- Speech therapist.No
- Dislalia (FNR)
Phonetic speech disorder is a group of speech disorders represented by disorders in which the leading symptom is a violation of sound pronunciation. The child's intellectual and mental development corresponds to his age. There may be disturbances in attention, behavior, and motor disorders that are concomitant.
This group includes dyslalia (simple, complex) or otherwise “tongue-tied.”
Dyslalia is a violation of sound pronunciation with normal hearing and intact innervation of the articulatory apparatus. In practice, the pronunciation of any of the phonemes of the native language can be impaired (dyslalia) or difficult (paralalia).
Phonetic speech disorder (FSD) in medical classification: F80.0 Specific disorder of speech articulation.
Forms of dyslalia
Monomorphic (simple) One sound or several sounds from one group suffers (S-Z-C or Sh-Zh-Ch). Polymorphic (complex) Several sounds from different groups suffer (S-R-K-SH). Physiological (age-related) Sound pronunciation disorders up to 5 years of age, caused by insufficient development of articulation organs. After 5 years it goes away on its own. This is the only form of dyslalia that is present in all people at some stage of development. Functional Impairment of sound pronunciation in the absence of deviations in the articulatory apparatus and the functioning of the central nervous system, auditory and peripheral articulatory apparatus. The ability to voluntarily accept and maintain certain positions of the articulatory organs necessary for pronouncing sounds is impaired. Violation of sound pronunciation may be associated with the inability to distinguish and differentiate phonemes. Quite often, isolated use of a sound may not be disrupted, but changed in spontaneous speech. The degree of severity is determined by the severity of the defect and the number of disturbed sounds. Organic (mechanical) Caused by hereditary, congenital or acquired anatomical defects of the peripheral articulatory apparatus (malocclusions - progeny, prognathia, “thick” tongue, short frenulum, etc.).
Dyslalia (sound pronunciation problems)
In NeuroLogopedics, specialists, in addition to traditional staging, massage and universal probes, use vibration massagers Z-Vibe®, DnZ-Vibe®, Z-Grabber™, ARK Animal Menagerie in their work.
The principle of operation of Z-Vibe is to influence (the tongue, the inner and outer surfaces of the cheeks, forehead, cheeks, chin) a person with high-frequency vibrations. Allows you to very effectively stretch the “frenulum”. Support the tongue, massage the hollow of the tongue to help produce the C sound and much more. With sufficient skills of a speech therapist, this massager allows you to “set” the sound R to a child during 1 lesson. The Z-Vibe speech therapy electric massager is recognized by many speech therapists as the best equipment in the world for conducting speech therapy massage and preparing a child’s articulatory muscles for special classes.
This electric massager, with proper and constant speech therapy massage, can reduce the time spent on correcting a child’s speech by at least 3-5 times compared to traditional massage probes.
In our center, a speech therapist, defectologist, and speech therapist conduct classes with children. To do this, our center’s specialists have everything you need:
- more than 18,000 developmental, educational speech and speech therapy games;
- sensory room;
- Montessori environment;
- sensory integration room;
- interactive giant sandbox;
- light and water tables;
- unique innovative equipment;
- neuroacoustic programs (Tomatis Method and IN Time)
- rhythm therapy and color therapy;
– and all these most advanced developments in the field of education, development and correction of children are tools in the hands of speech therapists, allowing them to achieve high, sustainable results in solving the most difficult issues.
But parents must remember that speech disorders, as a rule, do not go away without leaving a trace. Even after correcting the sound defect, the child’s brain has already formed incorrect stereotypes that need to be changed. If this is not done in time, then speech disorders can subsequently cause serious problems with learning at school , leading to dyslexia, dysgraphia and dysorthography. And these problems are much more difficult and take longer to eliminate; they can cause serious psychological problems. That is why it is very important to eliminate sound pronunciation disorders and carry out neuropsychological correction in a timely manner, without “delaying” time and without “postponing” for later.
Speech therapy classes for the correction of dyslalia should be conducted regularly, at least 3–4 times a week. It is important that speech therapist tasks and articulation gymnastics are also performed at home. The duration of classes for simple dyslalia is from 3 months; for complex dyslalia – 3-6 months.
In most cases, dyslalia can be successfully corrected. The success and timing of overcoming dyslalia are determined by the complexity of the defect, the age and individual characteristics of the child, the literacy of the approach, the regularity of classes, and the participation of parents. In preschoolers, sound pronunciation defects are corrected faster than in schoolchildren, and in elementary school students - faster than in middle and high school students.
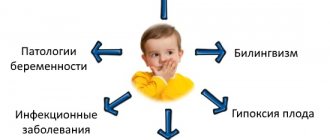
Causes of functional dyslalia
Somatic Physical and neurological weakness due to long-term chronic diseases of the body (indigestion, frequent colds) Social
- Pedagogical neglect (parents do not correct deficiencies in their children’s speech and do not demonstrate examples of correct sound pronunciation).
- Bilingualism in the family (When parents speak different languages, the child inserts another into one language. For example, French + Russian = throat sound “R”).
- A sample of incorrect speech in a child’s environment (by imitation).
Incorrect articulation Selecting incorrect articulation Underdevelopment of phonemic hearing Physical hearing can be preserved, but phonemic hearing is impaired.
Disadvantages of pronunciation of individual sounds
| Defective sound | Phonetic defect (sound distortion) | Phonemic defect (confusion, sound replacement) | ||
| Name of pronunciation defect | Types of defective pronunciation | Name of pronunciation defect | Types of substitutions | |
| Sound R | Rotacism | Velar, uvular, lateral, buccal, single-impact, “coachman” | Pararotacism | Р = Р' Р = Л' Р = J Р = Г Р =Д |
| Sound L Sound L' | Lambdacism | Bilabial, softened | Paralambdacism | L = Y L = G L = L' L = R |
| Sounds S, S' Sounds Z, Z' Sound C | Sigmatism | Interdental, labial-dental, lateral, subdental, sibilant | Parasigmatism | S, Z, C = W S, Z, C = F S, Z, C = T S, Z, C = Shch S - W; C = H |
| Sound Ш Sound Ж Sound Ш Sound Ш | Sigmatism | Mesdental, buccal, lateral, “lower”, posterior lingual, softened, shortened, affricative | Parasigmatism | Sh, Zh, Shch = T Sh, Zh, Shch = F Zh = Sh Zh = Z Shch = S' Sh = Shch Ch = T'; Ch = Sh' |
| Sound j | Yotacism | Soft lower and upper articulation | Paraiotacism | J = L' |
| Sounds K, K | Kappacism | Vocal, laryngeal | Paracapacism | K = T |
| Sounds G, G | Gammacism | Fricative velar, pharyngeal | Paragammatism | G = T |
| Sounds X, X | Hitism | Vocal, laryngeal | Parachytism | |
Dysarthria
Dysarthria is a violation of sound pronunciation caused by insufficient innervation of the speech apparatus (organic damage to the central part of the speech motor analyzer).
The speech of a dysarthric person is slurred, incomprehensible to others, like “porridge in the mouth.” The articulation of many groups of sounds is impaired: hissing, whistling, sonorants, and sometimes vowels. Speech breathing is shallow, arrhythmic. Hypersalivation (increased salivation) is observed. The mobility and sensitivity of the speech muscles suffers. Dysarthric has difficulty finding an articulatory posture (licking lips, placing tongue behind upper teeth, etc.). Impaired sound pronunciation with dysarthria is one of the symptoms of a more complex speech disorder. Speech hearing and auditory differentiation of sounds also suffer, a poor vocabulary, and unformed grammatical structure of speech are observed. Secondary mental layers (behavioral problems) are also observed. All these difficulties lead to persistent poor performance in school (dysgraphia, dyslexia, dysorthography).
Despite its similarities with dyslalia, dysarthria is a more complex and persistent disorder that requires help and psychological support.
In adults, correction of dysarthria is even slower than in children, but it is possible.
Case from practice
Kolya, 5 years old. The sound pronunciation of the sounds Ш, Ж, Х, Л, Л, Р, Рь is impaired . There is hypersalivation and difficulty in repeating the articulatory pattern. Phonemic processes are disrupted, lexico-grammatical structure is disrupted. As a result of 3 courses of correctional classes, dysarthria was compensated, sounds were automated, work continues on coherent speech, improving vocabulary and grammar.
Find out more about the Center's services and sign up for a consultation or lesson
You can call (812)
640-90-77
, or by filling out the form below.
Speech therapy technique for dyslalia
Stages of speech therapy for dyslalia
Preparatory stage
- Trusting relationship with the child.
- Development of auditory attention, auditory memory and phonemic perception.
- Formation of the articulatory base.
Stage of formation of primary pronunciation skills
- Sound production.
- Automation of sound (in isolation, in syllables, in words, in phrases).
- Sound differentiation.
Stage of formation of communication skills
- The use of sound in all communication situations.
- Speech control
Phonetic speech disorders in children: symptoms, causes and treatment
Phonetic speech disorder manifests itself in distorted and inaccurate pronunciation of sounds of one or more categories (hissing, whistling, and so on). In this case, no hearing impairment is observed. What are the full symptoms of the disease? What causes it? And what treatments are most effective?
Symptoms
The symptoms are as follows. A child can simultaneously pronounce sounds that are problematic for him, insert them incorrectly in words, and replace them with ones that are easier for him to pronounce. In addition, children with phonetic speech disorder have difficulty coming up with words containing these sounds. And, most importantly, they do not understand the meaning of sounds, so they use them randomly in a variety of words.
| Name | List of sounds |
| whistling | “ts”, “s” (soft and hard), “z” (soft and hard); |
| sonorous | “r” (soft and hard) and “l” (soft and hard); |
| voiced | “d”, “b”, “c”, “d”, “g” and “h”; |
| soft | “d”, “n” and soft “t”; |
| posterior lingual | “g” (hard and soft), “k” (hard and soft), “x” (hard and soft); |
| sizzling | “sh”, “sch”, “zh” and “ch”. |
Depending on the identified symptoms, the degree of the disease is determined.
Degrees
- A simple violation. If a child does not pronounce sounds only from a single group, then this disorder is called monomorphic. Other names: “simple”, “partial”.
- Complex violation. If it is two or more, it is polymorphic. Other names: “complex”, “diffuse”.
Consequences
A child with a similar speech defect, firstly, makes mistakes in pronunciation. Secondly, when he comes across letters that are problematic for him, he reads them slowly and/or incorrectly. And thirdly, while writing, he replaces letters with others or completely skips them. This negatively affects the performance of children in kindergarten, primary school, and then in secondary school.
Causes
Phonetic speech disorder occurs due to difficulties associated with the development of the organs of the articulatory apparatus. The causes of the defect are provoked by problems in the formation of articulatory motor skills or neurodynamic disorders. In the first case, the causes are paresis of the nerve (facial, trigeminal or hypoglossal). In the case of neurodynamic disorders, there is a lack of inter-analyzer connections or difficulties in the processes occurring in the cerebral cortex (excitatory and inhibitory processes).
Phonetic speech disorders in children: treatment
Who chooses the strategy?
How to get rid of the disease is decided jointly and mutually by the following experts: pediatrician, child psychologist and children's speech therapist. Most of the responsibility rests, of course, with the speech therapist.
How does the treatment work?
Classes with a speech therapist are the key to correcting a speech defect. During lessons, the specialist first of all provokes the child’s desire to learn other sounds. As soon as interest appears, children begin to imitate sounds, try to distinguish them from each other, and so on.
As a result of classes with a speech therapist (depending on the chosen treatment tactics):
- accurate and correct pronunciations of sounds are developed;
- the functioning of the organs of the articulatory apparatus is normalized;
- hearing, attention, memory develops;
- the perception of surrounding speech improves;
- a practical skill is formed: children can differentiate sounds;
- the skill of connected speech develops, and so on.
What other useful activities are there?
Speech therapy lessons not only help you get rid of phonetic speech disorders. Children become more concentrated, attentive and adapted to acquiring new knowledge and skills.
How are the lessons going?
The postulates that the expert focuses on are accuracy, gradualism in actions and mandatory adherence to systematicity. Typically, classes are conducted individually and last no more than half an hour. Depending on the degree of development of the defect, two to three weekly sessions with a speech therapist are prescribed.