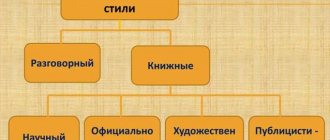
In the modern Russian literary language, there are 5 functional styles of speech: colloquial, journalistic, official business, artistic and scientific style of speech.
In this article we will analyze in detail the scientific style of speech. You will find answers to the following questions:
- what is scientific style of speech;
- its main function and tasks;
- scope of application;
- features and characteristics of the scientific style;
- substyles or varieties;
- genres of scientific style of speech;
- example of a scientific text.
What is the scientific style of speech, its functions and tasks
The scientific style of speech is a functional style of speech of the Russian literary language, which is a means of communication in the field of scientific, scientific-professional and educational-scientific activities.
The main function of the scientific style of speech is informative. It consists in conveying objective information about man, nature, and society.
The task of the scientific style is to explain natural and social phenomena, identify patterns and identify cause-and-effect relationships.
Scientific style texts are distinguished by clarity, logic, accuracy, objectivity and evidence-based presentation of information.
Historical excursion
In Ancient Greece, the privileged class used special terminology that ordinary people did not understand. It was to this time that experts attribute the appearance of the first signs of the scientific style. All terms were called only in Latin, but over time, scientists began to translate details into other languages.
Narrow-profile areas of activity began to expand. Initially, the scientific style of speech differed little from the artistic one, but over time, characteristic features began to appear and the style became clear and concise.
As an example, we can recall Descartes’ negative review of Galileo’s works. The French philosopher and mathematician believed that the Italian physicist tended to use a large number of artistic devices in the text. Kepler also held a similar opinion. For a long time, the standard of style was the work of Isaac Newton. Everyone tried to imitate him in their works.
In the Russian state, a style for scientific work began to take shape only at the beginning of the 18th century. Mikhail Lomonosov especially helped in its development, who developed certain characteristics of the style.
The formation process was finally completed in the 19th century and was associated with the activities of major scientists. Today, the style of scientific works has a number of features that make it easy to distinguish it from other styles of the Russian language:
- Logicality - all parts of the text have a strict sequence and end with a conclusion. Sentences are linked by repeating nouns and demonstrative pronouns. Adverbs, conjunctions, and introductory words also indicate consistent presentation.
- Precision - all words are used only in the literal sense. Terminology is widely used. Key phrases may be repeated many times.
- Objectivity - describes the results of experiments and the patterns that were identified.
- Generalization - when writing a text, the author uses abstract concepts that are almost impossible to imagine, feel, or understand.
If necessary, the text is illustrated with graphs, diagrams, diagrams. You can apply formulas, calculations, and make tables. The author’s task is to fully disclose the topic.
Scope of application of scientific style
The scope of application of the scientific style of speech is the field of science and educational and scientific activity.
First of all, it is used in written form of speech: textbooks, articles, dissertations, reports, encyclopedias, etc. But it is also found in oral form (for example, during scientific conferences).
To design presentations, printed materials, and publications, I recommend using Canva. This is a very simple and convenient all-in-one visual editor. With thousands of professional templates, images, and other quality elements, you'll get a great starting point to bring your best ideas to life.
Journalistic style
Journalistic style is a type of literary language that is used by the media (television, radio, newspapers, magazines, etc.) to communicate important information in the world of politics, national economy, culture, as well as influence readers and listeners in order to form them from a certain point of view.
This style is used in periodicals, socio-political literature, in speeches and speeches at rallies, election campaigns, congresses, etc. Let us indicate its characteristic stylistic features:
- emotionality
- relevance
- use of appeals
- brightness
In journalistic style texts, along with neutral ones, socio-political vocabulary, speech journalistic stereotypes, rhetorical questions, appeals, and incentive sentences are widely used.
Example
According to the results of the last vote in the parliamentary elections, the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) became a contender for the Bundestag, which narrowly beat Angela Merkel's CDU/CSU party. Olaf Scholz (from the SPD party) is considered the main candidate for the post of chancellor.
Main features and characteristics of the scientific style of speech
The features and characteristics of the scientific style include:
- Logical presentation - information is presented consistently and in a clear sequence.
- Generality, accuracy and objectivity in the presentation of information.
- Evidentiary and rich presentation (many arguments, facts).
- Application of terms and general scientific words. On average, terms occupy about 15-20% of the total text volume.
- The use of words with an abstract meaning (these are words that do not evoke specific images in the mind and memory, for example: property, essence, worldview, reality).
- Most often there is a monologue character of speech.
- More nouns and adjectives, and a minimum of verbs.
- Complex sentence construction.
- The sentences are mostly long.
- Practically no means of expression are used (epithets, comparisons, metaphors, etc.) and there is no expressive-emotional vocabulary (admirable, son, inspire, despise, sycophant).
- Correct word order.
- Strict sequence of presentation.
Types of speech
I will also briefly mention the types of speech that are widely used when writing articles for the Internet. Many of you remember them from school, but it’s always good to refresh any knowledge. So, there are three functional types of speech:
- Narration . The main feature is a clearly distinguishable plot and logic. There is a predominance of nouns and verbs. Narration is widely used in blog articles, storytelling, step-by-step instructions, and “about the company” texts.
- Reasoning . The author discusses a particular topic. Lots of value judgments, assumptions, rhetorical questions, conclusions. Examples are blog posts, sometimes selling texts.
- Description . The descriptions are dominated by adjectives and all kinds of characteristics. The most obvious example from web writing is product cards.
In one text there can be a mixture of not only styles, but also types of speech. Well, this is all natural: an experienced web writer must be able to use all linguistic means in order to solve the task assigned to him.
Scientific style of speech: its varieties or substyles
Like other styles of speech, the scientific style is rarely found in its “pure” form. Scientific texts may contain elements of both journalistic and official business style of speech.
Because of this interaction with other styles of speech, and depending on the purpose and specific application, the scientific style is divided into 6 substyles :
- Proper scientific or academic: dissertations, reports, communications, monographs, speeches;
- Educational and scientific: textbooks, lecture courses, course work, seminar report;
- Popular science: popular science books and magazines, children's encyclopedias;
- Scientific and informative: abstracts, reviews, summaries, theses;
- Scientific reference: encyclopedias, dictionaries, reference books;
- Scientific and technical: patents, standards, descriptions of inventions, specifications, technical conditions.
| Substyle name | Target | Genres |
| Actually scientific | Definition and description of new phenomena, facts, patterns. | dissertations, reports, communications, monographs, speeches, scientific articles. |
| Educational and scientific | Transferring scientific information to students, teaching, describing the facts necessary for mastering and mastering the material. | textbooks, lecture courses, course work, seminar report, notes, oral response. |
| Popular science | Familiarization with facts and phenomena. | popular science books and magazines, children's encyclopedias, articles. |
| Scientific and informative | Transmission of scientific information with a description of scientific facts. | abstracts, reviews, theses. |
| Scientific reference | Providing the reader with the ability to quickly find the necessary scientific information. | encyclopedias, dictionaries, reference books. |
| Scientific and technical | Application of scientific achievements in practice. | patents, standards, descriptions of inventions, specifications, technical conditions. |
Substyles (varieties) of scientific style of speech and examples of genres
Tips for beginners
Well, is the knowledge more or less sorted out? Don’t worry, the rest will come with practice, and a rare customer will be interested in your knowledge of aspects of linguistics. The main thing is efficiency, expressed in increasing the site’s rankings and increasing conversion. And for dessert - a couple of tips for beginners:
- Ask for a sample. Ideally, the customer fills out the brief and gives specific instructions in what style the text should be written. But this is not always the case, so sometimes you have to play a guessing game. Unfortunately, we are not endowed with the gift of telepathy, so getting it right the first time can be problematic. Therefore, immediately ask the customer to provide a link to a competitive resource with a similar topic, where, in his opinion, good texts are posted. All! And don’t get smart by throwing around terminology - do the same, but even better.
- Don't forget to clean your texts. Sometimes you just want to pour more water, which is inherent in lively conversational speech, or to drill in hated words like “given” or “is.” Try to get rid of this habit by mercilessly clearing your texts of verbal garbage. You shouldn’t squeeze the content dry, as many infostyle apologists preach, but even the works of classics of world literature need editing, not to mention articles by modest writers.
- Develop your own style. Yes, yes, this is exactly the author’s style that I spoke about just above, which distinguishes texts created by a true professional. They are interesting, bright, lively, and not at the expense of information content and the implementation of the main goals. There’s no point in flaunting your virtuoso command of words, because the reader should also receive information that can easily be lost behind all sorts of “beauties.” In the end, he will go to the library for high literature. However, any author should be able to vividly talk about quite complex things, because this is part of professional skill.
While writing this article, I adhered to a predominantly conversational style with scientific and journalistic elements. If you noticed this, then my efforts were not in vain!
Genres of scientific style of speech
Genres of scientific style are types of scientific texts that differ in their structure and functions.
There are several classifications of genres of scientific style. For example: primary and secondary scientific works or genres with free (articles, reviews) and with a fixed writing structure (dissertation).
In this article we will consider the classification of genres depending on the specific communicative and information functions that they perform.
Scientific style of speech: genres of the scientific substyle
The main function of this substyle is to identify and describe original research results, to present new facts, phenomena and patterns.
Genres of the scientific sub-style include:
- A monograph is a scientific study devoted to one specific phenomenon, fact, issue or topic. The volume of the classic text of the monograph is more than 120 pages in A4 format. This is a full-fledged scientific work.
- A scientific article is a short essay in which the author describes the results of his own research.
- A dissertation is a qualifying work, the successful completion of which is necessary for the award of an academic degree. Volume: from 50 to 500 pages. Available in the form of a book or bound manuscript.
Genres of this substyle also include reports, messages, and speeches.
Texts of the proper scientific substyle have a general writing structure, which includes:
- Name.
- Introduction.
- Main part.
- Conclusion.
Genres of educational and scientific substyle
Educational and scientific speech is used in the learning process, namely for the transmission and development of scientific information by students.
There are oral and written genres of educational and scientific substyle. Oral ones include: message and response .
The main written genres of this substyle are:
- A report is a detailed message on a specific issue, based on documentary data. The purpose of the report is to inform and provide recommendations or suggestions.
- A textbook is a teaching tool designed to assimilate, deepen and expand knowledge.
- Note - a summary or brief recording of a lesson, lecture, article.
- A course of lectures is a collection of lecture texts by one or more authors on individual topics or on the course as a whole. Covers the content of the academic discipline.
Popular science genres
This substyle is intended to disseminate scientific information among the mass recipient (for example, among a certain category of readers - children, teenagers, etc.).
Popular science genres include:
- Popular science books are literary works about science, scientists, scientific achievements and research, intended for a wide range of readers.
- Popular science magazines.
- Children's encyclopedias.
- Articles.
Genres of the scientific and information substyle
The function of the scientific information substyle is to convey scientific information.
The main genres of this substyle:
- An abstract is a short report on a specific topic, which collects information, most often from several sources.
- A review abstract is a report that compares different points of view on a particular issue. Compiled based on several sources.
- An abstract is a short report that outlines only the main points.
- The thesis is the leading genre of scientific style. It is a short record that outlines the main points of scientific research.
Genres of scientific reference substyle
The task of the scientific reference sub-style is to provide the reader with the ability to quickly find the necessary scientific information.
The main genres of the scientific reference substyle are:
- Encyclopedia is a scientific reference review of all or individual branches of knowledge in the form of a dictionary.
- A dictionary is a collection of words with their translation, interpretation and explanation.
- A reference book is a book that contains brief information of a scientific, social, industrial or applied nature.
- Catalog is a list of information about objects, the purpose of which is to facilitate the search for these objects by a certain criterion.
Scientific style of speech: genres of the scientific and technical substyle
The scientific and technical substyle is common in technical documentation. The texts of this substyle serve to apply in practice all the achievements that have been obtained as a result of theoretical and experimental scientific research.
The genres of the scientific and technical substyle include:
- A patent is a document certifying the exclusive right to an invention, product or process.
- Specification is a definition and list of specific features, a refined classification of something.
- Technical specifications are a document establishing the technical requirements that a specific product, material, substance, etc., or a group of them must meet.
- Standards.
- Description of inventions.
Stylistics as a branch of linguistics
I won’t bore you with scientific terminology, although it is difficult to do without it entirely: linguistics is as exact a science as, for example, mathematics. And stylistics is one of its sections devoted to the capabilities and means of language, as well as the patterns of their use in a given situation.
A person who is fluent in speech (both oral and written) rarely thinks about what style he is currently expressing his thoughts in and whether this or that expression is inherent in him. At a subconscious level, he differentiates vocabulary and the construction of phrases, cutting off those that are alien to a given situation. However, not everyone has such a gift, and the school curriculum devotes catastrophically little time to this topic. So let's try to bridge this gap, paying attention not only to theory, but also to examples.
Structure of scientific text
Any scientific text, regardless of genre, is built according to a single logical scheme.
The basis is always a thesis - a statement that requires justification. To confirm and substantiate this thesis, the text must present argumentation and provide evidence . Often, for a more complete argument, illustrations - examples that confirm the scientific assumptions put forward.
The text ends with a conclusion or summary , which outlines an assessment of the research conducted and also presents prospects for further study.
Linguistic characteristics
Each style can have its main characteristic features - lexical, morphological, syntactic. The linguistic features of the scientific style include the use of certain vocabulary.
Its distinctive features:
- words are used only in the literal sense;
- artistic means of expression are not used - metaphors, hyperboles, epithets, etc.;
- abstract sentences and terminology are used.
Three groups of words can be used in the text - those with stylistic neutrality, general scientific and highly specialized. The use of terms depends on the substyle and audience. For example, in popular science books it is undesirable to use a large number of special words and a simplified presentation of information is allowed.
Features of morphology:
- a small number of first and second person singular verbs;
- a large number of present tense verbs and verbal nouns;
- adjectives are rarely used.
Syntactic features make it possible to distinguish the scientific style from others. This group may include such features as the use of special phrases, for example, according to experience or according to Newton. “Next” is often used as an introductory word. To logically link sentences use:
- "corresponding";
- "famous";
- “given”, etc.
A large number of complex sentences of complex type are used. With their help, generalizations are made or certain phenomena are described. Conjunctions are used to logically connect sentences.
The text necessarily uses references to the works of other scientists, especially if the author wants to show different points of view on one problem. Sentences include participles and gerunds.
An example of texts written in a scientific style of speech
“A tornado is a strong small-scale vortex that arises in a thunderstorm (cumulonimbus) cloud and spreads in the form of a dark “trunk” towards the water or earth’s surface.
In the upper part, below the lower boundary of the cloud, the vortex has a funnel-shaped expansion. The barrel of a tornado descends to the earth's surface, its lower part, in contact with it, takes the form of an overturned funnel. The height of a tornado can reach 800–1500 m. The air in it rotates most often counterclockwise, rising in a spiral upward, drawing in dust or water, and fragments of objects destroyed on the ground.
The air rotation speed can reach 50–100 m/s with a strong upward component and cause catastrophes. destruction, sometimes accompanied by loss of life. At the same time, near his path there may be complete calm. Inside the tornado, the air pressure decreases, condensation of water vapor occurs there, which, together with the elongated part of the cloud, dust, water and decomposition. the debris makes death visible. Its axis is vertical, but often has a curved appearance.”
Electronic encyclopedia
» Existing territorial planning schemes for environmental management do not contribute to the creation of environmentally-oriented economic activities, which leads to conflict situations between economic entities both within the Kaliningrad region and outside it. Analysis of the features of socio-economic development and environmental policy made it possible to identify a number of significant methodological and methodological shortcomings in territorial planning and development. In particular, the development of the Kaliningrad region is carried out on the basis of poorly coordinated and poorly environmentally oriented departmental plans: urban planning, agricultural, reclamation, water, forest management, recreational and others.
Environmentally-oriented landscape planning can help in solving problems of territorial development. The landscape program of the Kaliningrad region is a strategic planning document for the use of the territory, forming an information and reference field for a wide range of organizations and officials responsible for the development and adoption of management territorial planning decisions, as well as state and non-state environmental and environmental funds, international organizations in the field of environmental control and management.
One of the most important tasks in implementing the program is the development of an integrated map of environmentally-oriented use of the territory and a map of environmental management conflicts. Solving these problems without the use of geographic information technologies is very complicated and sometimes impossible.”
Excerpt from the scientific article “Introduction of open geoinformation technologies into environmental planning methods”
Information sources:
- Russian language for technical universities. Scientific style. Author: Yu. Smirnova
- Wikipedia
- Russian language and culture of speech. Authors: Tatyana Balykhina, Mikhail Rybakov, Marina Lysyakova.
- Stylistics of scientific speech and editing of educational and methodological materials. A textbook for teachers and educators of the secondary education system.
- Photo on the cover of the article - science.sciencemag.org
PS: Did you like the article? Share the link on social networks, thank you!
Choosing a style depending on the task
And now we come to the cornerstone of copywriting: how to determine the style that is optimal for achieving specific goals?
Yes, choosing an adequate style is sometimes difficult at first. And not the first ones either, especially if the author’s ideas are diametrically at odds with the customer’s opinion. This is why I practice long-term cooperation, and only with customers whose ideas about good writing coincide with mine.
When choosing a text style, consider:
- Portrait of the target audience . It is impossible to speak to an audience of specialists and uninitiated people in the same language: the former will laugh at you, the latter will not understand. As I said, the conversational style is a priority, and the degree of “scientific” or “official” should be correlated with the perception of the target audience.
- Text tasks. The main task of the text is to attract attention, induce emotion or action. Sometimes the author chooses a conversational style, oversaturated with reduced vocabulary in order to evoke response emotions, creating a kind of holivar.
- Customer requirements . This is the basis, because whoever pays is the owner. It is advisable to convince the customer of your professionalism and ability to choose a style for dialogue with a specific target audience. You see that a free conversational style with light humor is suitable here, but the client craves officialdom - this is a common problem.
Artistic or literary
Artistic style is used in literature. Its task is not only to convey information, but also to create accurate visual and emotional images in the reader, to make him experience certain feelings. Divided into three substyles:
- poetic - poems, poems;
- prose - stories, novels, novellas, short stories, fables;
- dramatic - plays, dramas, comedies, tragedies, tragicomedies.
The artistic style is expressive. It is believed that it is in it that the beauty of language is most clearly revealed. Its main features:
- expressiveness;
- constant use of artistic techniques - metaphors, comparisons, allegories, epithets, contrasts;
- figurative phrases;
- aesthetic significance;
- use of the author’s individual style;
- playing with sentence length and pacing to create emotional effect;
- the use of syntax as a means of expression;
- deviations in sentence structure;
- the use of speech means from other styles to achieve an emotional impact on the reader;
- freedom, lack of strict text structure.
Artistic style can be used in descriptions, discussions and narratives. It is considered the freest, since it practically does not limit the writer. The quality of information delivery largely depends on his talent, experience, abilities and diligence.