Hard and soft consonants
Consonant sounds are divided into two types: hard and soft. When they are pronounced, articulation softens and the position of the tongue changes. During pronunciation, the main part of the tongue moves forward towards the teeth, and the middle part of the tongue moves towards the hard palate.
Soft consonant sounds include: [p'], [b'], [f'], [v'], [t'], [d'], [w'], [zh'], [k'] , [g'], [x'], [h], [m'], [n'], [p'], [l'], [j].
Many of them form pairs with hard consonants. For example, soft [n'] is consistent with hard [n] - [n']yos - [n]os, [m']el - [m]al, dust[l] - dust[l']b.
The softness of consonant sounds in writing is expressed by the vowels E, Yo, Yu, Ya, I, as well as using the soft sign b, but is indicated by the softness sign (apostrophe) only in transcription.
To distinguish soft consonants from hard ones there are a number of rules:
- after the consonant sound there is a vowel i, e, e, yu, i - the consonant sound has a soft meaning. Aunt, canopy, shadows, since after the consonants come the vowels ё, я, е, и - the consonants will be soft;
- the position of the consonant sound is at the end of the word, and the letter b comes after it - a soft consonant (laziness, migraine, steppe);
- the sounds j, ch, sh will always be soft, no matter what position they are in, and regardless of what vowel is present in a given word.
Feel the difference in the sound of [p] in the words [P'et'ya] and [pol'e]. You will notice that in the first word, the middle of the tongue rises to the roof of the mouth. And in the second word, the tongue even moves down a little and the sound is lower.
Best article on the site : Soft sign - dividing or softening?
Distinctive features of soft and hard sounds
- When a consonant is followed by the letters a, o, u, s, e , then we can definitely say: this consonant is hard. Let's check: house, garden, goose, cheese, rap. Here the first sounds in the words [d], [s], [g], [s], [r] are hard.
If two consonants are in a row, then the first one will give hardness. Let's check: shift - [sm'ena]. The hard sign ъ is an indicator of the hardness of a consonant: [congress], [entrance].
- When a consonant is followed by the letters e, e, i, yu, i , then we can definitely say: this consonant is soft. Let's check: lion, flax, strength, muesli, ball. Here the first sounds in the word [l'], [l'], [s'], [m'], [m'] are soft.
Also, a soft sign behind a consonant helps the child determine softness. Let's check: [coat], [porch], [teacher]. Note that the soft [l'] in the middle of a word is always denoted in writing by the soft sign ь : [mul'tik], [chair]. For other letters you need to check the dictionary.
Table of signs of hard and soft sounds
| Solid | Soft |
| before a, o, y, s, uh | before e, e, i, yu, i |
| ъ | b |
| before another consonant |
Always soft sounds in Russian
The letters ch, shch, th are always soft, even if they are followed by the vowels a, o, u, y, e: [ch'ash'a].
Always hard sounds in Russian
The letters zh, sh, c are always hard, even if they are followed by the vowels e, e, i, yu, i: [gutter].
Sounds of the Russian language
Our speech consists of words that are combined into a sentence. Each word can be considered as a semantic component of a sentence, filled with content, and also as a sounding object.
A word can be divided into syllables, which are made up of individual sounds. From a phonetic point of view, a word is made up of sounds.
Sound is the basic unit of language, just like words and sentences. Sounds form words at the phonetic level. Sounds, depending on their set, quantity, and location in a certain sequence, help to distinguish one word from another:
- treasure - contribution;
- crown - crown;
- cat - current.
Depending on how sounds are formed in the speech apparatus, vowels and consonants are distinguished in the Russian language.
The vowel sounds [a], [o], [e], [u], [i], [s] consist entirely of voice. When they are formed, air passes freely through the tense vocal cords and mouth, without encountering any obstacles on its way. In Russian, vowel sounds are musical. You can drag them out for a long time and sing: a-a-a, o-o-o, o-o-o.
Vowel sounds form a phonetic syllable in a word, but consonants cannot form it. When syllabled, they are combined with vowel sounds in pairs or whole groups:
- collar - collar;
- beauty - beauty.
Voiced and voiceless consonants
If a vowel is pronounced with a voice, then a consonant is pronounced with a combination of voice and noise. If there is more voice, then the consonant is voiced, and if there is more noise, then it is voiceless.
The Russian language has only 21 consonants and 36 consonant sounds. They are divided by hardness and softness, by sonority and dullness, paired and unpaired.
The sonority of consonant sounds is manifested by the sound and structure of the speech apparatus. When pronouncing them, in addition to the voice, vibrations and various noise obstacles are added. These barriers distort the wave of sounds, so that not clean air, but sound, passes into the oral cavity.
For example, when pronouncing the sound [b], our lips close, and the air we exhale tries to break through the barrier. Based on this, we select voiced consonant sounds. These sounds include b, c, d, d, g, z, j, l, m, n, r - their pronunciation contains noise and voice.
Most sounds have pairs, these include: b - p (beam - stick), v - f (moisture - flask), g - k (goal - stake), d - t (house - volume), z - s (angry - layer), w - w (vein - awl).
The remaining voiced consonant sounds: th, l, m, n, r are called sonorant, which means sonorous. Sonorant sounds differ from other voiced consonant sounds in that during pronunciation the noise level is practically not involved in the formation of sound.
Paired by voicedness/voicelessness
There are 21 consonant letters in the alphabet, which represent 37 consonant sounds.
Many consonant sounds form voiced/voiceless pairs. Such consonant sounds can be voiced or devoiced depending on their position in words.
All voiced consonant sounds consist of noise and voice, all voiceless consonant sounds consist only of noise.
Let's list paired consonant sounds by voicedness/voicelessness using the table “Voiceless/voiced consonant sounds”:
| Voiced consonants | Voiceless consonants |
| [b] | [P] |
| [V] | [f] |
| [G] | [To] |
| [d] | [T] |
| [h] | [With] |
| [and] | [w] |
The correct spelling of paired consonants based on voicedness/voicelessness is an orthogram that requires a test word.
Let us give examples: the word “tooth” is pronounced with a dull consonant sound [p] like [zup]; the word “teeth” is pronounced with a voiced consonant sound [b] like [teeth].
Unpaired voiced
In the Russian language there are only voiced consonant sounds, that is, such consonant sounds are not paired, they do not have pairs of sounds due to deafness.
The sound of unpaired voiced consonants does not depend on position.
Unpaired voiced consonant sounds include: [l], [m], [n], [r], [th].
Let's give an example: the word “crowbar” is pronounced with unpaired voiced consonant sounds [l] and [m] like [crowbar].
Unpaired deaf
There are also consonant sounds that do not have a voicing pair. Such sounds are called unpaired voiceless consonants.
The sound of unpaired voiceless consonants does not depend on position.
Unpaired voiceless consonants include: [x], [ts], [h], [sch].
Let's give an example: the word “thicket” is pronounced with unpaired voiceless consonant sounds [h] and [sch] as [ch'ash'a].
How to teach children to distinguish between hard and soft consonants
The child will learn the difference if he is shown it visually or if he is allowed to feel it through experience. For example, Zaitsev's cubes with soft consonants are small in size, and with hard consonants they are large. The child makes up words and sees this difference every time.
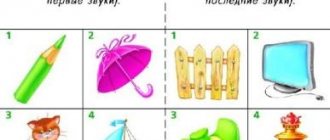
Also, when analyzing words, you can take pictures that remind the child of something soft and something hard. For example, a pillow and a stone. Hearing a soft sound, the child shows a picture of a pillow. Pictures can be attached to cards or drawn next to letters in a notebook.
Voicing of voiceless consonants
Voiceless consonants always sound muffled at the end of words or when paired with vowels or sonorant sounds. If there is any doubt about the spelling of the corresponding letter at the end, then it is necessary to change the form of the word so that the consonant appears before the vowel:
- dill - dill leaves;
- rental - no rental;
- mowing - mowing time;
- language - languages.
Voiceless consonants change the quality of their sound only if they are followed by a voiced consonant. It influences a dull sound and turns it into a voiced sound. This phonetic process is called voicing.
Definition
Voicing is the replacement of a voiceless consonant sound before a voiced consonant, except for [l], [m], [n], [p], [th'], [v], with a paired voiced one.
Let's see this by looking at the following examples:
- run away [z b' and g a t']
- beat off [a d b' and t']
- request [p about z' b a]
- harness [br u y a].
Voicing of voiceless consonants creates difficulties in spelling words. In such cases, you cannot rely on the sound of the word, but you should look at the morphemic composition of the words “run”, “beat off” and find out that there are no prefixes з- or ad-.
If voicing occurs in the root, then we select a test word so that after the dubious consonant there is a vowel or sonorant sound that will clarify its sound:
- request - ask;
- mowing - to mow.
Examples of tasks for children
Voiceless or voiced:
- A simple and vivid way that helps you understand the difference is to put your palm to your throat when pronouncing. Go through all the consonants, let the child discover which letter vibrates and which does not give sensations.
- Choose pictures that resemble ringing and deafness. For example: bell and ear. Say different words of one or two syllables, and if the child hears a ringing sound, he should show a picture with a bell. Then play the same way with a dull sound. When the child gets comfortable with simple words, take longer ones.
Hard or soft:
- Offer to take one letter and sing syllables with vowels that give hardness. Let the child feel the firmness in his voice. Then, with the same letter, sing syllables with vowels that give softness.
- Name the syllable and throw the ball to the child. If it's hard, you should catch it. If it's soft, push it away.
- Make a chain of words. For example, chair-horse-money-guitar...
General tasks:
- Create your own table with colorful images and hang it in a prominent place. When a child chooses a picture or color himself, he becomes more involved in the topic and remembers it faster.
- Offer to name a word that has both a voiced and a voiceless word. Or deaf and, at the same time, hard.
What have we learned?
Many consonant sounds form pairs based on voicedness/voicelessness: [b] – [p], [v] – [f], [g] – [k], [d] – [t], [z] – [s], [g] – [w]. These consonant sounds can be voiced or voiced depending on their position in words. In the Russian language there are unpaired voiced consonants ([l], [m], [n], [r], [y]) and unpaired voiceless consonants ([x], [ts], [ch], [sch] ). Such consonant sounds do not have pairs for deafness (unpaired voiced consonants) or for voicing (unpaired voiceless consonants); their sound does not depend on their position in words.
Check the spelling of paired consonants at the root or at the end of the word?
When sounds are pronounced, sometimes dull sounds are heard more often. But despite this, you must write the correct letter. All letters in words cannot change. Even though there is a different sound. To make sure that a word is written correctly, you will need to study certain rules. Thanks to them, it will become clear which sound is used in a word, voiceless or voiced, and the possibility of replacing paired consonant sounds will be excluded.
Paired consonants: rule
Rules for checking the spelling of voiceless and voiced consonants:
- Basically, when writing, the letters do not change; to check the spelling of a particular letter, you need to select a word with the same root in a different form. If there is a vowel after a dubious consonant, then you will decide which letter to write, voiced or unvoiced.
- It is easy to determine which consonant is written in a particular word when it is followed by a sonorant consonant: th, r, m, l, n .
Examples: in order not to make a mistake, in the word sugro b ( p ), you will need to change this word so that there is a vowel at the end: in sugro ba x. The word eye ( s ) , check: eyes , oboz ( s ) - oboz , code d ( t ) - code yes , chat ( d ) - chats .
IMPORTANT: There are some words that cannot be verified. These include - kofta . This word must be remembered and always written in it with the letter - f .
Syllables starting with P
The letter P is the most common of the letters of the alphabet, not including the vowels, O, I, E, so syllables can be composed indefinitely.
Let's look at some of them:
- pa - po - pe - pi - pu - py - from two letters;
- pli - plya - plya - pla - plya - plo - from three letters.
You can make syllables from more letters - this will be your task No. 1: make syllables from 4 or more letters containing the letter P.
It can be located at the beginning of a syllable, in the middle or even at the end.
Write your answers in the comments.
Games with the letter P
Game "Say the word"
Players take turns naming words that, according to the assignment, begin with the letter P. The one who runs out of vocabulary with this letter before everyone else loses.
Game "Finish the drawing"
P is drawn on a large sheet of paper. This sheet is distributed to all players. The task is to add any details to P to make an original drawing, something meaningful. For example, if you draw a string to P on one side and a ball on the other, you might end up with some kind of animal.
Game "What is P like?"
Players must take turns coming up with what the letter looks like in its outline. For example, a football goal, horizontal bar, door frame, etc. The one who can no longer come up with associations loses.
Consonant devoicing rule
In the Russian language, it is not uncommon for a letter to be written in writing to denote a voiced consonant, but in speech it turns into a voiceless consonant. This happens, for example, when a voiced letter appears at the very end of a word, as in the word mushroom, the transcription of which will look like [flu].
Due to the fact that voiced consonants are deafened at the end, difficulties often arise when reproducing such words in writing. However, there is an easy way to check which letter to use: you need to change the word so that the consonant appears before the vowel, for example, mushroom - mushroom. Then it will immediately become clear what needs to be written. The same applies to cases when there is a voiceless consonant at the end, and in writing it is voiced “according to the general rule.” You can check which letter is written in the same way: krik - krik, lot - lota.
Voiced consonants located in positions at the beginning and in the middle of a word can also be deafened if they are followed by a voiceless consonant. This is easy to understand using an example: booth [booth].