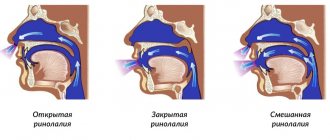
Dysphonia is a voice disorder in timbre, strength or pitch. With this condition, the voice may be weak, hoarse, or slurred. This condition develops against the background of local damage to the muscles of the vocal apparatus or speech centers of the brain.
Depending on the affected area, the pathology clinic and prognosis when prescribing treatment may vary. Only a competent speech therapist and speech therapist in Moscow will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe therapy.
Dysphonia can develop due to congenital disorders; organic lesions can predispose to pathology. Many patients have a family history, but this does not mean that the disease is incurable. Patients who immediately began undergoing training successfully master normal speech.
Dysphonia can be recognized by the following clinic:
- the voice may be too quiet or loud at first, but fade away during the conversation and become hoarse at the end;
- conversational speech can be monotonous, monotonous, unemotional;
- Often there is noisy and wheezing breathing, which is heard during a conversation.
Hypotonic dysphonia
The word “hypotonicity” means weak tone, in this case, of the muscles of the larynx. In simple terms, the muscles of the speech apparatus contract with insufficient strength, which leads to a weak or hoarse voice, speech becomes illegible and poorly understood.
The cause of hypotonic dysphonia is organic in nature; it develops when the muscles of the larynx themselves or the nerves that control the contraction of these muscles are damaged. Before treatment, an examination by an otolaryngologist and a neurologist is required to exclude pathology. Only with a comprehensive diagnosis can the exact cause of the disease be determined.
Causes
- Congenital defect of the larynx (congenital stridor or laryngomalacia): abnormal development (or underdevelopment) of the cartilage of the larynx, especially the epiglottis, which leads to prolapse (sagging) of the epiglottis and incomplete opening of the entrance to the larynx (manifested by abrupt, noisy inhalation).
- Vascular anomalies of the larynx (formation of vascular tumors - angiomas) as a result of impaired development of blood and lymphatic vessels in the embryonic period.
- Developmental disorder (underdevelopment or absence) of the vocal folds. Congenital dysfunction of the vocal folds.
- Organic dysphonia is the result of acute or chronic pathologies of an inflammatory, allergic, neurological or oncological nature in various parts of the larynx or lower respiratory tract.
The causes of functional dysphonia are:
- Chronic diseases (diseases of the heart, lungs, blood vessels, endocrine system.).
- Professional factor associated with constant tension of the vocal cords (vocals, teaching).
- Past infectious diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract.
- Occupational hazards (increased gas pollution, work in high dust concentrations).
- Obstruction (impairment of the lumen) of the upper respiratory tract due to foreign bodies.
- Taking anabolic steroids and medications.
- Psycho-emotional, stressful conditions.
- Complications after surgery in the neck area (damage to the vocal apparatus of the larynx).
- Diseases of the spine in the cervical region (arthrosis, osteoporosis).
- Vitamin deficiencies, anemia (reduced amount of hemoglobin in the blood).
- Allergic diseases.
Functional dysphonia
This disease develops due to dysfunction of the laryngeal muscles without organic pathology. In functional dysphonia, there are no anatomical changes in the vocal cords, and speech problems arise due to their weak or incomplete closure.
The reasons can be very different - congenital features of the speech apparatus or problems of central origin. In the latter case, a disorder of muscle innervation occurs due to stress, psycho-emotional stress or damage to peripheral nerves. The exact cause can only be determined through clinical examination.
GBOU "NIKIO im. L.I. Sverzhevsky" of the Moscow Department of Health
Functional dysphonia is a violation of vocal function, characterized by a violation of the closure of the vocal cords in the absence of pathological changes in the larynx.
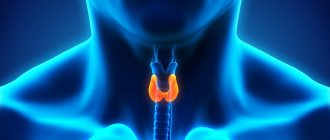
The causes of a functional voice disorder can be constitutional, anatomical, congenital features of the vocal apparatus, voice overstrain, traumatic factors, previous respiratory diseases, asthenic syndrome of any etiology. Hypotonic disorders can also develop against the background of prolonged silence, as well as after surgical interventions on the larynx or with atrophy of the vocal folds. Anxiety and depressive disorders can contribute to the development of functional dysphonia. Hormonal disorders, most often thyroid diseases, play a significant role in the occurrence of functional dysphonia. Other causes are neurological diseases such as Parkinson's disease and myasthenia gravis, traumatic brain injury, cerebrovascular accident, etc.
Functional changes are reversible, but in some cases they can lead to organic changes in the larynx.
The clinical picture of functional dysphonia is caused by a violation of the vocal function of varying degrees of severity.
Hypotonic dysphonia is a violation of vocal function caused by a decrease in the tone of the vocal folds and other muscles involved in voicing. Rapid voice fatigue and aspirated hoarseness are noted.
Hypertonic dysphonia is a violation of vocal function caused by increased tone of the vocal folds. Phonation is carried out with tension in the neck muscles, the voice is sharp, and hoarseness is pronounced.
Hypo-hypertonic dysphonia (vestibular-fold voice) is a violation of vocal function due to a decrease in the tone of the vocal folds with the formation of phonation at the level of the vestibular folds with the subsequent development of their hypertrophy.
Aphonia is the lack of sonority of the voice while maintaining whispered speech.
Psychogenic dysphonia or aphonia is a disorder of vocal function, the leading etiological factor of which is considered psychogenic.
Mutational dysphonia is a voice disorder that occurs during the period of mutation.
Spasmodic dysphonia is a voice disorder characterized by tense and compressed intermittent phonation, tremors, hoarseness, and impaired speech intelligibility. There are abductor and adductor forms. During speech, twitching of the diaphragm is noted. Articulation disorders and changes in the psycho-emotional sphere are diagnosed. Clinical and neurological examination reveals organic pathology in the form of dystonic syndromes (such as writer's and blepharospasm, torticollis, etc.).
In the process of diagnosing and treating voice function disorders, a multidisciplinary approach is required with the involvement of a neurologist, endocrinologist, psychiatrist and phonopedist in the rehabilitation process.
Treatment of functional dysphonia
The approach to the treatment of functional dysphonia should be comprehensive. It is necessary to influence etiopathogenetic factors: treatment of general somatic diseases, somatomorphic disorders, sanitation of foci of chronic infection.
The prognosis for functional dysphonia is often favorable. Persistent impairment of vocal function and a long-term course lead to a deterioration in the patient’s communication.
Prevention of vocal function disorders consists, first of all, in maintaining vocal hygiene, developing correct phonation skills, and developing the speaking and singing voice, especially in people of voice-speech professions. Timely diagnosis and treatment of general somatic diseases leading to the development of dysphonia are of great importance.
Spasmodic dysphonia
With such dysphonia, a spasm of the muscles of the larynx occurs, resulting in problems with the voice. Due to muscle overstrain, hoarseness is observed, and the voice may be completely absent. This condition occurs due to muscle spasm, for example, during prolonged singing or after reading a lecture. Spasmodic dysphonia usually goes away after rest, and consultation with a specialist is often required.
Often, with spasms, disturbances occur in the psycho-emotional sphere - due to fear, it becomes difficult for patients to talk and breathe normally. Due to twitching of the diaphragm, breathing is disrupted and various side sounds appear.
Dysphonia Treatment Methods
Treatment for dysphonia involves medication and physical therapy. Patients with a functional type of disorder (including somatics) can be absolutely healthy. Then medications are simply not needed.
So, treatment of hypotonic dysphonia means that the doctor will prescribe B vitamins. For the hypertonic version of the disorder, they will prescribe some kind of sedatives and antispasmodics. Homeopathic remedies are often used to relieve symptoms.
In the functional form of dysphonia, good results are achieved by external procedures: electrophoresis, amplipulse therapy, magnetic therapy. If necessary, the laryngeal mucosa is directly affected. For this purpose fluctuarization is used.
Inhalations and drip administration of medications directly onto the walls of the larynx help well. Ozone therapy is useful. To relieve muscle spasms in the muscles of the neck and larynx, botulinum toxin injections are given.
To normalize the psycho-emotional sphere and nervous system, acupuncture and massage are prescribed. Perhaps you need the help of a psychologist or psychotherapist. Autogenic training, psychotherapy, and the use of relaxation techniques help with dysphonia.
To restore the voice, phonopedic correction is necessary. The patient will have to strengthen the vocal apparatus and laryngeal muscles, and learn proper breathing. He needs to do breathing and articulation exercises, speech therapy massage, and special exercises.
Hypertonic dysphonia
This form of dysphonia develops due to overstrain of the vocal muscles, which are responsible for generating sounds. Due to the high tone, tension in the neck muscles is noted, the phonation is sharp, and pronounced hoarseness is observed. Hypertonic dysphonia in severe cases may be accompanied by shortness of breath with dry wheezing due to narrowing of the glottis.
Sometimes patients need urgent help - the earlier treatment is started, the easier and faster it is to restore a normal voice. Muscle contraction also develops with certain diseases of the larynx or with psycho-emotional stress.
Is it possible to restore voice function with Dysphonia?
To restore voice function, the help of a speech therapist is needed. During a diagnostic examination, a specialist determines which aspects of voice-forming activity are impaired; draws up an individual recovery program; conducts individual classes (procedures), including breathing exercises, speech and vocal exercises, speech therapy massage, vibration stimulation of speech and neck muscles. If necessary, initiates drug therapy (consultations with a neurologist, psychotherapist). The methodology and duration of classes are determined individually.
The sooner the patient is referred to a specialist for help, the sooner he will reach the maximum level of social functioning, thus improving the quality of life.
Speech therapy service of the State Clinical Hospital named after. S.S. Yudina
Organic dysphonia
With organic dysphonia, various pathologies of the speech apparatus are present: inflammation of the tonsils, cysts in soft tissues, neurological disorders, etc. All diseases can be confirmed by clinical examination of the patient. If such a diagnosis is made, mandatory treatment by a specialized specialist is required: otolaryngologist, neurologist, oncologist and other doctors, depending on the type of pathology.
Consultation with a speech therapist is necessary to restore normal speech in case of organic dysphonia. In severe cases, several courses may be required; rehabilitation is prescribed only when treating the underlying pathology.
Diagnostics
A characteristic symptom of functional dysphonia is prolonged impairment of voice function.
Voice deterioration can occur after a viral infection, severe vocal stress, or as a result of a deterioration in general health. To diagnose voice disorders, there are special texts that need to be read for 40 minutes. In addition, there is psychological testing that is performed in order to identify somatoform disorders (perceived by the patient). While listening to speech, experts pay attention to strength, timbre, diction, posture, the condition of the neck muscles and some other signs. In order to make a final diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a number of studies: laryngosmicroscopy, acoustic and spectral computer analysis of the voice, electromyography, glotography, and assess the function of external respiration.
In hypotonic dysphonia, incomplete closure of the glottis is observed during phonation. The hypertonic form is characterized by hyperemia (redness) of the mucous membrane, hypertrophy of the vestibular folds, as well as excessive closure of the vocal folds. In some cases, during phonation, you can see the closure of not the vocal folds, but the vestibular folds.
Mutational dysphonia
Mutational dysphonia usually occurs in boys during puberty, when the voice “breaks” and becomes rougher. The reason is various functional changes in the speech apparatus due to hormonal changes. If these processes occur significantly and disrupt normal speech, it is recommended to consult a specialist.
A speech therapist will help the child quickly adapt to such changes; with the help of training, speech can be maintained within acceptable limits. If due to dysphonia there is a loss of voice or its quality is impaired, a specialist will help you quickly rehabilitate in a difficult situation.
Forecasts
Dysphonia goes away forever if help comes on time and the rehabilitation plan is drawn up correctly. Difficulties arise if the patient is again faced with a traumatic factor, if psychological problems are added to this (lack of faith in one’s own strengths and the possibilities of therapy), or if the treatment process has been delayed.
The NeuroSpectrum Center for Children's Speech Neurology and Rehabilitation offers a full examination for the presence of dysphonia, consultations with specialized specialists, as well as comprehensive treatment. Together we will restore the voice, return its timbre and tonality.
Psychogenic dysphonia
With psychogenic dysphonia, there is a deterioration in the voice up to its loss due to some psychogenic reasons. Usually, when exposed to a stress factor, a person begins to become very worried and worried, after which problems with speech appear. In terms of symptoms, they resemble hyperfunctional dysphonia with unstable speech and typical squeezing.
In the psychogenic form of the disease, a mandatory consultation with a psychologist or psychiatrist is required. Doctors set themselves the goal of stopping and, if possible, eliminating a negative reaction to the stimulus. A speech therapist will help with restoring normal speech and returning to normal communication.
Speech specialists are engaged in the diagnosis and professional correction of speech disorders. We will determine the cause of dysphonia and help restore speech without drugs or hypnosis.
What does speech therapy work for dysphonia involve?
Classes with a speech therapist will help cope with voice disorders and restore normal speech.
Corrective measures include exercises:
- aimed at developing correct breathing during a conversation;
- articulation gymnastics;
- breathing exercises;
- phonopedic tasks;
- exercises that stimulate coordination of phonation.
For children, all classes are conducted in an easy, playful way, so as not to cause additional tension and stress. A skilled speech therapist will turn the mandatory articulation gymnastics into a funny tale about the Tongue’s travels, and breathing exercises into an entertaining game.
Exercises for coordinating the pronunciation of sounds are based on the principle of repeating the same words or combinations of sounds, first silently, but with increased articulation, then in a whisper, and again loudly. Having learned to control phonation, the child will be able to maintain vocal mode and protect the cords.
Breathing exercises can also be a fun activity. The speech therapist will encourage the child to blow on cotton balls, blow soap bubbles, and even play musical instruments. Dynamic gymnastics expands the child's control over his breathing.
During classes, children learn to speak with different strength, intonation, duration and pitch of the voice, which allows them subsequently not only to get rid of dysphonia, but also to avoid its recurrence thanks to self-control. Learn more about how speech therapist-defectologist classes work.
Treatment
Treatment should be comprehensive and include both local, which consists of sanitizing foci of infection, and general somatic treatment. It is aimed at increasing the endurance of the voice-producing apparatus and developing stable phonation skills. Treatment without the use of medications includes:
- Carrying out phonopedia - pedagogical education of correct voice production;
- Breathing and articular gymnastics;
- Acupuncture and physiotherapy, which include procedures such as dynamic currents, electrophoresis on the larynx area, amplipulse (pulse current treatment)
- Psychotherapy;
- Massage of the collar area.
During drug therapy, stimulant drugs are prescribed. In cases of severe and persistent hypophonia, implantation therapy is used.