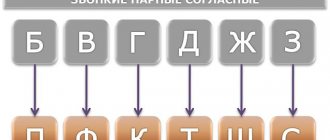
In the Russian language there are no two types of letters to denote hard consonants and soft consonants. In writing, paired hard and soft consonants are denoted by the same letter (see paragraph 1.5. Speech sounds and letters).
To indicate a soft consonant in writing, the Russian language has a special letter ь ( soft sign , or “er”).
Wed: table - so, bank - bathhouse.
| b is written | Examples |
| 1. At the end of a word. | Thread [n'it'], seven [s'em']. |
| 2. In the middle of a word, after a soft consonant and before a hard consonant. | Fate [sud'ba], darkness [t'ma]. |
| 3. In the middle of a word between two soft consonants if, when a word is changed or in related words, the second consonant becomes hard, and the first retains its softness. | Kuzmich [Kuz'm'ich'] - Kuzma [Kuz'ma], but: bow [ban't'ik] - bow [bow]. |
| 4. After a soft consonant l [l'] before any consonants. | Ballroom [bal'nyj], herring [s'el'd']. |
| 5. In instrumental plural forms. | People, children, horses. |
| 6. In the middle of numerals ending in -ten, -hundred. | Fifty, nine hundred. |
| 7. At the end of numerals ending in -twenty. | Eleven fifteen. |
| 8. In adjectives formed from the names of months using the suffix -sk. | September, October (but: January). |
| b is not written in combinations | Examples |
| -chk- | Barrel, river, stove. |
| -chn- | Ultimate, heartfelt |
| -LF- | Whisk, babysit. |
| -nsch- | Bath attendant, mason. |
| -rsch- | Lamplighter, welder. |
| -rch- | Spoiled. |
| -st- | Bridge, tail. |
| -nt- | A screw, a bow. |
| -schn- | Assistant. |
Note!
1) It is necessary to distinguish between the words: nanny and nurse; thinner and subtler.
- In the words nanny, the thinner second consonant is hard, the softness of the first consonant is indicated by the letter ь.
- In the words nurse, thinnest there is a combination of nch, which is written without ь.
2) b is not written between two l and two n.
Alley, pulp, early.
In which part of the word is the separating soft sign written?
In a word, the separating soft sign can be in the root or after it, but never after the prefix.
After a prefix that ends in a consonant, and before the vowels e, e, yu, i, a separating solid sign .
Here are examples of words with a separating soft sign in different parts of the word:
1. At the root of the word:
2. Between root and suffix:
3. Between the root and the ending of a word:
4. Between suffix and ending
1.11.2. Using b to denote grammatical forms
The soft sign, or ер (ь), can be used as an indicator of a certain grammatical form.
| b is written | Examples |
| 1. After sibilants in feminine nouns of the third declension in the singular form of the nominative and accusative case. | Night [night'], silence [t'ish]. |
| 2. After hissing adverbs (exceptions: already, married, unbearable). | Completely [completely], gallop [fskach']. |
| 3. After hissing in the second person singular verbs of the present and simple future tense - the questions what are you doing? what will you do? | You go [id'osh], you carry [voz'ish]. |
| 4. After sibilants and other consonants in the imperative mood - questions, what are you doing? what should you do? | Eat [sjesh], eat; stand up [fstan'], stand up. |
| 5. In the indefinite form of the verb (after t and h) - questions what to do? what to do? | Take [brat'], take, cut [str'ich'], get a haircut. |
| 6. In the genitive case of the plural of nouns in -nya (I declension), if there is a vowel before -nya, as well as in four exception nouns (young lady, hawthorn, village, kitchen). | Apple tree - apple trees, slave - slaves. Young lady - young ladies, hawthorn - hawthorn, village - villages, kitchen - kitchens. |
| b is not written | Examples |
| 1. After sibilants in nouns of the masculine gender of the second declension in the singular form of the nominative case. | Knife [nosh], doctor [doctor']. |
| 2. After hissing adjectives in the short form (masculine gender). | Hot, flammable. |
| 3. After sibilants in three adverbs-exceptions. | I can’t bear to get married. |
| 4. After sibilant plurals of feminine nouns in the genitive case, they begin with -a (I declension). | Cloud - cloud, grove - grove. |
| 5. In the genitive case of the plural of nouns in -nya (1st declension), if the -nya is preceded by a consonant (exceptions: young lady, hawthorn, village, kitchen). | Tower - towers, cherry - cherries. |
| 6. In verbs in the third person singular and plural form of the present and simple future tense - questions what does? what will he do? what are they doing? what will they do? | He hopes, he doesn’t believe it, they hope. |
Exception words with a soft separator
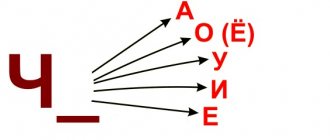
In native Russian words, the separating soft sign occurs only before the vowels e, ё, yu, ya, i. But in foreign words (especially French) it can appear before the letter o:
- postman;
- bouillon;
- medallion;
- canyon;
- cotillion;
- battalion;
- pavilion;
- companion.
Let's remember!
When transferred, the separating soft sign remains on the previous line: monkey-yana, curious.
Designation of softness of consonants
- At the end of a word, the sign b is written after any soft consonant, for example: horse (cf. windows), coal (cf. corner), lantern, blow (cf. blow).
- In the middle of the word a soft sign is written:
- after a soft L , standing before any consonant (hard or soft), for example: sick, herring, boy, sawyer ;
- after a soft consonant standing before a hard consonant , for example: Kuzma, less, struggle ;
- between two soft consonants only if, when the word changes, the second consonant becomes hard, and the first remains soft, for example: in a request (request), Kuzmich (Kuzma), about struggle (struggle).
How to avoid a mistake in a word with a soft separator
To write words with a soft separator correctly, you need to be able to parse the word according to its composition and know the exception words. Remember a simple procedure to determine when to write a soft and when a hard separator.
- Look what vowel comes after the consonant. The separating soft sign occurs only before the vowels e, ё, yu, ya, i. And also before o in borrowed words-exceptions.
- Parse the word according to its composition. If the prefix ends in a consonant and is followed by e, e, yu, i or i, we write a hard sign. At the root and after it it is soft.
Softening soft sign - when used: rules, examples
Softening soft sign
A soft sign can be used to indicate a paired consonant at the end: farrier, bologna, crucian carp, bittern, pain, moth.
It is important to note that the soft sign can be used to indicate softness before any letters that begin the second half of the word: melpomene, salvage, village council
Peculiarities of use in foreign words
The soft dividing sign (the rules of use are given in the next section) will not give two sounds to the letter in all cases. After all, if we take the word “battalion” as an example, we can see that the letter “o” has one sound of the same name, and the sign only gives the “n” softness. However, “ь” is still a separator, since it is in the middle of the word. However, this feature is observed only in those words that were originally borrowed from another language. Here are some interesting examples:
- pavilion;
- cotillion;
- canyon;
- postman;
- champignon;
- medallion;
- bouillon.
We recommend reading The Writer's Assistant - Bragalog
For the Russian language, the use of “ь” before the vowel letter “o” is atypical, therefore, in almost all cases, in this way one can almost accurately determine where in the text a word borrowed from a foreign language is located. This can be called the unspoken fourth role of this interesting letter.
However, we should not forget that Russian spelling can change over time, so the list of borrowed words becomes more extensive every year.
Other cases
The soft sign is used:
- in the instrumental case of the plural of some nouns (for example: children, people, four )
- the numeral eight in all cases (for example: eight, eight, eight );
- in the indefinite form of the verb : to carry - to tinker, to shave - to shave ;
- in the imperative mood of verbs (see Note 1): prepare, prepare, get ready .
- at the end of the following numerals (nominal and vin. case) five, six. seven, eight, nine, ten, eleven, twelve, thirteen, fourteen, fifteen, sixteen, seventeen, eighteen, nineteen, twenty, thirty ;
- before the letter O in some numerals : sextillion, quadrillion, quintillion, septillion, etc.
Notes:
(1) Pay attention to the use in the imperative mood of forms of a verb that has only two forms: the form of the 1st person singular. numbers - lie down and the form of the 2nd person, h. - lie down .
(2) There is a variant spelling of the following numerals: sextillion, quadrillion, quintillion, septillion , etc.
(3) Note: the nouns daughter, bone and whip are in the plural instrumental case. hours have the ending -yami ( daughters, bones, lashes ), and obsolete forms ( daughters, bones, lashes ) in modern language can only be found in phraseological units ( lie with bones, beat with lashes ).
(4) Remember: if the ending -nya is preceded by the letter l , then write a soft sign after it: bathhouse, bell tower, ironing room, smokehouse , etc.
(5) Remember the spelling of adverbs: exactly and colloquially before .
(6) Distinguish the spelling of suffixes -t-(sya ) and others, the infinitive from the suffix -t-(sya) of the form of the 3rd person of the present tense. Compare: She wants to study at the conservatory. studying there ?
(7) Pay attention to the spelling of the following words: that is (that is, namely), tush (musical greeting) and mascara (paint), thinner and thinnest , nanny and nurse .
(8) Pay attention to the peculiarity of the spelling of the word love . The common noun love in indirect cases loses the vowel o: there is no love, to love, about love. The proper name Lyubov retains this vowel in all forms: Young Blok spent a lot of time with Lyubov Dmitrievna Mendeleeva.
Possessive adjectives
Among the examples of “ь” there are often words that are formed by declension and placing possessive adjectives in indirect cases. However, it is worth remembering that this part of speech may not be inclined in all cases. Although in the Russian language you can still find several interesting words that will lend themselves to this rule, for example, “Cossack”. If you try to inflect a possessive adjective, you will see the following picture:
- nominative - Cossack;
- genitive - Cossack;
- dative - Cossack;
- accusative - Cossack;
- instrumental - Cossack;
- prepositional - about Cossack;
Particular attention should be paid to the dative, instrumental and prepositional cases, because it is in them that, in most cases, novice writers make common mistakes, simply forgetting that it is necessary to put “b”. However, it is worth understanding that not all possessive adjectives can decline, and even more so, the root will not always include the letter that must be preceded by “b”.
Test on the topic
- /10
Question 1 of 10The soft sign in Russian can
Start test
Hall of Fame
To get here, take the test.
- Natalia Barsukova
8/10
- Tatyana Kutukova
7/10
- Nadezhda Zaitseva
9/10
- Sergey Efremov
9/10
- Elena Skopina
8/10
One letter - three roles
The soft sign is one of the few letters that has remained virtually unchanged over many centuries. However, earlier it was called “er” and denoted a reduced vowel sound. Although the meaning of “b” did not change in any way. It was still an integral part of the Russian alphabet and was used to separate letters or soften sibilants. By the way, precisely because “er” was present earlier, today people often have to observe words with alternating vowel sounds: stump - stump.
In addition, it should be noted that a soft sign can have three meanings at once. Firstly, it can act as an indicator of softness (a striking example is the words: day, shadow, laziness, and so on). Secondly, this letter can indicate a grammatical feature of the noun, for example, its declension (help is a noun of 3 declension, since there is a soft sign at the end). And thirdly, “er” can be separative and add several sounds to those letters where there is usually one sound.
A little about the transfer
How to hyphenate words with a soft sign in the middle of a word? This is worth considering separately. Words with a soft sign in the middle of a word often cause difficulties when you need to move the word to another line. And there are many mistakes of this kind made in the texts.
Words with a soft sign in the middle are hyphenated as follows: first, you need to divide the word you want to hyphenate into syllables. We remember that, as many vowels in a word, there are as many syllables.
Step 1. Example: oh-no-me.
It is important to remember that when transferring a word with a separating soft sign to another line, you cannot separate the soft sign from the consonant in front - the transfer must be carried out only with it.
Step 2. Example: monkey-yana (example of correct transfer).
An important detail: if a soft sign is located at the end of a word, it cannot be moved to another line.
Incorrect example: mother-in-law, love, bear.
Correct example: father-in-law, love, honey.
When hyphenating, you cannot leave one letter on a line. This rule applies not only to words with a soft sign in the middle of the word, but also to any others.