. The essence of the method is the drawn-out pronunciation of the sound “ts”. The child will not have to change the position of the tongue. The sound is automatically transformed into “s”. After this, it is recommended to consolidate the result with the help of tongue twisters or poems.
Examples of whistling languages
As of 2021, there are approximately 70 whistling languages recorded in the world. The most famous and studied habitat of the whistling community is La Gomera, one of the non-tourist Canary Islands. Silbo Gomero was the first whistling language to receive UNESCO living heritage status; it also has the largest number of speakers - about 20 thousand.
The Silbo Gomero language now plays an important role in daily life on the island. It is taught in schools, and is used to attract the attention of tourists - in some restaurants, waiters convey order details by whistling.
Teenagers sometimes earn extra money and put on a whole show for visitors, managing to adapt the whistle for other languages. However, since the start of the coronavirus pandemic, such practices had to be abandoned - putting fingers in the mouth has become unsafe. Now schoolchildren do not practice whistling themselves, but listen to recordings.
The older generation notes that it is more difficult for them to understand young people who learn to whistle at school rather than in the pastures. For them, such a whistle is too elegant and precise, and the vocabulary is richer and more diverse. Elderly residents of La Gomera recall using silbo to alert locals that the police were coming. In the recent Romanian thriller The Whistlers by Corneliu Porumboiu, Silbo is used by gangsters as a secret code language.
On the Greek island of Euboea, in the village of Antia, Sfirian is spoken, the sound of which is reminiscent of bird sounds. Sfiria is one of the most endangered and rare languages in the world. Most native speakers are farmers and shepherds.
Now the population of the village is 37 people, but most of them have lost their teeth, so they cannot whistle. In 2021, only 6 people spoke Sfiri fluently. Local residents are trying their best to preserve their language - they organize classes, write to the local administration with a request to open a school and invite scientists to record the sound of the language. Scientists learned about the Sfirian language only in 1969, when a plane crashed in the mountains near Antia. Members of the search party heard the shepherds talking in a whistling language. The range of communication in Sfiri can reach 4 kilometers.
In Mexico, Sochiapan Chinantec and Mazatec are used for whistling. The theoretical range of whistling can reach two kilometers, but residents prefer to communicate over short distances and for them it is more a way of socialization rather than a forced tool.
Residents of Mexican communities use whistling to speak in the market, a situation unique to whistling languages. Another surprising fact is that in Mexico only men communicate by whistling, although women usually understand what is being said.
In northern Turkey, in the village of Kuskoy, they speak the “language of birds.” It has been used in this area for many centuries and has approximately 10,000 speakers. In 2021, along with silbo gomero, it was included in the UNESCO list of oral and intangible cultural heritage in need of protection. Every year the village holds a festival dedicated to the traditions, history and culture of bird language. Recently, it began to be studied in primary schools and the Turkish University of Giresun at the Faculty of Tourism.
The Hmong people, who live in the foothills of the Himalayas in Vietnam, have their own version of a whistling language that is used by hunters and farmers. However, it has another popular use - courtship language. Although rarely practiced today, young people used the Hmong whistling language as a flirting language. The boys wandered around the villages whistling poems to attract the attention of girls. If the girls reciprocated, this could be the beginning of a relationship.
***
Rapid developments in technology have significantly reduced the need for whistling, but network coverage still suffers in high mountain areas. Elderly residents of whistling communities try to pass on their knowledge to young people, participate in festivals dedicated to language traditions and often ignore mobile phones, preferring to communicate using a proven method. Teenagers resort to whistling much less frequently, but still periodically practice and become interested in the ancient skill. For them, this is a way to get closer to history and understand the origins of local traditions. From time to time, another important feature of whistling comes in handy - it can quickly convey information that is not intended for other people's ears. One way or another, whistling tongues remain a unique phenomenon, many of whose mysteries have yet to be revealed.
What methods exist for sigmatism
The production of the sounds “s”, “z” and “ts” with sigmatism is carried out in several ways. They are selected based on the nature of the deviation. Sigmatism is a distortion of the pronunciation of the sound “s”. The nature of the origin of the pathology is determined in the speech therapist's office. Possible causes of sigmatism include:
- neuritis;
- perceptual deviations;
- improper development of the maxillofacial apparatus;
- recently lost baby teeth;
- disturbances in figurative thinking.
Most often, sound pronunciation is corrected with the help of exercises, but in some cases a mechanical method may be required. The set of articulation exercises will vary in each individual case.
Interdental sigmatism
The deviation is characterized by the incorrect placement of the tongue between the teeth. It rests against the edges of the upper or lower incisors, which creates an obstacle to the passage of the air stream. “C” in this case changes to “t”. The main reason for this violation is considered to be the incorrect structure of the conversation between parents and the child. The likelihood of interdental sound is reduced with the necessary interaction between the baby and adults.
To correctly pronounce whistling sounds, they resort to imitation. In this case, the child tries to repeat after the adult. If this method does not produce results, installation is carried out mechanically.
Lateral sigmatism
Speech impairment with lateral sigmatism is accompanied by insufficient activity of the muscle tissue on the sides of the tongue. When trying to pronounce sounds, the tip of the organ rests on the area of the alveoli. Speech becomes completely unclear. A set of special exercises helps to improve sound pronunciation. Among the most effective are:
- alternate inflation and retraction of the cheeks;
- maximum opening and closing of the jaw, provided that the tongue is located at the bottom of the mouth;
- prolonged imitation of chewing with the mouth closed;
- rotation of the tongue in the predental area with the oral cavity slightly open;
- suction of an air stream through a tube made from the tongue.
Nasal sigmatism
Nasal sigmatism develops as a result of incomplete closure of the posterior wall of the pharynx with the soft upper palate. This happens when there is damage to the nervous system or when there are clefts in the palate. An exercise that involves blowing out the sound “f” helps to cope with this form of deviation. The child should place the wide part of the tongue between the lower lip and the upper incisors. From this position the sound “f” is pronounced. In the meantime, the tongue should be gradually retracted behind the teeth.
Dental parasigmatism
One of the causes of parasigmatism is malocclusion of the teeth. In this case, speech therapy exercises are used to produce speech. The emphasis is on the baby's tactile sensations and the correct location of the articulation organs. Initially, a soft “s” is set. Breathing work is being done. For these purposes, the child puts his hand to his mouth and directs the air flow onto it, after taking a deep breath. If he manages to pronounce “s”, there is no need to complete the lessons. It is necessary to consolidate the result by periodically repeating the exercises.
Causes
Sigmatism occurs in children for various reasons. It is impossible to say exactly what was the impetus for dysfunction of the passive or active organ of the articulatory apparatus. But it is possible to identify which organ’s work disrupts phonemic harmony and correctness of speech.
The main causes of whistling and hissing sigmatism are:
- Lack of formation of articulatory praxis
- Perceptual impairments
- Disorders of the innervation of the organs of articulation
- Sensorimotor disorders
- Anomalies in the development of speech organs, jaw and dental apparatus
- Other functional disorders
- Adenoids
- Malocclusion
- Lost baby teeth
The occurrence of sigmatism can be provoked by anatomical abnormalities:
- Violations of acts of biting, swallowing, chewing
- Neuritis
- Paresis of the mouth muscles
- Bulbar palsy
In this case, the aberration is of an organic nature. The place of innervation will be the cheeks, lips, jaws, tongue, facial muscles, pharynx, larynx, motor fibers. We are talking about pathologies of the cranial nerves. They are responsible for the activity of organs and their proper functioning. To determine which of them has dysfunction, you need to undergo audiography, nystamography, and electromyography. Based on the results of the study, build further work on the correction of speech disorders.
It is necessary to resort to brain examinations only in extremely difficult situations. As a rule, a speech therapist or defectologist is able to visually identify paralysis, underdevelopment of praxis and eliminate disturbances in the functioning of the articulatory apparatus without a complex medical examination.
A set of articulation exercises
Differentiation of whistling patients is based on the performance of exercises that the speech therapist selects individually. Among the most effective are the following:
- It is necessary to open your mouth wide in a smile without closing your teeth. After a few seconds, you can relax your lip muscles. The exercise is repeated 5-6 times.
- The starting position is the same as in the previous exercise. You need to run the tip of your tongue along the gums, simulating brushing. First, attention is paid to the upper teeth, then to the lower teeth.
- The mouth stretches into a smile, after which the tip of the tongue should touch the corners of the lips one by one. The chin should be motionless at this moment.
- The tongue protrudes as much as possible. First, it must be pulled to the tip of the nose, and then to the chin. After this, you should alternately touch the wide side of your tongue to your lips.
- With your teeth completely closed, you should stretch your lips into a tube as much as possible. The exercise is repeated 5 times.
Learning to “whistle” and “ring” correctly
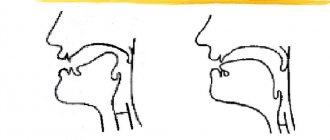
When working on any defective sound, articulatory gymnastics always helps us. Half of the success depends on its daily implementation. The whistling sounds [s] and [z] are identical in articulation, so the same set of exercises is suitable for them, the main thing is to understand what kind of articulatory structure we need. For the sound [s] it is like this: the lips are stretched in a smile, the teeth are exactly above each other in a “fence”, there is a small gap between the teeth, the tip of the tongue rests on the lower teeth, the back of the tongue tenses a little and rises to the palate, its edges touch the upper teeth , a shallow groove is formed in the center of the tongue, through which a stream of air passes freely and is exhaled between the gap in the teeth. Try it!
So, we need to develop a “groove” in the tongue, a slight upper deflection of the tongue supported by the lower teeth (“slide”), evenness of the position of the upper and lower teeth – a “fence”, a symmetrical stretch of the lips into a smile. In cases where a child has an overly tense or relaxed tongue, probe logomassage of the tongue is necessary.
How to consolidate the results of classes
To achieve the desired result, you should work with a speech therapist on an ongoing basis. It is strongly recommended not to quit classes at the first improvement in pronunciation. Sound fixation is carried out through automation. This process involves the use of individual sounds when pronouncing syllables, phrases and sentences. During classes with a speech therapist, you are given tasks that help improve your speaking skills. The automation stage is considered the most difficult. Activities help develop speaking skills and introduce learned sounds into everyday speech. The main task of parents is to facilitate the process by prompting and helping the child.
The most effective way to consolidate results is to read aloud. At the initial stages, you can pronounce simple tongue twisters. In the future, you need to move on to more voluminous texts. It is important to maintain a conversation with your baby. This not only trains speech, but also develops hearing.
For dysarthria in children, physiotherapy, drug treatment and speech therapy massage are used in combination with exercises. Dysarthria develops in 3-6% of cases. It is accompanied by increased tone and excessive tension in the muscles of the articulatory organs. A specific feature of the disease is the difficulty of overcoming defects. Therefore, the process of speech restoration takes much more time.
Recognition and learning
It is necessary to understand that whistling languages are not separate units, but rather other forms of habitual languages. Only the form of communication changes—the vocal register of speech—while the semantic content remains the same. Thus, whistling speech is a phonetic adaptation of natural language that has appeared for communication over long distances, when it is not possible to see each other face to face or the natural features of the landscape do not allow this.
The principle of whistling speech is simple: while whistling, people simplify and transform familiar words into whistling melodies, syllable by syllable.
Whistlers even emphasize that they whistle exactly as they think in their language, and that the whistling messages they receive are instantly interpreted as ordinary speech. In most cases, experienced native speakers can whistle through any information and recognize non-standardly constructed sentences.
Another important feature that makes whistling stand out from a whisper or shout is its inaudibility for people from the outside. It cannot be called completely unique - after all, it can be difficult to understand opera singing even in your native language. But in the case of whistling, people often perceive it not as communication, but rather as a joke. Perhaps it is this aspect of secrecy that has allowed whistling languages to survive for so long. At the same time, this mystery has significantly limited possible research: whistling languages were discovered by chance, and the number of speakers is decreasing every year.
They learn whistling in the same way as any language. Children subconsciously become accustomed to whistling speech signals if they hear them often enough, but mastering them takes a little longer. A child who speaks at 3 or 4 years old understands whistling language at 5–6 years old, but only masters it well by 10–12 years old. Another important point is that the vocabulary of whistlers is as rich and multifaceted as in ordinary speech. Another thing is that whistlers usually use a limited set of words that corresponds to their daily activities.
Whistling languages, although found on many continents, persist only in remote or isolated communities.
They are not limited to a specific territory, language family or structure. Depending on the features of the landscape, patterns of communication are formed: for what needs is whistling used and what equipment is chosen by local residents.
In the forests of Portugal and Brazil, they usually whistle during hunting. As a rule, people are not very far from each other; lips and hands are used to whistle. In the case of the densely forested mountains of Mexico, local people coordinate farming: distances become longer, and lips and teeth are used for communication.
If we talk about steep cliffs with sparse vegetation in Greece, Turkey, Spain or Africa, then shepherding predominates there, the distances are very large, and they resort to using their fingers to whistle. Whistling speech becomes a kind of indicator of the preservation of traditions: the whistling technique requires the transfer of skills from generation to generation, the continuation of the traditional way of life and the presence of the same ecosystem as before. Lifestyles change very slowly due to the isolation of communities: mountains and dense forests slow down the penetration of civilization and limit access to people from outside.
Note to parents
The sounds “ts”, “s”, “sh” can be made at home. In this case, responsibility for the outcome of the training falls on the shoulders of the parents. The following principles must be kept in mind:
- The load on the speech apparatus increases gradually. Otherwise, the baby will not be able to learn new information.
- During the exercises, it is recommended to make associations with the world of animals and insects. The sounds “s” and “z” are compared to the squeaking of a mosquito.
- It is necessary to allow the child to independently find a comfortable position for the organs of articulation to reproduce insulating sounds.
- If your child does the exercises without enthusiasm, it is better to stop exercising. This indicates that he is tired.
- Classes must be regular. The optimal frequency is 2-3 times a week. The duration depends on the nature of the baby’s speech deviation.
- When performing mechanical production of sound pronunciation, objects that are not dangerous to the child should be used. It is desirable that this be a special speech therapy probe.