Article:
Everyone wants to be heard.
For a speaker, not only information is important, but also the way it is presented. No one will support the point of view of a person who does not pronounce words clearly, “eats” endings or speaks too quietly. Diction is correct articulation, clear, intelligible speech that makes it easier for other people to understand what is said. A person with good pronunciation does not lisp, nasal or lisp. Every person has problems pronouncing individual morphemes or sound combinations. And for correct diction, training of the speech apparatus will be required. There are practically no problems with the pronunciation of vowels.
Correct diction is a guarantee of successful employment and communication skills. But good articulation is of particular importance for singers, actors, presenters and teachers. A vocalist with slurred pronunciation evokes double feelings in listeners: he seems to have sung everything correctly, but the words cannot be understood.
Diction is a fundamental element of human culture. Because a person with good pronunciation can convince almost anyone that he is right.
Speech diction
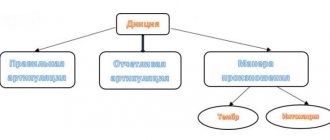
Diction is the clear pronunciation of sounds and words with their correct articulation. The speech apparatus produces sounds, and its violations and defects are the reason that a person’s diction is of low quality.
Speech diction consists of:
- From distinct articulation;
- Correct articulation;
- Manner of pronunciation: tempo and intonation.
Clear articulation - correct and clear pronunciation of sounds. It is thanks to clear articulation that the speaker’s speech is legible and his interlocutors easily understand what he wants to convey. Violation of this indicator of diction may occur due to the physiological characteristics of a person. You can improve the clarity of pronunciation of sounds by training your tongue and lip muscles.
Correct articulation is the coordinated movement of the muscles of the articulatory apparatus. Malocclusions and frenulums have a negative effect on articulation. With such physiological deviations, burr and nasal sound may appear.
Timbre. Often, the manner of pronunciation is influenced by a person’s temperament. The speaker may tend to monotony or speed up his speech. Often it is haste that occurs in people with poor diction. But, as practice shows, almost anyone can “defeat” this problem.
Intonation. As for intonation, it is formed primarily from the ability to clearly pronounce vowel sounds and stress.
You can set intonation with the help of some breathing exercises and reading aloud. Improving intonation is very difficult and painstaking work.
Problems with diction in children
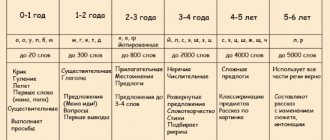
A pronunciation defect in children is considered to be a discrepancy between speech and age standards. The following is considered a violation:
- 0-1 month of life: the baby does not cry, even if he feels discomfort;
- 1-4 months: the baby does not respond to speech addressed to him;
- 4-6 months: does not track the toy with the eyes, does not pronounce combinations of phonemes (does not hum, does not coo);
- 6-7 months: does not try to attract the attention of adults by saying anything;
- 7-9 months: pronunciation of simple phonemes is difficult or completely absent;
- 9-10 months: the baby does not speak syllables and does not respond to gestures from adults, does not comply with requests to wave his hand, nod or shake his head;
- 12-18 months: does not speak simple words: dad, mom, give, ball, drink;
- 2 years: no meaningful spontaneous speech.
The norms of speech development are average. All children are individual, so their development may vary. A slight lag is normal. However, it requires attention from parents.
In preschool children, diction disorders such as unintelligibility of speech and inability to pronounce individual sounds are recorded: hissing, whistling or sonorant.
Working on diction and pronunciation
Oratorical talent is extremely rare. Almost all famous people intensively prepare for every public appearance. It is known that Cicero could not utter a single word without preparation. And he is still held up as an example as a great rhetorician.
There are many exercises with which your speech can become clear and beautiful. Among them are both universal exercises and those that are designed to help correct a specific problem. For example, a whistling “S”, an indistinct “L” or a violation in the pronunciation of the sound “R”. In order to solve these problems you will have to work.
Stages of development and formation of speech in a child
The skills and inclinations of a normally developing child directly depend on his age. But even in infants, experts are able to predict speech disorders in the future based on some signs. If motor development in the first year of life lags behind the norm, this is a possible sign that speech and mental development will also lag behind. We would also like to note that development standards were established in Soviet times and were quite strict. Now, unfortunately, many modern children do not meet them. Children of the new generation speak less and their speech takes longer to develop. The reasons for this are global “gadgetization” and the transition of people to virtual methods of communication.
| Age | Skills |
| up to 6 months |
|
| 6-9 months |
|
| 9 months-1 year |
|
| 1-1.5 years |
|
| 1.5-2 years |
|
| 2-3 years |
|
| 3-5 years |
|
Experts recommend regular examinations to identify delays, if any, as early as possible. One child is one of those who “harnesses slowly and rushes quickly.” He will start speaking later, but within a month he will catch up and surpass his peers. Then consider yourself lucky. But for another child, prolonged silence may hide such gloomy diagnoses as autism spectrum disorder, alalia and others. And it is very important not to miss them and start correction on time.
If you have any doubts about whether your child’s development rate is within the normal range, it is better to visit a specialist. What if he has a general
speech disorder
(general speech underdevelopment - GSD) or delayed speech development (SDD)?
For a child with severe speech impairment
It is often difficult to perceive the world around us positively. He grows up as a gloomy beech, touchy and aggressive, feels insecure, and with age begins to feel his inferiority. You can read more about the symptoms and degrees of speech underdevelopment here. Consult with specialists! Both minor and more significant speech deviations are usually identified in the first few years of life as a result of comprehensive diagnostics.
The spheres and areas of responsibility of specialists in speech problems are distributed as follows:
- Speech therapist
: Consults from 1.5 years old, conducts classes from 2 years old. At the consultation, he makes a final diagnosis, if it is a disease, and refers to a neurologist if there are suspicions of disorders of a corresponding nature; - Speech pathologist
: works with non-speaking children; in case of delays in psycho-speech development and pre-speech diseases (alalia, autism spectrum disorder), it helps to “start” speech and develop other cognitive functions to the level of the age norm.
We are primarily talking about young children. also occur in adults
- due to a brain injury or stroke.
Their correction is carried out by speech therapists and aphasiologists. Sometimes speech impairment in schoolchildren
and adults remains from neglected/undertreated pronunciation defects in childhood.
Exercises for diction and voice
When speaking in public or during normal conversation, we use the muscles of the tongue and throat. It is logical that in order to speak beautifully, you need to “pump up” these muscles.
Exercises that will help prepare the necessary muscles:
- You can pump up the muscles involved in producing sounds by regularly pronouncing “A-E-O”. At the same time, it is important to try not to open your mouth too much. The effect can be achieved by pronouncing sounds as deep as possible in the oral cavity.
- A very good effect can be achieved in diction and by training your lips. To do this, you need to say: “GL”, “VL”, “VN” - for the upper lip and “KS”, “GZ”, “VZ”, “BZ” - for the lower lip.
- You can also shape your tongue into a shovel shape and say “I” and “E” several times. Now let’s give the tongue a hook shape and simultaneously pronounce “O” and “U”.
- We continue to “pump up” the muscles of the tongue. We close our mouth and, using internal movements of the palate, cheeks and lips, make the sound “M”.
Do you need a doctor for problems with diction?
In most cases, if diction is impaired, they turn to a speech therapist. However, it is also worth consulting with your dentist and facial surgeon. The latter will rule out bone tissue pathology, prescribing surgery if necessary. The cause of unclear diction may be ankyloglossia, a congenital anomaly in which the frenulum of the tongue is underdeveloped. If the defect does not disappear on its own during preschool age, surgical intervention is necessary.
The dentist will sanitize the oral cavity and evaluate the dentures. Installing a denture that is too tight or too small changes the anatomy of the jaw, impairing diction.
When a malocclusion is diagnosed, the patient is fitted with a mouthguard, plate or braces. Depending on the severity of the disorder, eliminating the pathology will take from six months to several years. Correcting the bite improves articulation and voice timbre.
An examination is not always enough to detect the pathology that provoked a violation of diction. To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor refers the patient to clinical and instrumental studies:
- CT (computed tomography) or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- X-ray examination of the skull;
- general blood and urine analysis;
- examination of hearing and phonetic perception of oral speech.
Additionally, consultation with a neurologist and otolaryngologist may be required. The latter will exclude problems with hearing and ENT organs. And the neurologist will check whether the violation of diction is associated with improper functioning of the brain.
Exercises for diction and articulation
Since the tip of the tongue is actively involved in clear pronunciation, we use exercises that develop its flexibility:
- Imagine that your tongue is a hammer and hit your teeth with its tip. During such blows, “pronounce” yes-yes-yes-yes. Then try to clearly pronounce the letters “T-D”.
- To clearly pronounce the letters “K” and “G” you need to “pump up” your larynx. To do this, inhale through your nose and completely empty your lungs through your mouth. The release of air through the mouth should occur sharply and resemble the sound “Fu”. Do this exercise several times.
- If you notice that you have a problem pronouncing the letters “P” and “B,” then train your labial muscles. To do this, you need to puff out your cheeks and release the air from your mouth with a vigorous clap.
- It is also very important to learn how to control the amount of air. To do this, you need to use breathing exercises and practice in front of a mirror. Try reading a short text at normal volume. As a rule, you can easily control your voice. Now, do the same, but increasing the volume. There must be problems.
How to improve a child's diction?
According to the age norm of 5–6 years, a child should pronounce all sounds well. Alas, articulation itself does not become correct. You need to work on good diction, and the sooner you start working with your baby, the better. Where to begin?
Take care of yourself
A child learns to speak by imitating adults. If you yourself are bad at pronouncing sounds, then your baby will most likely also have problems with them. Listen to yourself, try to pronounce words clearly and correctly, practice problematic sounds. We'll talk about how to do this quickly below.
Do gymnastics
The muscles that are involved in the production of sounds also need training. Be sure to do articulation exercises with your child every day. These exercises should be performed in front of a mirror at first to make it easier to monitor the correct technique. To prevent your child from getting bored, give gymnastics a playful form.
Work on your breathing
Teach your baby to control his breathing. For example, there is a good exercise called “Candle”. Ask your child to imagine that he needs to blow out a big, big candle. Have him place his hands on his tummy, inhale, hold his breath for a second and blow on the flame. Did not work out? Try again together. Now you need to slightly “sway” the flame in different directions. Will it be possible to blow out a few candles? The game is quite simple, but effective, and there are several variations you can come up with. Does your child not like to blow out the candle? Let him imagine himself as a little dragon who needs to use the flame sparingly.
There are a lot of breathing exercises for preschoolers posted in the public domain. Don’t be lazy to find them and do them every day.
Tongue Twisters
These are wonderful and fun exercises that are time-tested and children really like them. We recommend starting with small tongue twisters of three or four words, and gradually move on to longer ones. First, learn how to pronounce them correctly yourself and only then teach your child.
The first time, speak the words slowly and clearly. A little faster the second time. Gradually increase the tempo until the child can pronounce the entire phrase clearly and quickly. Learn tongue twisters unobtrusively - while walking or swimming. You can also play with a ball: whoever throws the ball speaks. To avoid getting bored with your daily exercises, learn new tongue twisters. By the way, then you can arrange a competition: who knows them more and pronounces them better.
Seek help from a speech therapist
Classes must be carried out under the supervision of a specialist, because without special knowledge, using books alone, it is impossible to make sounds for a child correctly. On the contrary, you can achieve the completely opposite effect; correcting such errors is always more difficult. The speech therapist will identify problematic sounds for the baby, determine the causes of the difficulties and explain how to continue studying at home.
Features of correct pronunciation in adults
A common flaw in adults is unclear diction. And this is not necessarily due to congenital defects. In the speech of an adult, you can often hear the sounds of “nucking,” a drawn-out “uh,” swallowing of endings, or simply unintelligible words. Therefore, often the main reasons for hasty and unclear presentation are:
- Poorly developed articulatory muscles;
- Problems with voice production;
- Incorrect technique and tempo of speech;
The peculiarity of the development of diction in adults is that instilling correct pronunciation is much more difficult than in children. If for a long time some sounds were pronounced incorrectly, then it will take a long time to get used to the new pronunciation. It is necessary to constantly control yourself, overcoming the psychological barrier.
Actors, TV presenters, and announcers constantly improve their diction by resorting to certain exercises and training:
- Regular exercise of the speech apparatus;
- Reading books, texts aloud and speaking tongue twisters;
- Systematic repetition of complex sound series;
- Listening to recordings of your speech on a voice recorder.
Diagnostics
The tactics of diagnostic examination depend on the suspected cause of slurred speech. The algorithm consists of medical and pedagogical aspects: the first allows for nosological diagnosis, the second - to establish the leading mechanism and degree of speech dysfunction:
- Neurological diagnostics.
Indicated for patients with dysarthric disorders. Cerebral MRI is performed to visualize focal brain lesions. To assess the severity of paralysis and paresis of articulatory muscles, electrophysiological studies are used: ENG, EMG. - Dental examination.
Required for persons with edentia, jaw dislocation, or poor-quality prosthetics. Diagnostics may include X-ray of the TMJ, orthopantomography, CT scan of the jaws. To make prosthetics, impressions are made and diagnostic models are cast. - Audiological examination.
If slurred speech is due to hearing loss, an audiogram, otoacoustic emissions, and auditory recordings are performed. An audiologist consults the patient with the test results. - Examination of the pharynx.
During pharyngoscopy, the peritonsillar abscess is visualized as a spherical, fluctuating formation. The mucous membrane is hyperemic, and pus can be seen through it in the place of greatest bulging. Sometimes a test puncture of the abscess is performed for differential purposes. - Speech therapy examination.
Assessment of the state of oral speech is necessary for dysarthria and rhinolalia. The speech therapist identifies articulatory difficulties, defects in sound pronunciation (substitutions, distortions, omissions), agrammatisms, and determines the coherence and intelligibility of speech.
Speech therapy classes
Content
- Components of diction
- Why do you need good diction?
- Causes of poor diction
- How to develop diction
- Exercises to improve diction and clarity of speech Warm-up
- Pronunciation of individual sounds
- Breathing
- Tongue Twisters
- Diaphragm training