Consultation: Speech disorders. What are they?
Marina Kasatkina
Consultation: Speech disorders. What are they?
SPEECH DISORDERS. WHAT ARE THEY?
Children with speech impairments are children who have deviations in speech with normal hearing and intact intelligence. Speech disorders can manifest themselves in impaired pronunciation , grammatical structure of speech , poor vocabulary, as well as impaired tempo and fluency of speech .
Once speech disorders , they do not disappear on their own, but become permanent and require speech therapy intervention. A child’s incorrect speech can affect his further development - various difficulties in learning at school are possible.
CAUSES OF SPEECH DELAY AND DISORDERS IN PRESCHOOL AGE
If a child was born healthy, a delay in his speech development may occur due to incorrect actions of adults: with insufficient verbal communication with the baby, inattention to his auditory perception, imitation of sounds and words of an adult, with untimely development of intonational expressiveness of speech and semantic connections between words and objects .
Before speaking, the baby trains the muscles of the speech apparatus. This happens when he walks, babbles, breathes, swallows, sucks, chews. Breastfed children encounter speech difficulties less often than artificially fed children, and those who were promptly introduced to solid food speak much more clearly than their peers who were stuffed with liquid porridge and pureed vegetables almost before school.
Speech disorders are caused by various reasons: congenital anomalies of the central nervous system, cerebral cortex, palate, tongue, defects in nasal breathing and decreased muscle tone of the soft palate, mental trauma (for example, in impressionable children prone to neuroses, a fear reaction can provoke stuttering) and etc.
The development of speech and thinking is closely related to the development of fine motor skills of the hands. Children who work with construction sets , engage in origami, plasticine modeling, embroidery and other types of handicrafts, as a rule, are able to reason logically, their memory and attention are quite developed.
Often, retraining a left-handed child to do everything with his right hand leads to delayed speech development and speech disorders . In a right-handed person, the actions of all moving parts of the body and especially the fingers, speech apparatus (larynx, pharynx, tongue, lips, soft palate)
genetically inherent in the left hemisphere of the brain, in left-handed people - in the right hemisphere. A left-handed child needs to be given freedom of action, and he himself will learn to do a lot with both hands.
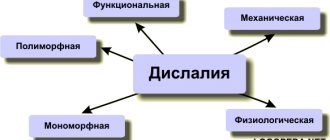
DYSLALIA
One of the most common speech defects is DYSLALIA ( violation of sound pronunciation with normal hearing and intact innervation of the speech apparatus.) The child either cannot pronounce a sound (misses it or distorts the pronunciation, or boldly replaces one sound with another.
Dyslalia can be simple (one sound or a group of similar pronunciation sounds is incorrectly pronounced (for example, whistling s, z, ts)
and complex (
the pronunciation of sounds of different groups is impaired (for example, whistling and hissing sh, sh, zh)
.
Until the age of three, it is too early to make lame sounds, but it is necessary to prepare the child and his articulatory apparatus for correct pronunciation and speech through the development of articulatory motor skills, the development of fine and gross motor skills, and the development of correct speech breathing.
DYSARTHRIA is a violation of the pronunciation side of speech , caused by insufficient functioning of the nerves that provide communication between the speech apparatus and the central nervous system, that is, insufficient innervation.
The main manifestations of dysarthria:
- disorder of articulation of sounds (speech is unclear, blurry)
;
— voice disorder;
- changing the tempo and rhythm of speech ;
- change in intonation.
The above listed manifestations of dysarthria appear to varying degrees and in various combinations ( there are mild , moderate, severe forms of dysarthria)
.
With dysarthria, speech therapists encounter great difficulties during the production and automation of sounds in speech . Children with dysarthria need long-term, systematic individual speech therapy assistance.
The main complaints with dysarthria: slurred, inexpressive speech, poor diction, distortion and replacement of sounds in words with a complex syllabic structure.
Most often, dysarthria is diagnosed by a speech therapist (who presupposes this diagnosis)
.
In such a situation, it is necessary to consult a neurologist to clarify or confirm the diagnosis and to prescribe adequate treatment, because for dysarthria, the method of correctional work must be comprehensive and include: medical intervention, psychological and pedagogical assistance, speech therapy work.
When examining dysarthria, the following is noted: disturbances in general motor skills - movements are awkward, the child gets tired quickly. Motor incompetence is especially noticeable in physical education and music classes, where children lag behind in tempo, rhythm of movements, as well as in switching movements.
Impairments in fine motor skills of the hands: children with dysarthria late and have difficulty mastering self-care skills: they cannot fasten a button, untie a scarf, etc. They hold a pencil poorly, their hands are tense . Many people do not like to draw; there is motor clumsiness in their hands during appliqué classes and with plasticine. Difficulties in the spatial arrangement of elements in the drawings and other difficulties can be traced.
School-age children in the first grade have difficulties in mastering graphic skills (poor handwriting, slow pace of writing, “mirroring”
letter, letter replacements).
Features of the articulatory apparatus:
the lips remain flaccid during speech the tongue is inactive, in a passive state (lies at the bottom of the mouth)
;
-facial muscles to the touch are hard, tense; lips in a half-smile: the upper lip is pressed against the gums; many children cannot make a tube out of their lips; the tongue is often changed in shape: thick, without a pronounced tip, inactive, there is no facial expression;
- trembling of the tongue, vocal cords, which is noted during exercise - increased tone;
- there may be an inability to perform certain movements of the articulatory apparatus or switch from one movement to another; Some children experience chaotic movements, “groping”
the desired articulatory posture;
- deviation of the tongue from the midline;
- increased salivation.
Sound pronunciation in dysarthria is characterized by: confusion, distortion, replacement and absence of sounds. Sounds with dysarthria are not automated for a long time and speech is not introduced. The most common defects in sound pronunciation are violations of whistling and hissing sounds . Quite often, interdental pronunciation and lateral overtones are noted. Children have difficulty pronouncing words with complex syllable structures.
The intonation-expressive coloring of the speech of children with dysarthria is sharply reduced. The voice suffers, vocal modulations in height and strength, speech exhalation is weakened. The timbre of speech is disrupted and a nasal tone appears. The pace of speech is often accelerated .
ALALIA - complete or partial absence of speech in children (up to 3-5 years)
with good physical hearing, caused by underdevelopment or damage to the speech areas in the left hemisphere of the brain, which occurred in the prenatal or early development of the child.
Contact a specialist if your baby: does not respond to speech addressed to him, even if he is called by name, but notices other, even very quiet sounds. Does not listen (as hearing-impaired children do, does not try to understand what is said from the lips, does not resort to facial expressions and gestures to express his thoughts.
THE MAIN ROLE IN HELPING CHILDREN WITH MOTOR ALALIA BELONGS TO PARENTS AND PARENTS WITH A CHILD WITH ALALIA SHOULD KNOW THAT THE FATE OF THEIR CHILD IS IN THEIR HANDS. IF A CHILD IS IN PLEASANT CONDITIONS, HE CAN BECOME A HEALTHY PERSON AND WILL TAKE A WORTHY PLACE IN LIFE. HELP FOR CHILDREN WITH ALALIA IS PROVIDED BY Speech Therapy GARDENS; Speech therapists, DEFECTOLOGISTS AND NEUROPATOLOGISTS IN POLYCLINICS. Some children manage to make such progress in speech that they go to public school, where it is still not so easy to learn, especially in the first year. And other children with alalia go to speech school.
STUTTERING is a violation of the tempo , rhythm, and fluency of speech caused by muscle spasms of the speech apparatus. When stuttering, forced stops or repetitions of individual sounds and syllables are observed speech Stuttering occurs most often between the ages of 2 and 5 years (during the period of intensive speech )
.
Stuttering should be eliminated as soon as it occurs. In the initial stage, this defect has the usual mild form.
Physiological hesitations, as well as hesitations that arose under the unfavorable influence of society or delayed speech development against the background of fast, chaotic speech , are hesitations of a non-convulsive nature.
Such hesitations are typical for a certain period of children's development. If no complications occur, then such hesitations go away as soon as the child gains confidence in himself and in expressing his thoughts. Thus, physiological hesitations and repetitions are a consequence of the fact that thinking is ahead of the development of its speech capabilities.
Contact a specialist if your baby:
Remember that hesitations and repetitions are natural for a child in this period of life and can continue for some time.
uses extra sounds (a, i)
;
finds it difficult to start speaking .
makes forced stops in the middle of a word or phrase;
repeats the first syllables or whole words at the beginning of a phrase;
Stuttering or hesitation of a convulsive nature
If stuttering does occur and several days or 2-3 weeks have passed since its onset (no longer)
- such stuttering is considered primary and to overcome it you need to follow the recommendations of a speech therapist.
Most often, if you follow these recommendations, stuttering disappears.
But if this does not happen, then your child will need a therapeutic and pedagogical complex of measures that provides an impact on the nervous system and the body as a whole, on his general and speech motor skills, on speech and personality. Collaborative work of a speech therapist, psychoneurologist and parents.
To eliminate relapses of stuttering, you should adhere to some rules, which the speech therapist will also explain to you.
A child who stutters should be under the supervision of a speech therapist and a neuropsychiatrist at all times.
TACHILALIA - pathologically fast rate of speech (20-30 sounds per second instead of 10-12)
without significant distortions of phonetic design, vocabulary and grammatical
BRADYLALIA - pathologically slow rate of speech . Speech is excessively slow, with prolongation of vowel sounds, with sluggish, unclear articulation.
NPOS ( impaired pronunciation of certain sounds)
.
Manifestations of UO
Mental retardation in a child manifests itself from an early age. It is expressed in reduced intelligence, sensory and motor disorders, and delayed speech formation. Depending on the degree of retardation, the child’s ability to learn, develop and be able to integrate into society is determined. The good news in this case is the fact that MR does not progress over time, and in the case of correctly carried out corrective measures, the condition even improves. However, it must be remembered that a child is capable of developing only within the limits of physiological capabilities. What stands out most clearly is the decline in intelligence and speech development. But for any level of adaptation, formed speech is extremely important. Therefore, one of the most important areas in the correction of children with disabilities is classes with a speech therapist-defectologist.
Diagnostics
Patients with impressive speech disorders require comprehensive neurological, audiological, speech therapy, psychological and psychiatric diagnostics, consultation with relevant specialists:
- Neurological examination.
At an appointment with a neurologist, perinatal risk factors and features of early development of children are clarified; In all patients, the current neurological status is determined. To understand the etiology of speech disorders, instrumental diagnostics are prescribed: cerebral MRI scanning, MR arteriography of the brain, EEG, ultrasound scanning of the vessels of the head and neck. - Examination of auditory function.
To exclude hearing loss as the main factor in misunderstanding speech, acoustic EPs, an audiogram are examined, acoustic impedance measurements are performed, and CT scans of the temporal bones are performed. Along with an examination by an otolaryngologist, a consultation with an audiologist is carried out. - Neuropsychological testing.
Involves the study of higher mental functions (memory, perception, thinking), auditory-verbal memory. During diagnosis, attention is paid to the state of various types of gnosis and praxis. A conclusion is made about the patient's cognitive abilities. - Speech therapy examination.
When analyzing speech function, the speech therapist conducts an in-depth study of impressive speech. Evaluates the patient's understanding of situational and extra-situational questions, verbal instructions, and complex prepositional phrases. Examines phonemic awareness, meaningful reading ability, and expressive language. - Consultation with a psychiatrist.
Necessary for assessing the patient’s mental status, excluding congenital forms of MR, acquired dementia, and ASD. The methods used are conversation, observation, pathopsychological examination, neurotests.
Logotherapy
Table of norms of speech skills by age
| Age | Speech skills, vocabulary |
| 1 year | 5-10 simple words denoting a loved one, object or action: mom, baba, bi-bi, give, bang, etc. |
| 2 years | 300-400 words, short sentences, use of verbs, adjectives. |
| 3 years | About 1500 words, use of the pronoun “I”, use of sentences of 3-4 words with the main parts of speech (verbs, adjectives, adverbs, etc.) |
| 4 years | 1500-2000 words, use of prepositions and conjunctions, temporal and spatial concepts. The softened pronunciation of consonants disappears. The child can pronounce hissing (Ш, Ш, etc.) and whistling (S) sounds. |
| 5 years | 2500-3000 words. The use of words is correct, without rearranging syllables and sounds. Using generalizing words (a skirt and a jacket are clothes, etc.) |
| 6-7 years | 3500 words. Figurative words and expressions are used (for example, “neither light nor dawn”), established phrases and sayings. A child can explain the meaning of a simple word and talk about its origin. |
If you liked the article, please share a link to it
Speech pathologist or speech therapist - who to contact?
Speech therapists and speech pathologists correct speech defects. What is the difference between them and which specialist should I contact?
A speech therapist is a doctor who restores the speech of children who do not have any abnormalities in mental or physical health and have a normally functioning central nervous system.
As a rule, speech therapists work with children over 3 years of age. The main task of a speech therapist is to correctly stage the child’s speech, teach him to correctly pronounce sounds and words.
To do this, special exercises are practiced for breathing, articulation, singing and pronunciation of sounds. Special tongue twisters are learned.
A defectologist is a doctor who works with children with disabilities in physical or mental development. This specialist receives special education, which includes courses in psychology, psychiatry, neurology and other disciplines.