Setting and automating the sounds “K” and “K” requires an integrated approach. Before starting a child’s education, it is necessary to develop in him an awareness of the mechanism of letter formation by the articulatory apparatus. Determine the procedure for conducting classes with the obligatory presence of articulatory gymnastics. Consolidation of results is carried out after the baby masters isolated sound.
Disturbances in the reproduction of phonemes K and Kь
Speech therapy divides errors in the pronunciation of the hard and soft sound K into 3 groups with characteristic types of deviations from the norm. Presented in the table:
| Name | Type of violation | Characteristic |
| Kappacism | Lack of correct sound reproduction. | The phoneme is replaced by a click of the vocal cords. |
| Letter distortion. | Nasal playback (occurs due to improper breathing). Lateral pronunciation is typical for children with incorrect articulation or the presence of organic defects. | |
| Complete absence of “K” and “K” in conversation. | The child systematically misses a letter in words (Kit - It, Cube - Ub). | |
| Paracapacism | Replacing "K" with "T". Cat - Thoth, Cube - Tub. | |
| Replacing "K" with "X". Kit – Hit, Com – Hom. | ||
All of the listed types of deviations are united by specialists into one concept - dyslalia (more about that here). The diagnosis also includes various defects in the pronunciation of voiced and voiceless consonants. The exception is vowel sounds. They are pronounced correctly when dislali.
Expert opinion
Margarita Sergeevna S.
Speech pathologist and speech pathologist with 15 years of experience working in various speech correction centers with children of different ages.
Important: if you do not work with your child at an early stage of detecting a problem before school, this can lead to the development of dysgraphia (writing errors) and dyslexia (reading errors). Correction in school-age children requires much more time and the mandatory intervention of a speech therapist.
Causes
To understand how to set the sound correctly, you need to know the root cause of the deviation from the norm. The occurrence of erroneous or complete absence of pronunciation of the sound “K” and “K” is influenced by the following factors:
- Organic defects associated with abnormal structure of the speech organs:
- abnormalities of the upper part of the oral cavity. The palate may be too high, soft, narrow. The soft part is hard and vice versa.
- the baby’s inability to distinguish sounds by ear (phonemic deviations);
- weak tongue muscles;
- poor sensitivity of the tongue muscles;
- mild physical hearing impairment.
- Social factors:
- omission of parents, educators, teachers;
- use of 2 or more languages in the family;
- lack of articulation exercises;
- repeating speech with errors for loved ones.
- A specialist can determine what factor predisposes the child to develop a defect and how to eliminate it. To do this, the speech therapist collects a detailed medical history on an individual basis, examines the condition of the speech organs and draws a conclusion based on the examination.
Stage II of work (conducted as a whole lesson)
Subject . Clarification of the pronunciation of the sound k.
Target . Achieve a clear, correct pronunciation of the sound k in onomatopoeia. Previous work. The movements of the tongue necessary for the correct pronunciation of sounds were clarified.
Preparatory work. The teacher prepares toys or pictures (chicken, rooster, sparrow, cuckoo, frog). Checks again how the children pronounce the sound k to find out who needs more attention.
The story “Who is screaming?” Short description
The teacher, turning to the children, says: “Remember, children, how you and I went for a walk in the forest at the dacha? We were going for a walk. We went out into the yard, and a chicken comes towards us (takes out a toy, puts it on the table) and shouts: “ko-ko-ko...” How does she scream? (“Ko-ko-ko.”) We move on, and the hen cackles: “Ko-ko-ko.” How does she cackle? (“Where, where.”) “Into the forest,” we answered her and moved on. A rooster sits on the fence (takes out the rooster) and shouts: “kuka-re-ku!” How does the rooster crow? (“Ku-ka-re-ku!”) We went further along the road, past the vegetable garden. We look, and the sparrows are pecking at the grains of the sunflowers (he takes out the sparrow). The children chased them away. How did you drive them away? (“Shoot-shoot.”) We came to the forest. It's good there. We started collecting flowers, and suddenly we heard a cuckoo cuckoo (takes out the cuckoo): “cuckoo.” How does a cuckoo crow? (“Ku-ku…”) We picked a lot of flowers and went back. We hear frogs croaking (takes out a frog): “kva-kva.” How do frogs croak? (“Kva-kva.”) We walked in the forest and returned home.”
Then the teacher asks the children who they saw and who shouted how. Methodical instructions. Make sure that in onomatopoeia children pronounce the sound k clearly and answer questions with complete answers.
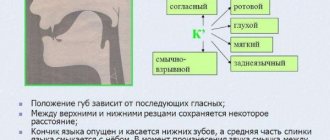
Normal articulation for the sounds K and Kь
When pronouncing the phoneme “K”, the organs of the speech apparatus take the following position:
- The lips are opened in accordance with the following vowel sound.
- The tip of the tongue is behind the lower teeth. The organ does not touch the teeth, but is located closer to the middle of the oral cavity.
- The middle of the tongue is lowered.
- The back of the organ focuses on the soft part of the palate. The edges on the sides slightly touch the hard palate.
- The soft palate is raised. It should block the passage into the nasal cavity.
- Vocal cords in a relaxed state;
- Air through the mouth.
The articulation of the sound “Кь” suggests the following features:
- The corners of the lips are pulled back.
- Lips pressed to teeth.
- The tip of the tongue focuses on the lower incisors.
- The middle of the tongue is raised. It touches the middle of the hard palate.
Visual demonstration in the picture:
Exercises to build correct articulation
The importance of articulatory gymnastics has been proven by scientific research. A child’s rapid mastery of reproducing any sound depends on the training of the speech organs. Such techniques are suitable for non-speaking children and the older group of people after an illness (stroke). Each letter has its own exercises.
Basic training sessions to prepare before making the sounds “K” and “K”:
- pancake They open the oral cavity well. The relaxed tongue is placed on the lower lip. Next, alternate a smile with a gloomy expression. The tongue is motionless.
- slide. The baby is asked to open his mouth wide. Bend the tongue to form a slide. Place the tip of the organ on the lower incisors. Hold the position for 10 seconds;
- massage. Exercise to relax muscles. Open your mouth slightly. Move the tongue along the lower lip. Bite it little by little with your teeth;
- the wind was blowing from the hill. To carry out the work, the respiratory system is activated. The child learns to move a stream of air across the tongue. The baby opens his mouth and performs the slide exercise with his tongue. Next you need to take a deep breath. Then exhale gradually, focusing on the position of the middle and root of the tongue. They should block the flow of air to the nasal cavity. It produces a groaning sound. This way you can develop the pronunciation of the phoneme “K”;
- the tongue is a strongman. The child is asked to play a game in which the tongue will resist a foreign object. A clean teaspoon is suitable for this exercise. An adult brings it to the tip of the tongue. The baby needs to try to push the object out of the mouth. The mouth is well open.
Important: the main task of an adult is to achieve the correct position of the tongue. The middle part should rise towards the hard palate and the root of the organ towards the soft palate. The exercise is carried out gradually so as not to overload the muscles.
Expert opinion
Margarita Sergeevna S.
Speech pathologist and speech pathologist with 15 years of experience working in various speech correction centers with children of different ages.
The detailed technology and sequence of exercises will be suggested by a speech therapist, taking into account the child’s abilities individually.
Recommendations for performing articulation gymnastics
Secrets to successfully mastering the exercises:
- Classes are held 2-3 times a day. Duration of execution is up to 5 minutes.
- All movements of the speech organs are repeated 3-4 times.
- Gradual increase in load on the speech apparatus. First, carry out statistical types of exercises (hold the position for 15-20 seconds). Then switch to dynamic ones, increasing the motor activity of the organs.
- Carry out tasks in a playful way.
- Use a mirror for clarity.
Important: you need to start performing a new task after you have mastered the previous one.
Structure of a lesson on automating sounds [K] and [G]
After setting the phonemes [K] and [G], it is necessary to begin their automation. Classes for each sound are conducted separately. The first to automate is [K], and after entering it into coherent speech, they move on to automating [G].
Each lesson is focused on the implementation of several groups of tasks.
Educational:
- Clarification of ideas about the method of reproducing an automated phoneme separately, in syllables, phrases, independent speech.
- Introducing the terms sound, syllable, word, sentence.
- Teaching basic reading skills.
- Increasing vocabulary on a specific lexical topic.
Educational:
- Improving the motor activity of the speech organs.
- Formation of sensory perception of articulatory position.
- Improving phonemic processes.
- Developing the ability to perform sound-letter analysis using graphic images.
- Improving non-speech mental processes.
Educational:
- Stimulating interest in the activity.
- Developing perseverance, determination, and an adequate attitude towards one’s speech disorders.
Corrective:
- Correction of incorrect position of automated sound.
- Elimination of speech negativism.
Methods for setting the sound K and Kb
Speech therapists use the following methods:
- By imitation.
- Carry out in front of a mirror. An adult coughs quietly as he exhales with his mouth wide open.
- The child should see the position of the tongue at this moment. When coughing, the sounds “K” and “E” should be heard. You should try to avoid a pronounced “X” between them.
- Afterwards the child is asked to repeat what he heard. He should cough into his palm.
- Under the baby's chin, you can put a little pressure on the baby's neck for a short time. This will create a clearer “K” sound.
- Ask your baby to take a deep breath and exhale. After exhaling completely, cough in a whisper. Try to remove the phoneme “X” when coughing.
- The exercise is performed 2-3 times a day. As soon as you get the closest possible “K” sound. The child is asked to cough and pronounce Ka-Ka-Ka, etc.
- After successfully completing the lessons, the baby is taught to pronounce an isolated sound.
- Mechanical method. The production is carried out from the sound “T” (plosive, anterior lingual, anterior palatal). Performed using a probe and spatula. Afterwards, the instruments are replaced with the finger of an adult, and then of a child. Press on the tip of the tongue, moving it deeper while pronouncing the syllables Ta – Ta – Ta. Almost immediately it turns out Ka - Ka - Ka. The result is consolidated over time, excluding mechanical assistance.
The soft sound “Кь” is made mechanically, just like the hard one. In this case, the syllables Tya - Tya - Tya or Ti - Ti - Ti are used. Setting with tools is the most common method used by specialists for the letter “K”.
Important Rules
Before you start producing any sound, you need to understand some points. You can’t try to “skip” one stage and move on to the next. In this case, it will not be possible to correct the defect.
It is necessary to devote time to articulation and breathing exercises. Dynamic exercises are performed to a count of ten, static exercises to a count of five. Execution rules:
- strictly in front of the mirror;
- The child’s attention is focused on the correct posture;
- do it every day.
With dysarthria, it may take several months to practice the correct movements. There is no need to rush into staging. In severe cases, drug therapy is used to correct increased or decreased tone. Physiotherapy can also help speed up the process.