12/03/2013 How to correctly assess the state of your child’s speech? How and when should a child speak? In what cases should you worry, and in what cases should you just wait? How not to miss the moment when he may need the help of specialists? These and other difficult questions are asked by those parents who care about how their children will grow up.
Often parents pay attention to how their child speaks - whether he pronounces all the sounds correctly. It seems to parents that the main indicator for assessing a child’s speech development is correct sound pronunciation. But this is only one of the components of speech development. Other, no less important, is the development of the child’s vocabulary, the ability to formulate his statement grammatically correctly and consistently. To understand whether your child has a speech disorder, you need to consider what types of speech disorders exist.
All types of disorders based on psychological and linguistic criteria can be divided into two groups: oral and written speech.
Speech apparatus defects
The speech apparatus is a set of organs that are involved in sound pronunciation and speech formation. It consists of 2 sections: central and peripheral. The central part includes the brain, and the peripheral part includes muscles, bones, cartilage, and ligaments. Therefore, when we talk about disorders in the peripheral region, we are talking about the tongue, lips, soft palate and lower jaw. Disruption of the functioning of one or several organs of the speech apparatus at the same time leads to the appearance of speech disorders.
Defects of the speech apparatus, from a diagnostic point of view, can be divided into 2 groups. The first group will include disorders that are diagnosed at an early age; more often, already in the first month of a child’s life, examination reveals disorders that can only be corrected surgically.
The second group includes disorders that cannot be diagnosed at an early age. Their presence becomes known during the development of speech, most often at 2-2.5 years. In this case, you should seek help from a pediatric speech therapist. At the first consultation, the speech therapist will diagnose the disorders and, if necessary, refer you to related specialists.
If the first symptoms of speech disorders occur, you should immediately contact a speech therapist for diagnosis and selection of a correct and effective correction program.
Parents should contact a specialist if they notice:
- Stuttering or pronunciation of words too slow/fast, pauses between words;
- Voice disturbances, nasality, changes in voice timbre;
- Distortion or “swallowing” of sounds, inaudible speech, and others.
Our center’s specialists successfully work with speech apparatus defects; the following methods are most often used to correct speech disorders:
- Speech therapy massage;
- Special speech therapy exercises;
- DENAS therapy;
- Classes using Forbrain (the device can also be purchased for home use);
- Exercises for speech breathing and others.
The most common speech apparatus defects and methods of their correction:
Dysphonia (aphonia) is popularly called “voice disorder” or “vocal disorder”. Signs: lack of phonation or changes in the strength and timbre of the voice, nasality or hoarseness. Requires urgent correction, since with age the symptoms intensify and are less amenable to correction. In the treatment of dysphonia, articulation and breathing exercises, massage of the collar area, and exercises with the DENAS apparatus are most often used.
Stuttering is a disturbance in the tempo, rhythm and fluency of speech caused by convulsions of the speech apparatus. In children, it most often occurs during the development of phrasal speech. In the absence of timely correction, stuttering can accompany a person into adulthood. This disorder is difficult to correct due to its obsessive nature. Treatment of stuttering at the Ember Center is aimed at eliminating the pathological factors that led to the onset of stuttering, as well as neutralizing its consequences, fear of speech - logophobia. It is thanks to an integrated approach that it is possible to get rid of stuttering not temporarily, but forever.
A short frenulum is a defect of the oral cavity, which, as a rule, is congenital. With this disorder, the child cannot pronounce some sounds. Often, with a short frenulum, it is recommended to solve the problem surgically, especially at an early age, when the work of a speech therapist is not yet possible. But this can often be avoided with timely contact with a speech therapist. With the help of special exercises, you can stretch the frenulum, thereby solving this problem.
A dome-shaped palate is a defect of the speech apparatus caused by the incorrect structure of the oral cavity. The speech therapist teaches how to pronounce sounds that are inaccessible to the client, which will not differ from traditional ones by ear.
Rhinolalia (cleft palate) is characterized by a defective structure and functioning of the speech apparatus. A cleft palate interferes with normal voice production. A person with such a defect grossly distorts sounds, pronounces words nasally, and his voice timbre changes. In the treatment of such disorders, a surgical method is often used, after which a course of sessions with a speech therapist is required.
Dysarthria is a violation of the muscle tone of the articulatory apparatus, which contributes to the development of speech production disorders. With dysarthria, speech motor skills, breathing, voice and pronunciation of sounds are impaired. In this case, correctional classes with a speech therapist are aimed at eliminating the cause of the violations. The specialist uses articulation gymnastics, speech therapy massage, and DENAS therapy.
Defects of the speech apparatus are often found in people, but it is in childhood that they can be most effectively treated. With age, correction of these violations becomes more difficult and time-consuming.
Correction of speech apparatus defects at the Ember center is carried out according to an individually developed program. For complex disorders, we recommend a joint consultation with several specialists: a clinical psychologist, a speech pathologist, a special education teacher, and a neuropsychologist. An integrated approach helps to accurately determine the diagnosis and its causes, develop a correction route, without missing important details.
If your child has a speech defect that interferes with normal speech, sign up for a consultation by calling +7 (812) 642-47-02 or leave a request on the website.
Violation of sound pronunciation
General information
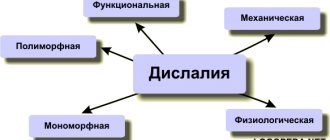
Sound pronunciation is the process of formation of speech sounds, which is carried out by the respiratory, vocal and resonator sections of the speech apparatus under regulation by the central nervous system. Sound pronunciation disorders include such nosological forms as dyslalia, rhinolalia, dysarthric and aphasia. Violations are differentiated with dialectal speech and incorrect pronunciation.
Dyslalia is a violation of sound pronunciation, which occurs due to anatomical defects of the articular apparatus, as well as as a result of functional disorders in the speech motor and speech-auditory systems. Also, the causes of violations may be unfavorable socio-psychological conditions. “Erased” dysarthria is a violation of pronunciation, which is accompanied by inaccuracy and limited range of movements of the articulars. Also, with “erased” dysarthria, intonation restrictions, distortion of timbre, strength and pitch of the voice are observed.
With open rhinolalia, there is a violation of sound pronunciation, nasal speech with congenital defects of the upper lip, hard and soft palate. Inferiority of the pharyngeal seal leads to hypertrophy of the root of the posterior parts of the tongue and to the formation of consonant sounds in the laryngeal-pharyngeal region with a specific clicking sound and nasal noise.
The reasons for pronunciation problems can be:
- defects in the structure of the speech apparatus (bad bite; improper structure of the palate, too thick lips);
- improper education of a child’s speech in the family;
- imitation of incorrect speech;
- bilingualism in the family;
- decreased physiological hearing.
Dysarthria and anarthria are also caused by organic lesions of the central nervous system as a result of the influence of various unfavorable factors on the developing brain of a child or on the brain of an adult:
- intrauterine lesions of the fetus;
- birth injuries (for example, asphyxia);
- incompatibility of mother and fetus according to the Rh factor;
- infectious diseases of the nervous system suffered in the first years of life (meningitis, encephalitis);
- cerebral palsy (CP);
- cerebrovascular accident (stroke), traumatic brain injury.
Sound pronunciation problems are almost always remediable. The most important thing in correcting violations is to correctly identify the causes of the speech defect. Each cause has a specific correction method. In addition, a speech therapist makes a diagnosis of dysarthria and prescribes medication. Thus, the elimination of sound pronunciation disorders should be comprehensive.
Types of sound pronunciation disorders
Incorrect pronunciation can occur with any consonant sound. Violations of simple methods of articulation m, n, t, p occur most rarely. The pronunciation of sounds is most often disrupted:
- sonorous (p, l);
- whistling (s, z, c);
- hissing (w, f, sch, h).
Soft pairs of these consonants are pronounced correctly, since they are easy to articulate (compared to hard variants). In children, usually only one group of sounds may be impaired. For example, only hissing or only back-lingual sounds. Such a violation of sound pronunciation is defined as partial. With complex disorders, problems arise with several groups of sounds at once: hissing, whistling, sonorous.
There are three forms of sound disturbance:
- distorted pronunciation of sound;
- lack of sound in speech;
- replacing one sound with another.
The reason for the distorted pronunciation lies in a violation of articulatory motor skills. Also, the child is not able to correctly perform movements with the articulatory apparatus (tongue). As a result, sounds are distorted or pronounced inaccurately. Such violations are phonetic. Also, one of the reasons for replacing sounds may be insufficient development of phonemic hearing or its impairment. As a result, children are unable to hear the difference between a sound and its substitute. There are also cases when a child’s sounds of one group are replaced, and the sounds of another may be distorted. For example, the whistling sounds s, z, ts are replaced by the sounds t, d, and the sound p is distorted. Such disorders are called phonetic-phonemic.
disorders (phonetic/phonemic):
- sigmatisms/parasigmatisms (sound);
- lambdacisms/paralambdacisms (sounds l and l`);
- rhotacisms/pararotacisms (sounds r and r`);
- iotacisms/paraiotacisms (sound th);
- cappacisms/paracappacisms (sound k).
Disorders of groups of voiced and soft sounds: voicing defects and softening defects). All types of pronunciation violations have their own ways of correction. Speech therapists also distinguish three levels of disorders:
- First level. The child is not able to independently pronounce sounds in phrasal speech or in individual words.
- Second level. Ability to produce sounds in isolation or in simple words.
- Third level. Mixing of sound in the speech stream, but it is possible to pronounce it.
Correcting pronunciation problems
Depending on the level of sound pronunciation, the speech therapist determines the work with the patient. It could be as follows:
- sound production (first level);
- input of sound into speech to the state of automation (second level);
- differentiation with another sound (third level).
Violation of sound pronunciation can manifest itself independently, as a speech defect, or be part of other speech disorders (dysarthria, alalia).
In the first case, the speech therapist works to correct the pronunciation of sounds. In the second case, it corrects the defect, depending on the characteristics of the violations. Work on pronunciation should begin from childhood, from 2-3 years. Correction of disorders by a children's speech therapist is an obligatory part of the full development of the child. The specialist’s work is aimed at developing the child’s speech, as well as developing the correct perception of sounds.