A person’s calling card is his speech. Without a doubt, all parents want to see their child healthy, happy and successful. An important role in this is played by the child’s ability to speak correctly and beautifully.
Unfortunately, recently such a phenomenon as speech disorder has become very common. As statistics show, every third child of preschool age has some kind of speech defect. Of course, caring parents try their best to help their child. But how to do that? To do this, you must, at a minimum, have information. To this end, the article provides useful informative material.
The concept of abnormal manifestations of speech
General underdevelopment of speech (GSD) - it means a speech disorder when normally hearing children with preserved mental abilities have unacceptable and completely defective speech: from its sound to its meaning.
This concept was caused by a vital necessity and became firmly established in educational structures for children, in which speech therapy groups were formed. The term OHP was coined by the founder of Russian speech therapy, R. E. Levina (the levels of OHP according to Levina are given below).
Regardless of the origin of the defect, there are systemic complications of speech. Signs of a speech disorder:
- Speaking begins at approximately 3-5 years of age.
- Incorrect wording of words and phrases.
- Pronounced sounds are distorted.
- Incomprehensible conversation.
To distinguish between speech impairment, a speech therapist must conduct a thorough study of the disease of a particular child!
Treatment and correction
Today, speech therapy has accumulated sufficient experience in the treatment and correction of level 3 OHP. To effectively eliminate such speech disorders in preschoolers, teachers and parents must set specific tasks before starting a course of classes, focusing on the symptoms that are observed in the child.
Correction principles:
It is necessary to enrich the vocabulary of a preschooler.
The child must learn to use participles, adverbs, adjectives, and complex prepositions.
Elimination of agrammatism.
It is necessary to pay attention to observing the grammatical norms of the language, agreeing words by number, case, gender. Development of fine motor skills
Development of fine motor skills.
The speech therapist can use drawing and modeling. In the process of such activities, the child prepares for writing and activates the speech parts of the brain.
Increasing the level of understanding of someone else's speech.
The teacher can use instructions, reading, games
It is important that the child listens carefully to the speech addressed to him and responds to it with answers, action
Development of attention, memory, concentration.
Children with speech disorders have difficulty concentrating, memorizing poems, and they have short-term memory.
Development of communication skills.
Preschoolers with level 3 ODD are very shy; it is difficult for them to find contact with peers due to a speech impediment and fear of expressing their thoughts out loud. The lessons are aimed at leveling self-esteem, overcoming phobias and maladjustment in society. Group classes are best suited for these purposes.
The table shows an approximate plan for working with a preschooler; it can be adjusted and expanded with your own experience. We recommend that speech therapists fill out an individual card for each pupil and note the effectiveness of correctional work in it.
| Tasks | Correction methods, exercises | Game options |
| Formation of auditory attention | Use speech and non-speech sounds and expand your child's vocabulary by studying one topic for a week. | “Guess what it sounds like” (musical instrument, rain, wind, etc.), “Echo”, Find out a vegetable, transport, toy by description.” |
| Development of visual attention | Use pictures, objects to remember the series, remove or hide one or two, ask to restore the chain. | “Do as I do” (movements, layout according to the model), “What is missing.” |
| Vocabulary expansion | The child must learn and speak more. Use calendar-based themes. Describe the subject in detail, retell texts, answer questions based on pictures, play story games with dolls. | “Signs of the seasons” (you can guess from pictures, clothes on dolls), “Animals”, “Professions”, “What grows where”, “What we will use to make soup”, “Shop”. |
| Development of communication skills (group classes). | Monitor how children communicate with each other on a given topic. Ask to ask questions, answer them, suggest game options. | "Who am I?" (introducing children), “I’ll tell you, and you continue,” “For yesterday... (story about a family or event), “I want to be” (profession). |
| Correction of grammatical violations in speech | Compiling phrases and sentences taking into account the category of number, case and gender of words. | “What is he/she like? (describe fruits, vegetables, animals, people - the lemon is sour, yellow, oval...), “Who does what? (mom came, arrived, sang, washed, dad came, arrived, washed). |
| Practicing word formation skills | Add suffixes and prefixes to words, look for words with the same root. | “Small-big (elephant-elephant), “Say kindly (water-water, pencil-pencil). “Add the prefix” (walked, walked, came, left). |
| Development of fine motor skills | Use modeling, drawing, shading, coloring, and copywriting. | “Draw according to the model”, “Trace the circles”, “Puppet theater” (modeling). |
| Development of articulatory breathing, control of intonation, voice pitch. | As a warm-up, use articulation gymnastics, songs, outdoor games with recitation of poems. | “Who is louder (quieter)”, “What do you feel (practicing expressions of emotions using joyful, sad exclamations). |
General underdevelopment of speech becomes a serious problem for the child and parents at school if you do not promptly seek help from a speech therapist. It will take 1-2 years to completely correct speech defects of this level, so delaying a visit to a doctor at the clinic or transferring the child to a special group at a preschool educational institution is extremely undesirable.
Classification of speech disorders (table)
The clinical-pedagogical and psychological-pedagogical classification makes an in-depth analysis of complications in the speech sphere, showing the problem from different sides. Thus, she paints a complete picture of this illness, which allows you to choose the best way to help.
| Clinical and pedagogical | Psychological and pedagogical |
| Speech background failure (external design) | Means of communication are disrupted |
|
|
| Defects in the construction of linguistic means and their significance | Communication difficulties |
|
|
R. E. Levina and her colleagues developed a unified pedagogical approach that made it possible to see the process of abnormal child development, taking into account certain indicators. The teacher systematized systemic speech disorders and substantiated a new method of organizing a system of corrective work to overcome them in preschoolers.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of onr can only be made by conducting a comprehensive study. Diagnosis is carried out at an initial consultation with a speech therapist. The specialist establishes contact with the child, the parents must have medical reports from a neurologist, pediatrician, and the results of the studies. Having received all available information, the specialist studies and determines the speech status of his patient.
Speech therapy research is carried out in two stages - orientation and language examination. The orientation is carried out through a conversation with parents. This way, all the features of the course of the disease are clarified, what reasons accompanied it, and how the speech apparatus developed. The patient himself is also assessed - his ability to make contact, articulatory motor skills.
When examining the language and its components, the formation of speech, its coherence, grammar, and vocabulary are determined. In the case of the presence of OHP of the first degree, there is a gross underdevelopment of all components of the language system, which is explained by the child’s lack of commonly used speech. After this, the specialist can draw up his conclusion and establish the clinical form of the pathology of the speech apparatus.
Recommended speech therapy examination
It is worth studying in detail the vocabulary of a person suffering from OPD. This will allow you to assess the ability to correlate a word with a specific subject. This is done in several steps:
- Selection of material, divided into individual lexical topics. This determines the child’s ability to communicate with the people around him.
- Pictures with objects are offered.
- Pictures with names of body parts are used.
- Selection of synonyms for the selected word.
During the diagnosis, the speech therapist must give his conclusion, which indicates the level of speech development, the clinical picture, the degree of OHP, and also draw up a plan for correcting the identified disorders.
Definition of speech anomaly
ONR often occurs in the following syndromes: dysarthria, rhinolalia, alalia, aphasia. Based on this, 3 groups are distinguished:
- Uncomplicated forms of OCD (slight impairment of brain function is observed).
- Complicated forms of OPD (those with mental personality disorders or pathological changes in the development of the central nervous system).
- Severe speech pathology (when the functioning of the parts of the brain responsible for speech is disrupted).
When it becomes clear what form of anomaly the baby has, the level of speech skills is determined.
Determining the level of speech development of a child
Typically, all patients with general speech underdevelopment always have a malfunction in the articulatory and auditory systems. Also, their lexical arsenal contains a small number of words.
OHP levels and their characteristics
First level. There are practically no words. The passive vocabulary is very small. There is no understanding of the meaning of most words. In everyday life there are either babbling words or syllables of an onomatopoeic nature, one-word sentences used situationally (gestures and facial expressions are used). More often, only sound combinations consisting of 1-2 syllables are inherited. A gross violation of the perception of the system of meaningful sounds and the syllabic structure of words. The articulatory system malfunctions, sounds constantly change places, and, unfortunately, children are not able to pronounce many of them.
Second level. First attempts at coherent speech. Although babbling and gestures are still present, words appear, albeit distorted, but already constant, which are in general use. The vocabulary is still poor. Syllables are rearranged. Simple sentences appear with 2-3 words. The sounds are defective, often mixed and replace each other.
Third level. Children actively use expanded speech, but mostly use simple constructions. The volume of the dictionary is noticeably expanding: almost all parts of speech are used. Sound pronunciation and phonemic processes still do not fit into the norm, but there are fewer violations.
The fourth level (according to Filicheva). Characterized by minor deficiencies in phonetics, vocabulary and grammar. All these violations are not clearly expressed: the structure of syllables of words (complex), the joint work of the speech organs and the process of receiving and transforming sound information, changing and forming words are disrupted. This level of speech underdevelopment can only be detected through a thorough examination of the child by a speech therapist.
It is very important to detect possible disorders in your baby in time in order to prevent or eliminate them!
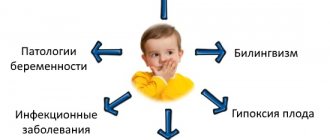
Reasons for OHP
The causes of OHP are mainly problems during pregnancy or childbirth, as well as in the first years of the baby’s life. The most basic reasons for OHP:
- infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy;
- toxicosis;
- birth injury;
- asphyxia, hypoxia;
- incompatibility of mother and child by Rh factor;
- disorders in the central nervous system;
- head injuries of a baby in his first years of life;
- the influence of nicotine, alcohol, drugs;
- deprivation.
Pathogenesis
OHP should be considered as a systemic disorder that affects language subsystems, that is:
- phonetic-phonemic;
- grammar;
- lexical;
- semantics.
Level 1 OHP in a child causes him to lag behind accepted age norms. This happens across the entire spectrum of indicators, both quantitative and qualitative. Such children have disturbances in the general course of speech development, the timing, and the order in which they master articulatory skills. Experts compare general speech development with linguistic infantility.
The very mechanism of the appearance and development of general speech impairment has a close connection with primary speech defects and their direct causes. In the presence of disorders of cerebral-organic origin, such as alalia or aphasia, severe speech disorder may occur, as well as misunderstanding of the speech of others.