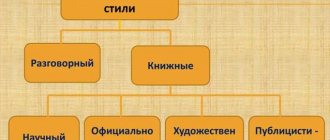
Types of visual and expressive means
- Tropes (words with a figurative meaning): allegory, hyperbole, litotes, metaphor, metonymy, oxymoron, personification, periphrase, synecdoche, comparison, epithet.
- Stylistic figures of speech : anaphora, epiphora, parallelism, antithesis, non-union, polyunion, gradation, inversion, parcellation, ellipsis, rhetorical constructions.
- Sound writing : alliteration, assonance.
- Lexical means : archaisms, neologisms, occasionalisms, dialectisms, barbarisms, exoticisms, etc.
- Stanza , size, rhythm.
In this article we will tell you about the trails and what tasks can be associated with them.
Syntactic means
Anaphora - The thunderstorm was not in vain. Repetition of words or combinations of words at the beginning of sentences or poetic lines.Antithesis - Long hair - short mind;.Contrast.Gradation - I came, I saw, I conquered! Arrangement of words and expressions in increasing (ascending) or decreasing (descending) significance.Inversion - Once upon a time there lived a grandfather and a woman. Reverse word order.Compositional junction (lexical repetition) - It was a wonderful sound. It was the best voice I've heard in years. Repeating at the beginning of a new sentence words from the previous sentence, usually ending it. Multi-union - The ocean walked before my eyes, and swayed, and thundered, and sparkled, and faded away. Deliberate use of a repeating conjunction.Oxymoron - Dead souls. A combination of words that cannot be combined in meaning.Parcellation - He saw me and froze. I was surprised. Silenced. Deliberate division of a sentence into semantically significant segments. Rhetorical question, exclamation, appeal - What a summer, what a summer! Who hasn’t cursed the stationmasters, who hasn’t sworn at them? Citizens, let's make our city green and cozy! Expressing a statement in interrogative form; to attract attention; increased emotional impact. Series, pairwise combination of homogeneous members - Nature helps to fight loneliness, overcome despair, powerlessness, forget hostility, envy, and the deceit of friends. The use of homogeneous members for greater artistic expressiveness of the textSyntactic parallelism - To be able to speak is an art. Listening is a culture. (D. Likhachev) Similar, parallel construction of phrases and lines. Default - But listen: if I owe you... I own a dagger, / I was born near the Caucasus. The author deliberately understates something, interrupts the hero’s thoughts so that the reader can think for himself what he wanted to say.Ellipsis - Guys - for the axes! (the word “taken” is missing) Omission of some member of the sentence that is easily restored from the context Epiphora - I've been coming to you all my life. I believed in you all my life. Same ending for several sentences.Allegory
Allegory is a trope; figurative expression; transfer of meanings from one subject to another; — isolation of concepts through an artistic image.
Functions of allegory
- increased imagery;
- creation of special expressiveness.
| Examples: | |
| Allegories can be introduced by the author from old fables and fairy tales, since they arose on the basis of myths. | |
| Fox | deceit |
| Wolf | greed |
| Snake | deceit |
| Bird | freedom, liberation |
| Libra, Themis | justice, impartiality |
| Scythe, Hades | death |
Hyperbola
Hyperbole is a trope; figurative expression; exaggeration that sharply emphasizes the strength or significance of some phenomenon.
Hyperbole is a figurative and expressive means opposite to litotes.
Hyperbola functions
- achieving a comic or satirical effect;
- emphasizing the predominance of a phenomenon over others;
- creation of special expressiveness.
| Examples: |
| “I lived a hundred lives , And I was with you only for a moment.”; “I, and you too, have eternity in reserve ...”; “ In a hundred and forty suns the sunset was burning ”; “If I wake up before the sun and wake up at midnight, then I’ll crush the mountain. ” |
Paths - means of expressive speech
What is a trope?
The linguistic term "trope" literally means "turn" in Greek. It is called a figurative turn of speech created by an artist of words, based on a rethinking of the direct meaning of the word and the emergence of a new, figurative meaning. The trope is based on a comparison of two phenomena that are similar to each other in some aspects or characteristics. The author, using the signs of one phenomenon, characterizes another object with their help, trying to explain it and at the same time create a vivid, figurative idea about it in the reader.
The music rang in the garden with such inexpressible grief. The fresh and pungent smell of the sea On a platter were oysters in ice.
A. Akhmatova. In the evening.
Definition
Let us define what a trope is.
Definition
A trope is a figurative figure of speech in which a word or expression is used in a figurative meaning based on the comparison of two objects or phenomena related to each other by semantic relations.
A trope can be called a form of poetic thinking. An artist of words easily manipulates words, creating new combinations of words in artistic speech, which in an unusual proximity to each other create an unexpectedly bright and visible image:
Litotes
Litota - trope; figurative expression; an understatement that emphasizes the lack of strength or weakening of the significance of some phenomenon.
Functions of litotes
- emphasizing the insignificance of a phenomenon;
- creation of special expressiveness;
- achieving a comic or satirical effect.
| Examples: |
| “I have lived a hundred lives without you, And I was with you only for a moment ”; “I go outcast, homeless and poorer than the last poor. ” |
Metaphor
Metaphor - trope; figurative expression; hidden comparison.
Usually expressed through a noun or verb.
For ease of understanding, we advise you to transform the proposed expression with a noun into a comparison (Golden, ripe fruits - fruits like gold), this way you will accurately define the metaphor. If the comparison (specifically with a noun) fails, then you made a mistake.
Functions of metaphor
- increased imagery;
- creation of special expressiveness.
| Examples: |
| “ The seething cauldron of the universe ” (the universe is like a seething cauldron); “And the sun’s yellow swords pierced the first hour of midday” (the rays of the sun are like yellow swords); “ The forest is full of silence . And yellow leaves. Flocks of birds left nature: the concert hall was left without artists ” (the forest as a concert hall); “Today there was a wonderful rain – Silver carnation with a diamond head ” (rain like a carnation) |
Literature and censorship: tricks of Russian classics
Russian writers used allegory to circumvent censorship. You can especially often find this technique in the works of Saltykov-Shchedrin, who interacted with his reader, hiding the true meaning from the censors. The fairy tale “The Wise Minnow” is very rich in artistic terms - it shows not only the desire to deceive censors, but also to reveal the essence of some life phenomena.
Drawing the image of a “small fish,” pitiful and cowardly, the writer perfectly reflected the essence of another man in the street. The apt characterization hits the mark, illustrating the breed of petty and worthless citizen through the minnow.
Endowing fish with human qualities , Saltykov-Shchedrin in his work touches on the philosophical problem of finding the meaning of life and the purpose of man.
Another example of allegory is the poem “Dead Souls”, where a hidden meaning is hidden even in the names of the characters - Sobakevich, Plyushkin. In this work there is a whole allusive world, showing the whole of Russia in cross-section, along with its vices and shortcomings.
The way of life of the time in which Gogol lived is described very figuratively - just look at the allegorical world of peasants who died or escaped from their masters! This world seems to be contrasted with the world of the living, thereby emphasizing the poverty of the morals of the main characters.
There are also many works in foreign literature that use allegory. For example, Dante depicted human passions in the form of animals in his Divine Comedy:
- panther - sensuality;
- Leo - pride and ambition;
- she-wolf - greed.
Medieval oriental poetry is also full of allegories - Alisher Navoi in “Seven Planets” talks about love and at the same time, in an allegorical form, denounces the rulers of that time. Sultan Hussein-Merza and his courtiers are subjected to veiled criticism - the author exposes tyranny, greed, ignorance and cruelty using allegorical literary means.
Thus , allegory is a way to give a work brightness , originality, expressiveness and originality. Through a hidden hint, you can express the idea more clearly and the image more colorful, which is not always possible when using conventional storytelling.
Metonymy
Metonymy - trope; figurative expression; replacing one word or expression with another based on similar meanings.
Functions of metonymy
- noticeable shortening of the author's thoughts;
- increased expressiveness.
| Examples: |
| “ Egypt went home ” (not Egypt, but the inhabitants of Egypt); “Tormented by the madness of Melpomene , in this life I thirst only for peace...” (not by Melpomene herself, but by the tragedy played in the theater (Melpomene is the muse of tragedy)). “ No one will offend the Field of Gaia “If not on silver, I ate on gold ” (not on gold in the literal sense, but on dishes made of gold); “ Watercolor in the grip of an old baguette seemed dull ” (baguette - frame made of baguette); “ Hearing the smell of foam ” (foamy is alcohol). |
Application of phraseological units
Phraseologisms deserve special attention - apt set expressions characteristic of one specific language.
In our case - Russian. Along with other linguistic units, they form an important lexical part in sentences, are independent and have their own indirect meanings.
They consist of two or more words that form a uniform semantic structure.
Relevance depends on the context or life situation. There is an expressive commentary for almost any event, behavior or character.
For example:
- Play blind man's buff - to hide something, to deceive.
- Hands folded - doing nothing.
- The cat cried - very little.
- You can’t ride a goat - about an unapproachable person who doesn’t know fun.
It can be difficult to understand the essence of a veiled phrase ; besides, there have been so many persistent constructions historically that it is impossible to remember them all.
Entire volumes of dictionaries with interpretation and examples of use are devoted to phraseological units. This is not only a reflection of the rich culture of the people, but also a treasure trove of research for linguists and simply interested people.
Oxymoron
Oxymoron (Oxymoron) - trope; figurative expression; connection of two contradictory meanings; connection of the incompatible.
Functions of an oxymoron
- focusing readers' attention;
- unusual reflection of feelings;
- expresses the thoughts of the poet/lyrical character about the presented phenomenon
| Examples: |
| “He lies to you so richly and so poorly !”; “ The eternal moment ”; “ I ask the beggar for bread , I give to the rich for poverty , ... I hand over the key to the robber , I blush the pallor with whitewash .”; “Even then there was no place ! Even then on earth there was a home for me everywhere .”; “And in my eyes there is always Hot snow , bloody snow” |
The role of the trope in a work of fiction
Paths serve not only to clarify details, signs and other characteristics of a phenomenon. They, as artistic means, reveal the peculiarities of the creative thinking of the author of the work, who, with the help of various tropes, achieves a figurative picture of the surrounding world. To clearly explain this, let us remember how in his “Notes on Art” the artist N. Zhukov wrote about the variety of ways of figuratively artistic embodiment of an object or object of reality:
How to convey in words the impression of a very fat person? We can say that he is disproportionately fat. You can say it differently: he could hardly move. Or: I had difficulty entering the door. Or again: he was so thick that he resembled a ball. You can determine the thickness by saying that the person was short, he weighed 130 kg. There are hundreds of ways to determine body build. But here’s how convincingly the feeling of a full body can be conveyed through a detail: he was so fat that his cheeks were visible from his back. And you immediately feel how ordinary the previous examples were and how sharp the artist’s eye was, capturing the main thing in the image of the person standing in front of him.
As we can see, the artistic trope (he was so thick that his cheeks were visible from behind his back) helped the author create a visible and vivid image. With its help, the essence of the phenomenon is succinctly conveyed.
The use of tropes gives the phenomenon being described that meaning, a new shade of meaning that the author needs in a given speech situation, and also conveys his personal assessment of the phenomenon .
Personification
Personification - trope; figurative expression; endowing inanimate objects with the properties of animate ones (the ability to think, speak, feel and act).
Impersonation functions
- increased imagery;
- creating expressiveness;
- reflection of the author's position through the choice of associative series.
| Examples: |
| “For the first time , the moon these chains and trembling... Sculpts a bust not sculpted by anyone”; “Spring, I’m from the street, where the poplar is surprised , Where the distance is afraid , Where the house is afraid to fall ,”; “And the streets of ancient Prague are silent , winding one another, But they play like ravines .” “Turning its face to the south, the Pine squints in the sun .” |
Periphrase
Periphrase - trope; figurative expression; replacing the name of a phenomenon or the name of a person by describing their essential features or indicating their characteristic features.
Paraphrase functions
- designation of a person, phenomenon, object;
- expression of the author's position;
- richness of speech by avoiding repetition.
| Examples: |
| “Here the horde followed the horde. Bringing fire and chains !” (fire and chains - war); “So to speak, a slave of honor ... struck down by a bullet...” (slave of honor - Pushkin); “ The Volga Stronghold , But the blind huts cannot be helped” (Volzhskaya Stronghold - Volgograd) |
Repeat
Repetition is a trope; figurative expression; partial or complete repetition of a word, expression, line.
Repeat functions
- sound recording enhancement;
- strengthening the quality of an object, phenomenon;
- emphasis on quantity, duration;
- achieving emotional impact.
| Examples: |
| “ Trucks sleep cranes sleep “And spins , we, the stars, and the whole ocean spins round and round .”; “But don’t be angry with me , Nadya, and don’t be angry with me , Martha.”; " We are Russians. We are children of the Volga." |
Synecdoche
Synecdoche - trope; figurative expression; replacing the singular with the plural and vice versa; the name of the part instead of the whole.
Synecdoche is a type of metonymy.
Functions of synecdoche
- saturation of speech by avoiding repetition;
- increased imagery;
- demonstration by the author of his skill in choosing associations / demonstration of his skill
| Examples: |
| “Working with our elbows, we ran” (elbows instead of elbows); “We all look at Napoleons” (we all want to be known as Napoleon); “The waters flowed quietly. The beetle was buzzing.." (beetle instead of beetle); “And it was heard until dawn how the Frenchman rejoiced” (the French rejoiced, and not just the Frenchman). |
Varieties of Tropes
All techniques with the help of which the meaning of the written text is enhanced are conventionally divided into 2 large groups: lexical and syntactic.
The first category is formed by tropes - familiar words with a figurative meaning.
Writers and poets often use this means, exaggerating some properties of an object or endowing it with uncharacteristic features.
Pushkin often did this, which is why his poems contain allegories, exaggerations, parcellations and many other figures.
The left side provides a brief definition of the term, and the right side contains possible uses.
Examples taken from poetry (excerpts), everyday speech, advertising and social slogans.
| An epithet is an emotionally charged adjective used in a figurative meaning, often used in poetry. | Examples of epithets: golden time, cheerful blossoming of trees, young spring, winged swing, fluffy snow, velvet season, gray morning, heated argument, soft voice. |
| Personification is giving an inanimate object characteristics characteristic of living beings. | Personification in literature: an angry blizzard, harsh rocks, an enthusiastic spring, surprised forget-me-nots, a sad willow, a laughing sea, a crazy wind, a gentle sun. |
| Metaphor is an expressive device in which the described object is endowed with the characteristics of another. The means is realized using a word or a figure of speech. | The forest is burning crimson, icy hands, goosebumps, a lacy shadow, a silver stream, the fire of desire is burning. |
| Comparison - reflects the similarity between two objects, and it may not be obvious. | Examples: water like glass; the blizzard howls like a wolf; snowflakes like fluff; hum, like from a barrel; work is not a wolf, hunger is not an aunt (negative comparison). |
| Metonymy - the meaning of this literary device is that it isolates a sign or characteristic feature, naming the object with the word it replaces. Example: a part instead of a whole, an object instead of what is in it. | The bucket spilled, eat 3 plates, the hand of Moscow, the kettle boiled, the audience applauded, live to see gray hairs. |
| Synecdoche is a special case of metonymy, often used in advertising and poetry. | Examples: the Frenchman rejoices; the Swede stabs and chops; first racket; save your penny; wave of discounts; the collection is waiting for buyers; victory over the microbe. |
| Irony is the use of a word or phrase in the opposite, mocking meaning. Evil irony is sarcasm. | Usage in everyday speech and literature: smart head - about a stupid person; I've been dreaming all my life - actually not; my mansions are about a modest home; what beauty - about some incident; the color of the capital is about unpleasant people; our benefactor is about a bribe-taker. |
| Grotesque is a complex technique that combines metaphor and hyperbole. | Examples of the grotesque in literature: Gulliver and the Lilliputians, Gogol’s “The Nose,” the dreams of Raskolnikov and Tatyana Larina. The essence of the technique is to bring a situation, phenomenon or human vice to the point of absurdity. |
Comparison
Comparison is a trope; figurative expression; comparison of one object/phenomenon with another.
Usually, comparison is achieved with the help of conjunctions like, so, exactly, as if, like, that, as if, etc.
Comparison functions
- creating richness of speech;
- creation of special expressiveness.
| Examples: |
| “I am leaving the bottomless, as if there is a bottom to something”: “My perceptions are still washing over me like streams ”; “You looked at me, as if encouraging me ”; “I lived like a stupid puppy ”; “And the plows and plows float, silver, along the ax, like seagulls in the morning...” |